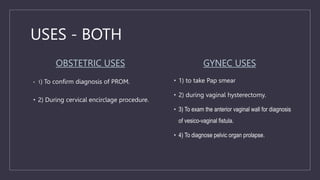
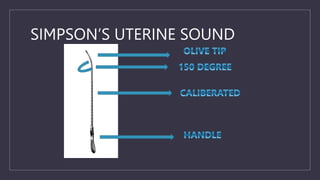
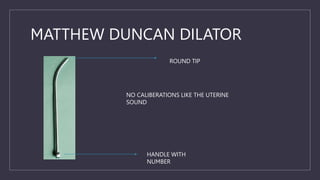
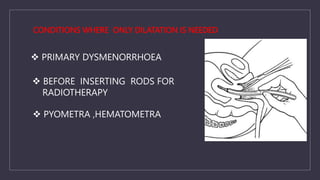
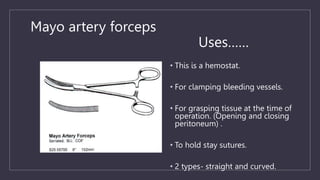
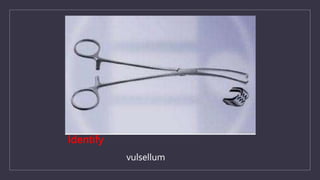
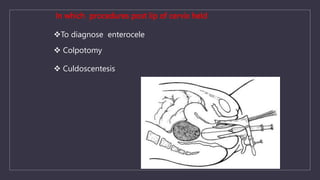
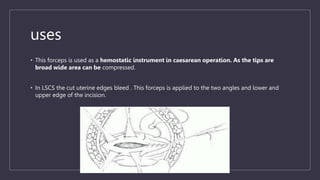
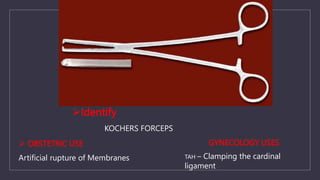
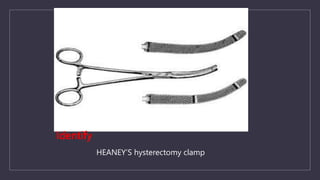
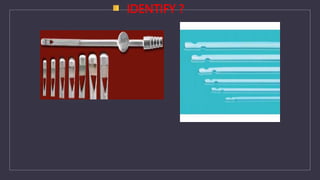
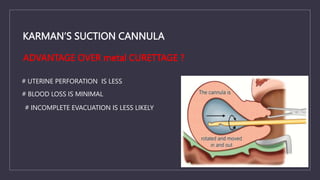
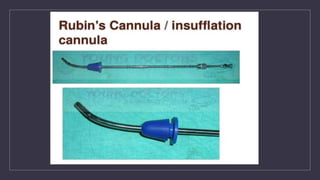
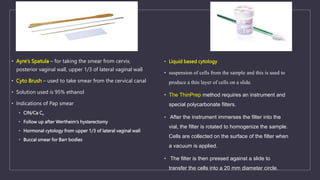
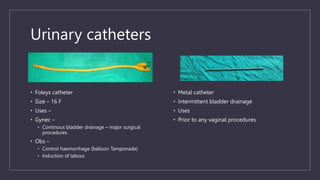
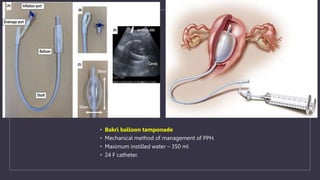
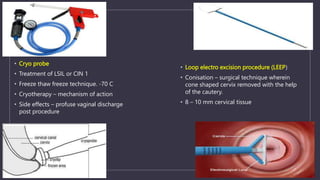
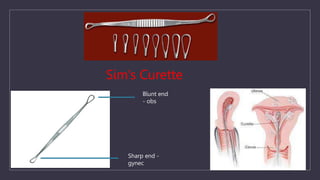
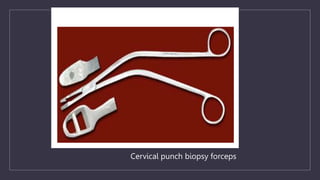
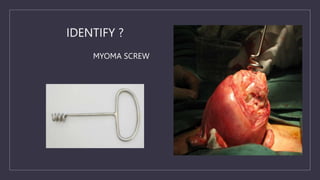
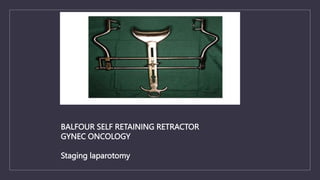
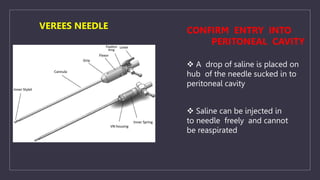
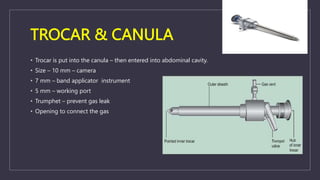
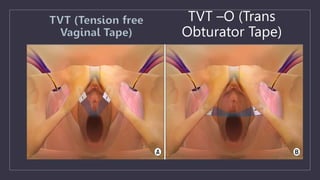
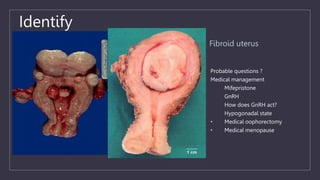
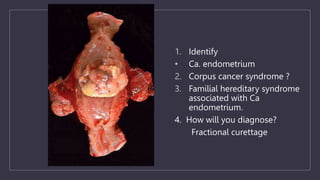
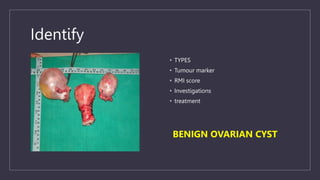
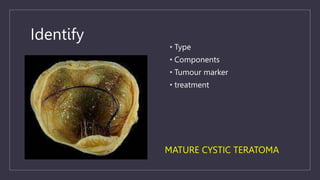
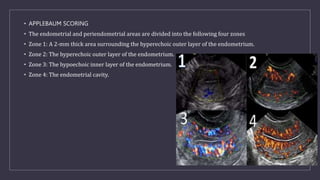
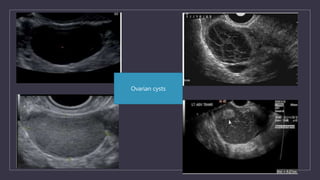
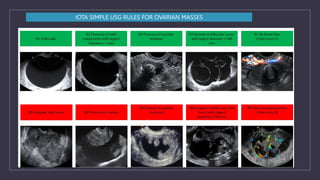
