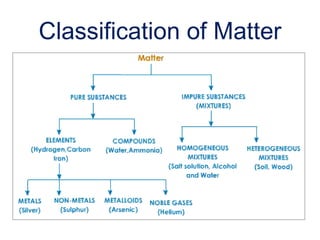
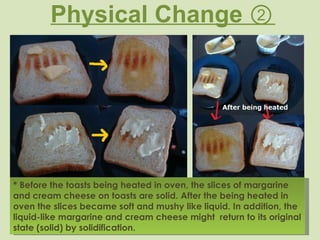
This document provides definitions and examples of key concepts in the classification and changes of matter. It defines matter, non-matter, pure substances, elements, compounds, mixtures, homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures, physical properties like mass, volume, density and states of matter. It also distinguishes between physical and chemical changes, providing examples of each type of change.