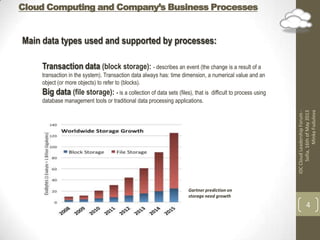
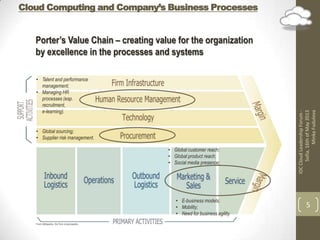
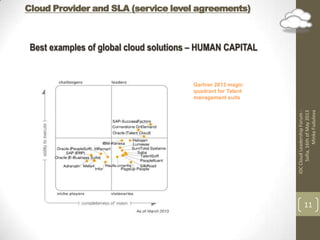
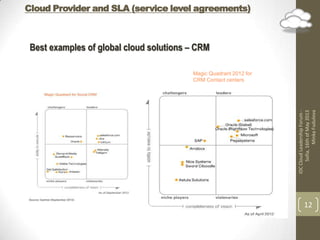
The document discusses implementing cloud technology for business processes and choosing a cloud provider. It highlights the benefits of cloud computing like availability, scalability, and cost savings. It also covers important considerations for cloud adoption like data types used, integration needs, and strategies. When choosing a provider, the document emphasizes clarifying topics in the service level agreement like security, privacy, compliance, and performance definitions.