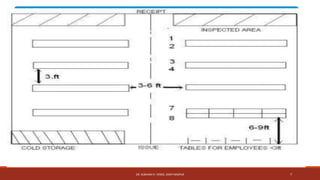
This document discusses drugstore management and inventory control in a hospital setting. It describes how the drug store is essential for proper hospital functioning and its objectives like stocking drugs, procuring supplies, and maintaining records. Success depends on factors like location, staff, and financial management. The document outlines guidelines for inventory control including storage conditions, purchase procedures, economic order quantity calculations, and analysis techniques like ABC, VED, and FSN analyses. Maintaining proper inventory control is important for ensuring adequate drug supplies without excessive costs.