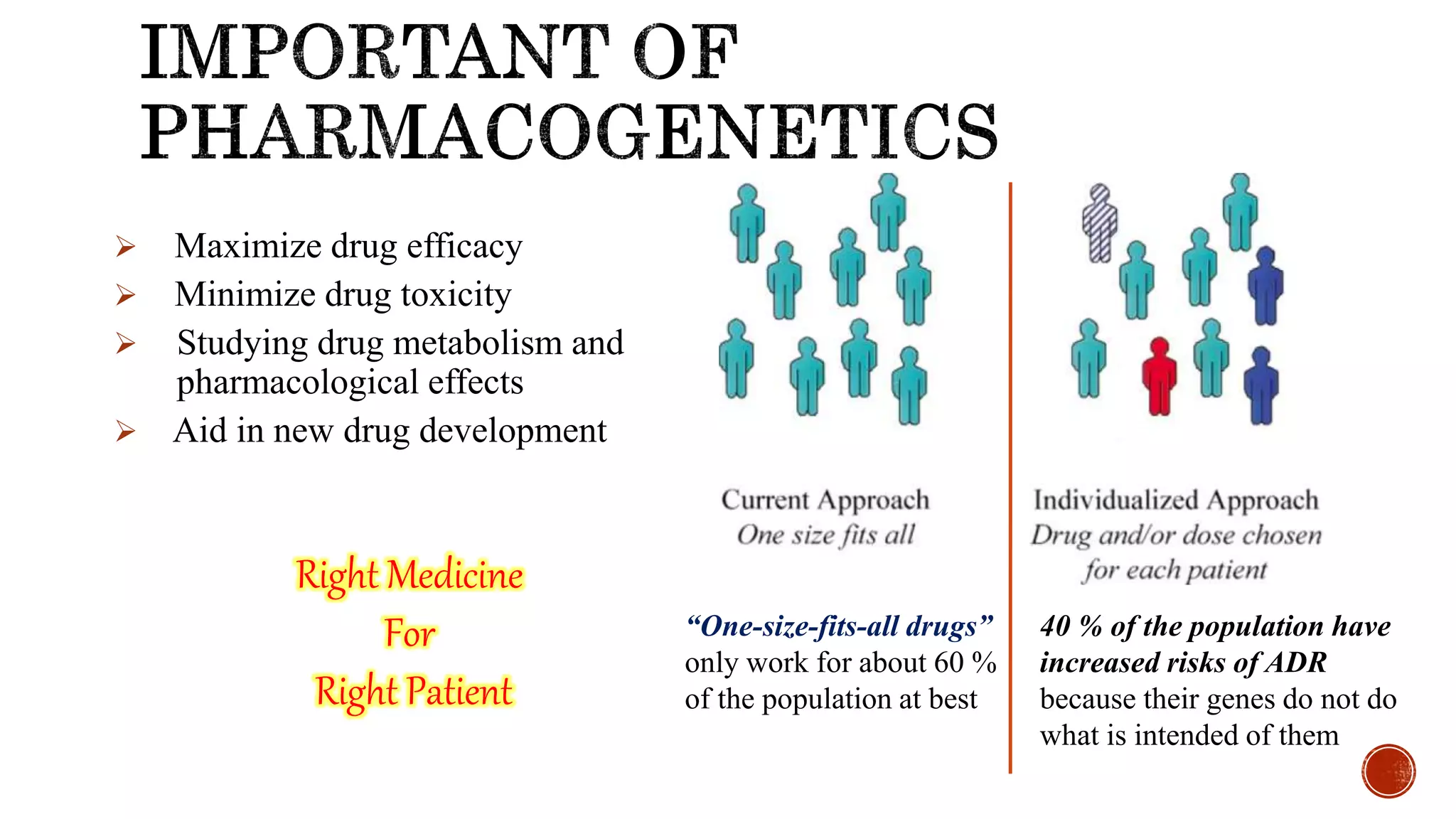
This document discusses pharmacogenetics, which is the study of how genes influence individual responses to drugs. It provides examples of genetic variants that can impact drug metabolism and effects. Specifically, it describes how polymorphisms in CYP2C9 and CYP2D6 genes can influence an individual's response to warfarin and tamoxifen, respectively, and how TPMT polymorphisms can increase toxicity risk from thiopurine drugs. The document also discusses the potential for pharmacogenetic testing to optimize drug therapy based on a person's genetic profile.