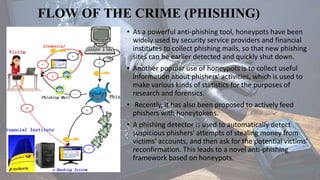
This document discusses phishing and defines it as a cybercrime where targets are contacted via email, phone, or text by someone posing as a legitimate institution to obtain sensitive personal or financial information. The information is then used to access important accounts and can result in identity theft and financial loss. It also describes how phishing works, including the planning, setup, attack, collection, and identity theft/fraud stages of a phishing attempt. Honeypots are discussed as an anti-phishing tool used to detect new phishing sites and gather intelligence on phishers.