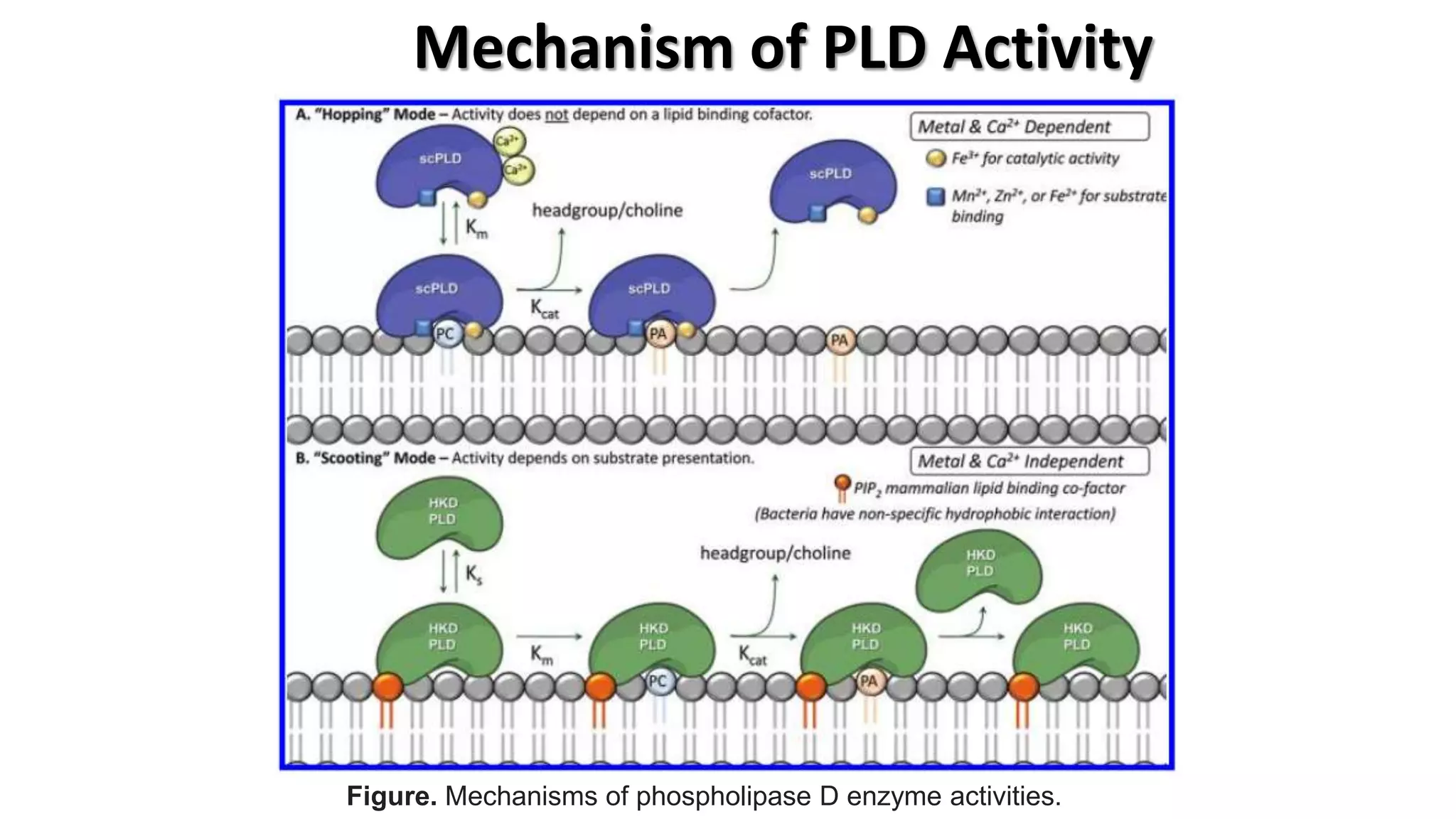
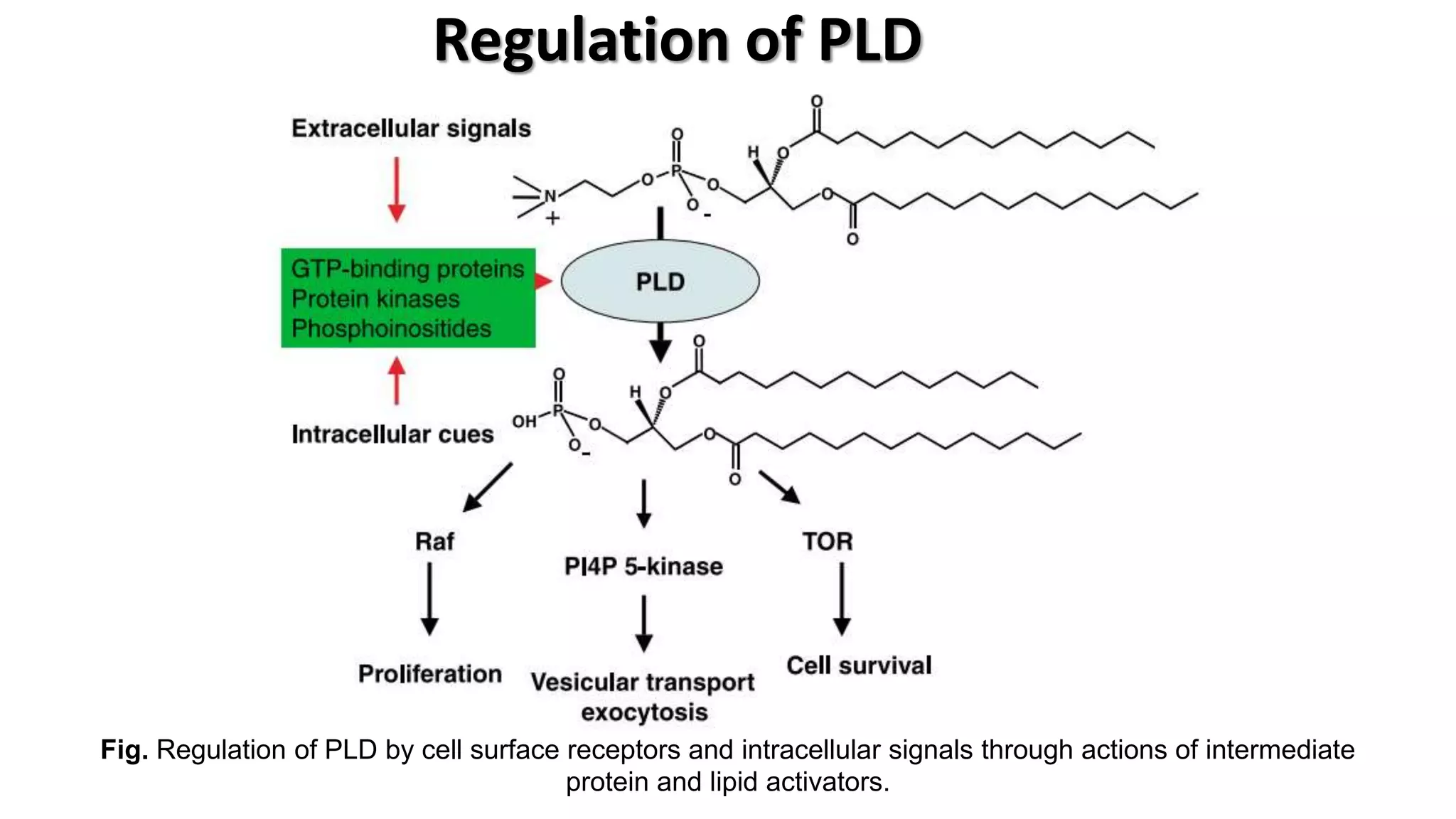
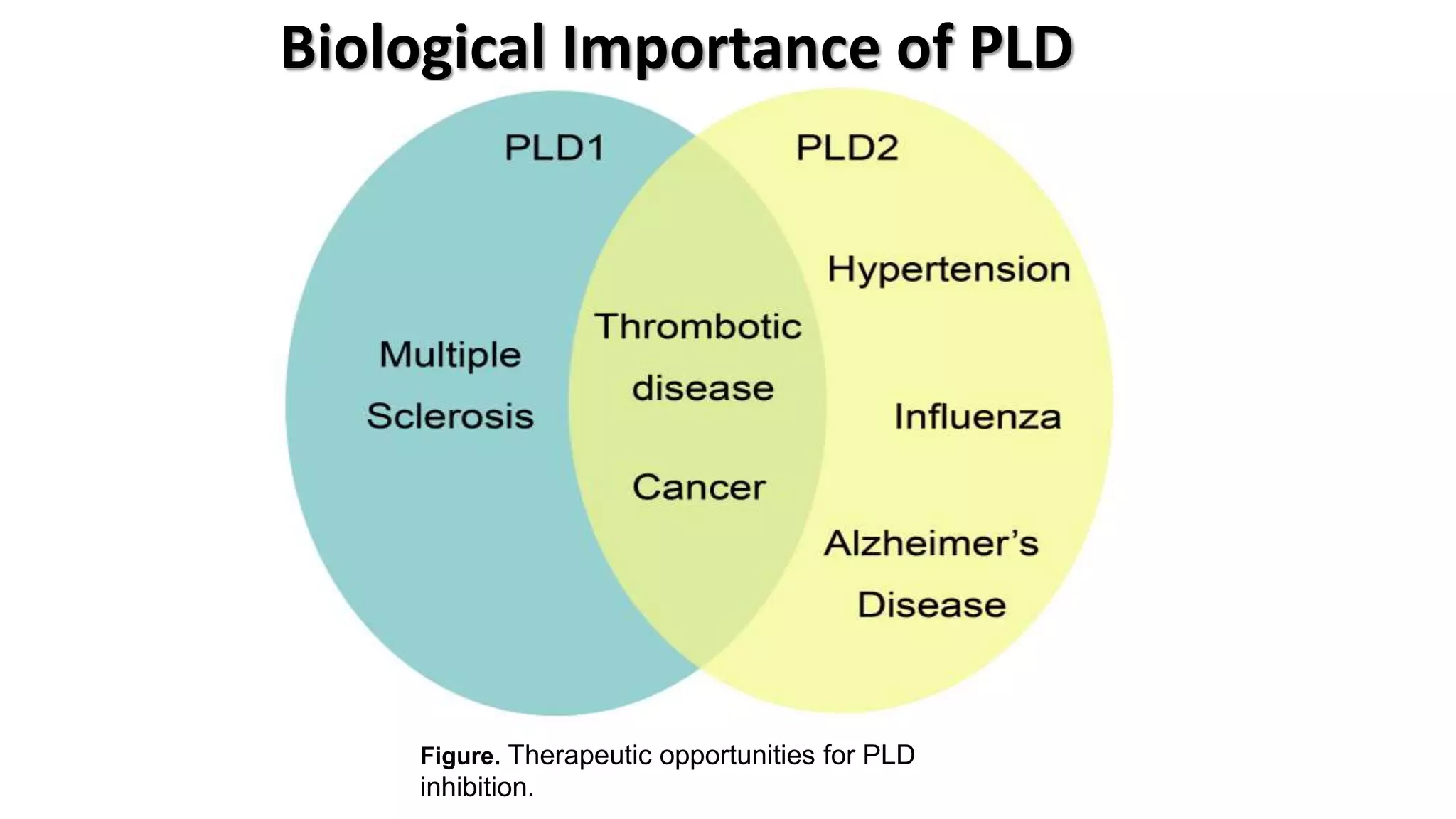
Phospholipase D (PLD) is an enzyme that hydrolyzes glycerophospholipids, leading to the production of phosphatidic acid and a free headgroup. The enzyme's structure is characterized by regulatory sequences and conserved regions that are crucial for its catalytic activity, which can occur in different modes of interfacial catalysis. PLD is regulated by cell surface receptors and intracellular signals and presents therapeutic opportunities for inhibition.