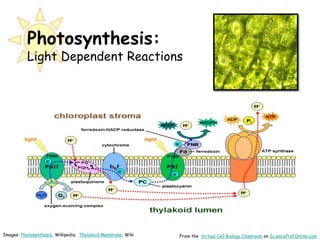
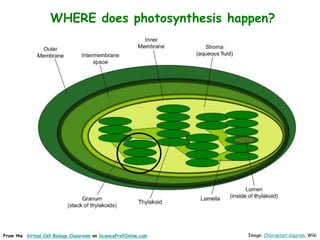
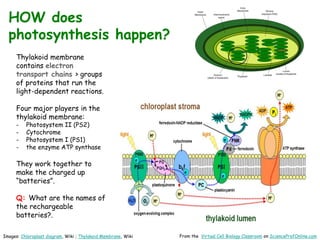
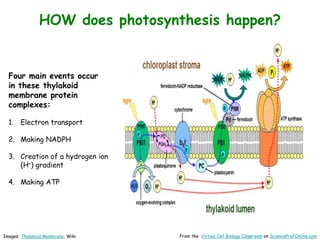
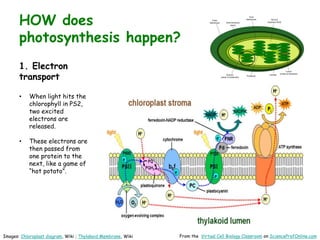
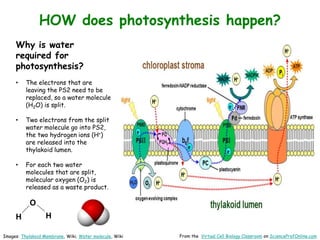
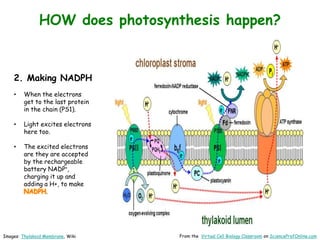
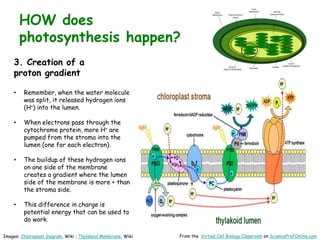
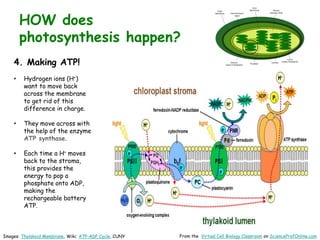
Science Prof Online provides free educational resources including PowerPoints, articles, and virtual classrooms. The site offers materials for science students and educators to use for learning. PowerPoints cover topics like cell biology and photosynthesis. They include learning objectives, review questions, and links to additional resources. The goal is to help people learn science through these digital teaching tools.