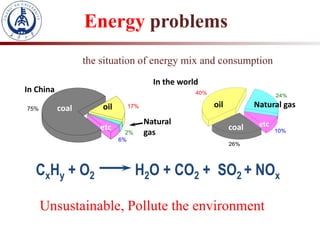
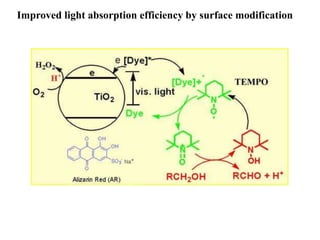
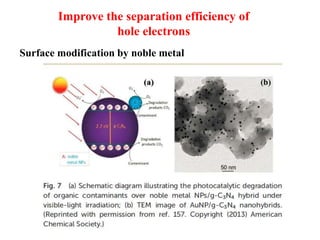
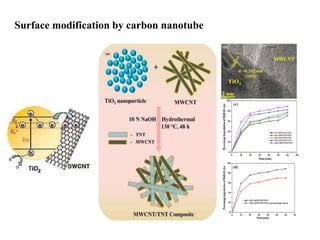
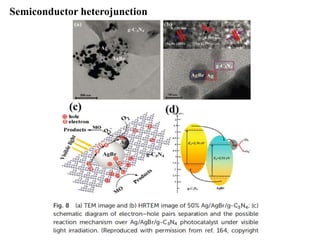
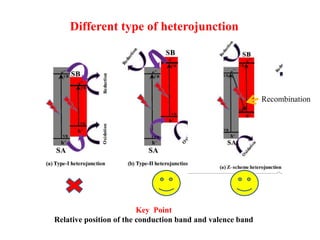
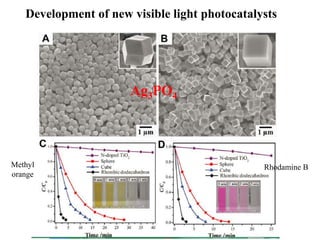
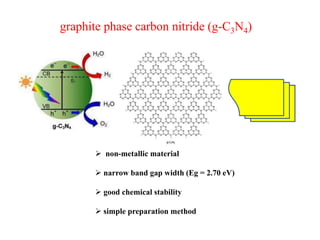
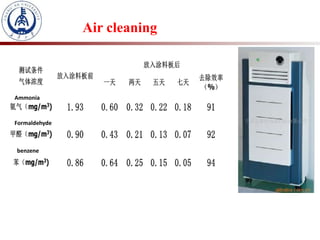
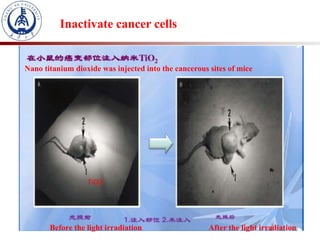
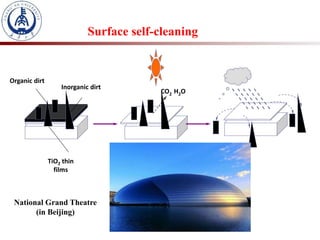
1. The document introduces a course on the principle and application of photocatalysis.
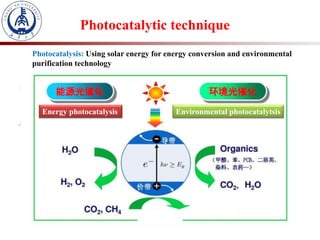
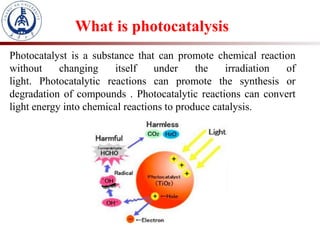
2. Photocatalysis uses solar energy to promote chemical reactions for energy conversion and environmental purification without changing the photocatalyst.
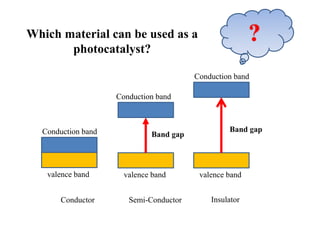
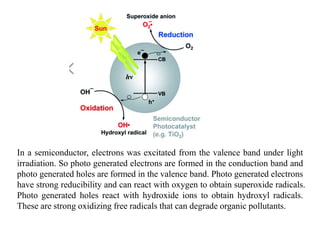
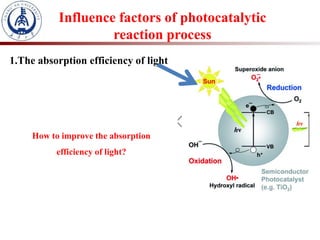
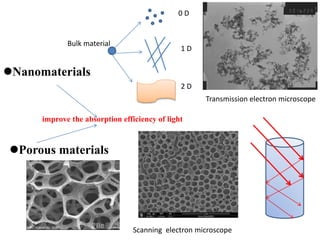
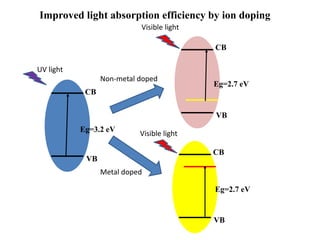
3. Semiconductor materials like TiO2 can be used as photocatalysts by generating electron-hole pairs when irradiated by light which then trigger redox reactions to degrade pollutants.