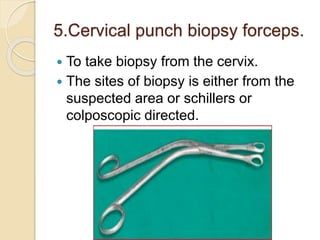
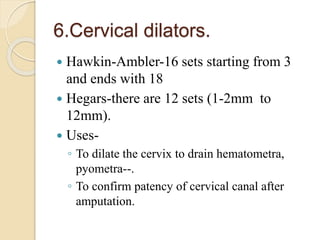
This document lists and describes various diagnostic tools used in obstetrics and gynecology. It discusses speculums, colposcopy, uterine sounds, endometrial curettes, laparoscopy, hysteroscopy, ultrasonography, and other imaging modalities. For each tool, it provides details on types, uses, procedures, indications, contraindications, and complications. The tools allow examination of the reproductive organs and diagnosis of various conditions affecting women's health.