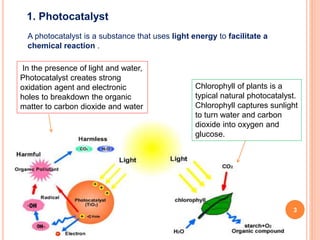
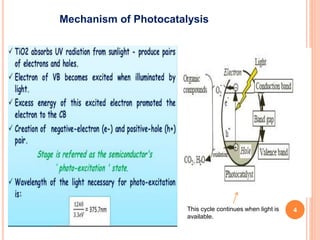
1) Photocatalysis involves using light energy to facilitate chemical reactions. Photocatalysts like chlorophyll and titanium dioxide are able to breakdown organic matter into carbon dioxide and water when exposed to light.
2) Nanoparticles are necessary for high activity photocatalysts due to quantum size effects. Smaller nanoparticles have a larger surface area and better adsorption potential.
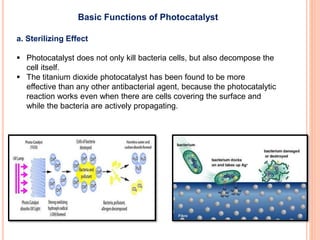
3) Photocatalysts have various applications including air purification by decomposing volatile organic compounds, self-cleaning surfaces, water purification by oxidizing pollutants, and dye degradation.