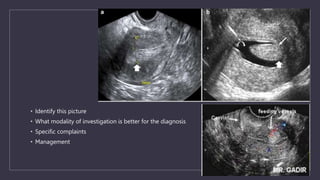
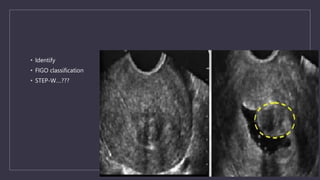
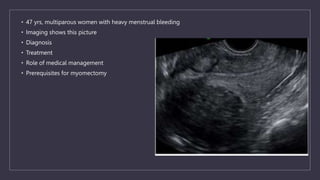
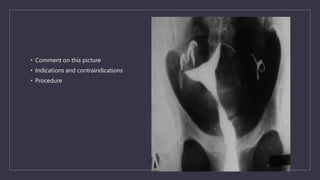
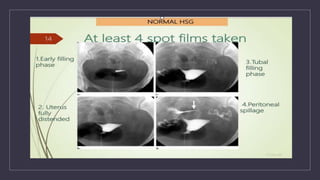
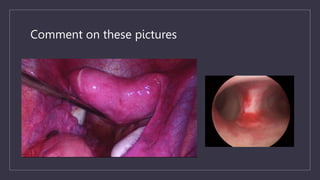
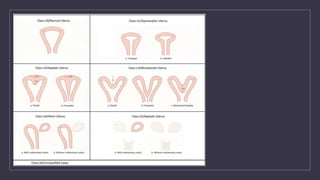
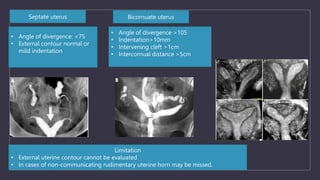
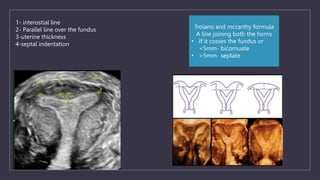
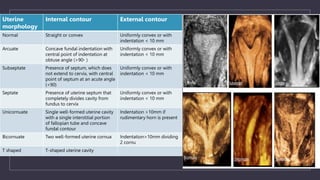
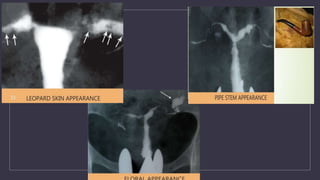
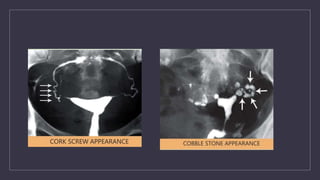
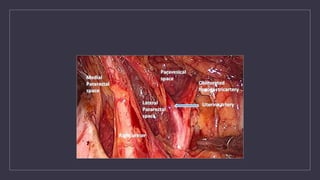
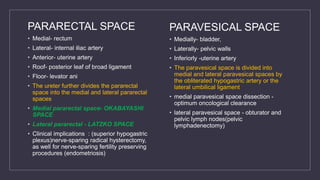
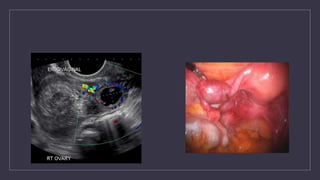
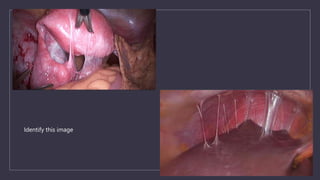
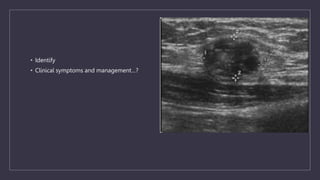
The document discusses various gynecological instruments including speculums, dilators, forceps and cannulas. It explains their uses in obstetrics and gynecology for examining patients, performing procedures like dilation and curettage, and managing conditions like postpartum hemorrhage. Key instruments mentioned are Sims speculum, Simpson sound, Matthew Duncan dilator, Mayo scissors, sponge holding forceps, and Green Armytage forceps. Conditions where only dilation is needed and contraindications for procedures are also summarized.