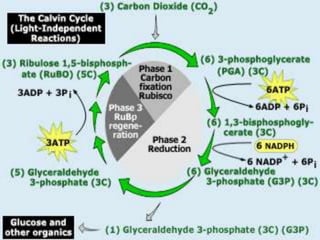
This document discusses photosynthesis and its key stages and history. It notes that:
- Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae and bacteria use sunlight to convert water, carbon dioxide and minerals into oxygen and glucose.
- Energy from photosynthesis carried out by plants millions of years ago is responsible for fossil fuels after the remains of these organisms were deposited and slowly converted over geological time.
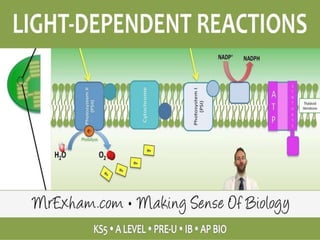
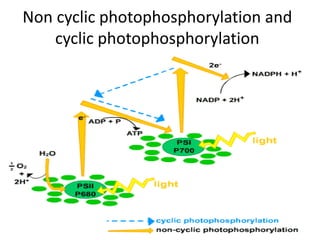
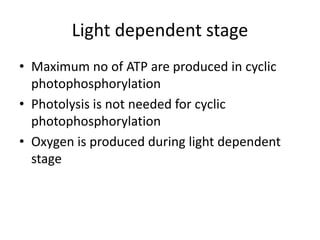
- The light-dependent and light-independent stages of photosynthesis are described, including the locations and key reactions in each.