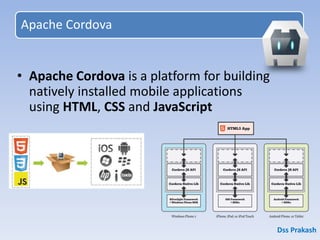
1. PhoneGap is a framework that allows developers to build mobile apps using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript instead of platform-specific languages. It works by wrapping web pages in a native container so they can access native device functions and be deployed to app stores.
2. The document discusses PhoneGap features like access to device APIs, cross-platform deployment, and debugging tools. It also covers setting up the PhoneGap development environment and creating a basic "Hello World" app.
3. The document provides code examples for the app manifest, JavaScript to access device functions, and HTML/CSS pages. It also discusses PhoneGap advantages like multiple platform support and disadvantages like lack of support for all native features.






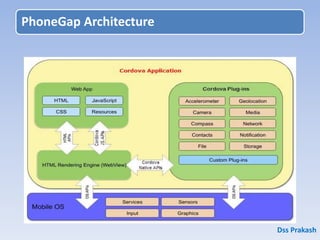
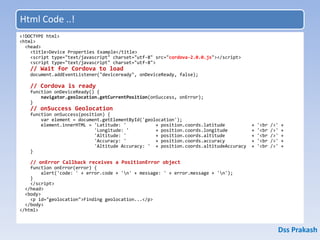
![How does PhoneGap Work?
• Include web code in a native app project:
- assets/www/js/, css/, images/, etc.
• Native code loads a URL to the web code through
the device’s internal browser:
- Extend a CordovaWebViewClient
- super.loadUrl( “file:///android_asset/www/login.html” );
• Apache Cordova exposes native device APIs
through JavaScript:
- navigator.device.capture.captureImage( captureSuccess(),
captureError(), [options] );
Dss Prakash](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prakashphonegap-150915055256-lva1-app6892/85/phonegap-with-angular-js-for-freshers-9-320.jpg)




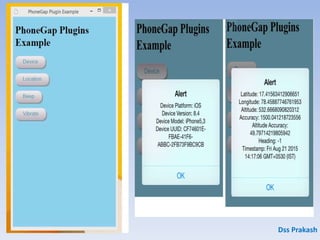
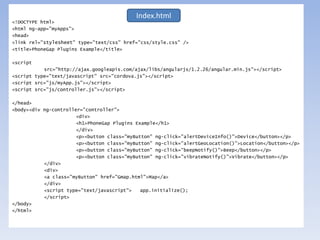

![var app = {
// Application Constructor
initialize: function() {
this.bindEvents();
},
// Bind Event Listeners
// Bind any events that are required on startup. Common events are:
// 'load', 'deviceready', 'offline', and 'online'.
bindEvents: function() {
document.addEventListener('deviceready', this.onDeviceReady, false);
},
// deviceready Event Handler
// The scope of 'this' is the event. In order to call the 'receivedEvent'
// function, we must explicity call 'app.receivedEvent(...);'
onDeviceReady: function() {
app.receivedEvent('deviceready');
},
// Update DOM on a Received Event
receivedEvent: function(id) {
console.log('Received Event: ' + id);
}
};
var myApp = angular.module('myApps', []);
Index.js
myApp.js](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prakashphonegap-150915055256-lva1-app6892/85/phonegap-with-angular-js-for-freshers-18-320.jpg)