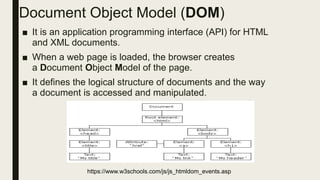
This document discusses PhoneGap development, testing, and debugging. It covers initializing a PhoneGap application by including the PhoneGap JavaScript file and setting up event listeners. It also discusses leveraging PhoneGap APIs, enhancing apps with jQuery Mobile, testing in emulators and on devices, and dealing with cross-platform issues. Debugging techniques like console.log() are presented. Finally, it briefly discusses building PhoneGap apps using PhoneGap Build.