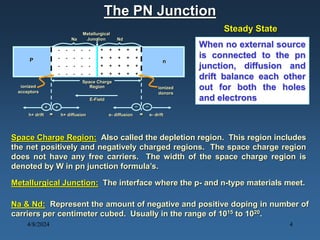
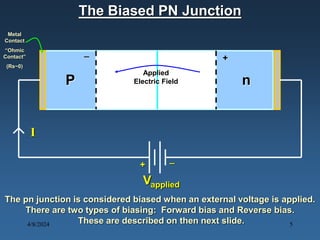
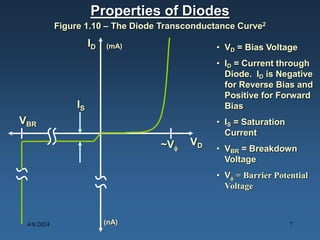
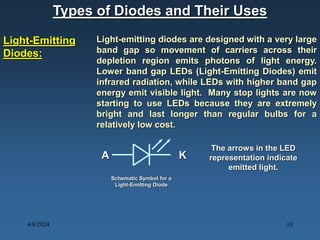
N-type materials are produced by doping silicon with group V elements like arsenic or phosphorus, which add extra electrons. P-type materials are produced by doping with group III elements like boron, which create "holes" where electrons are missing. When a p-type and n-type material are joined, a pn junction is formed with a depletion region of no free charges between the charged p and n regions. When a voltage is applied across the junction, it can be forward or reverse biased, affecting the width of the depletion region and allowing or blocking the flow of current. Diodes made of pn junctions demonstrate the Shockley diode equation and have uses including rectification, zener regulation, light emission