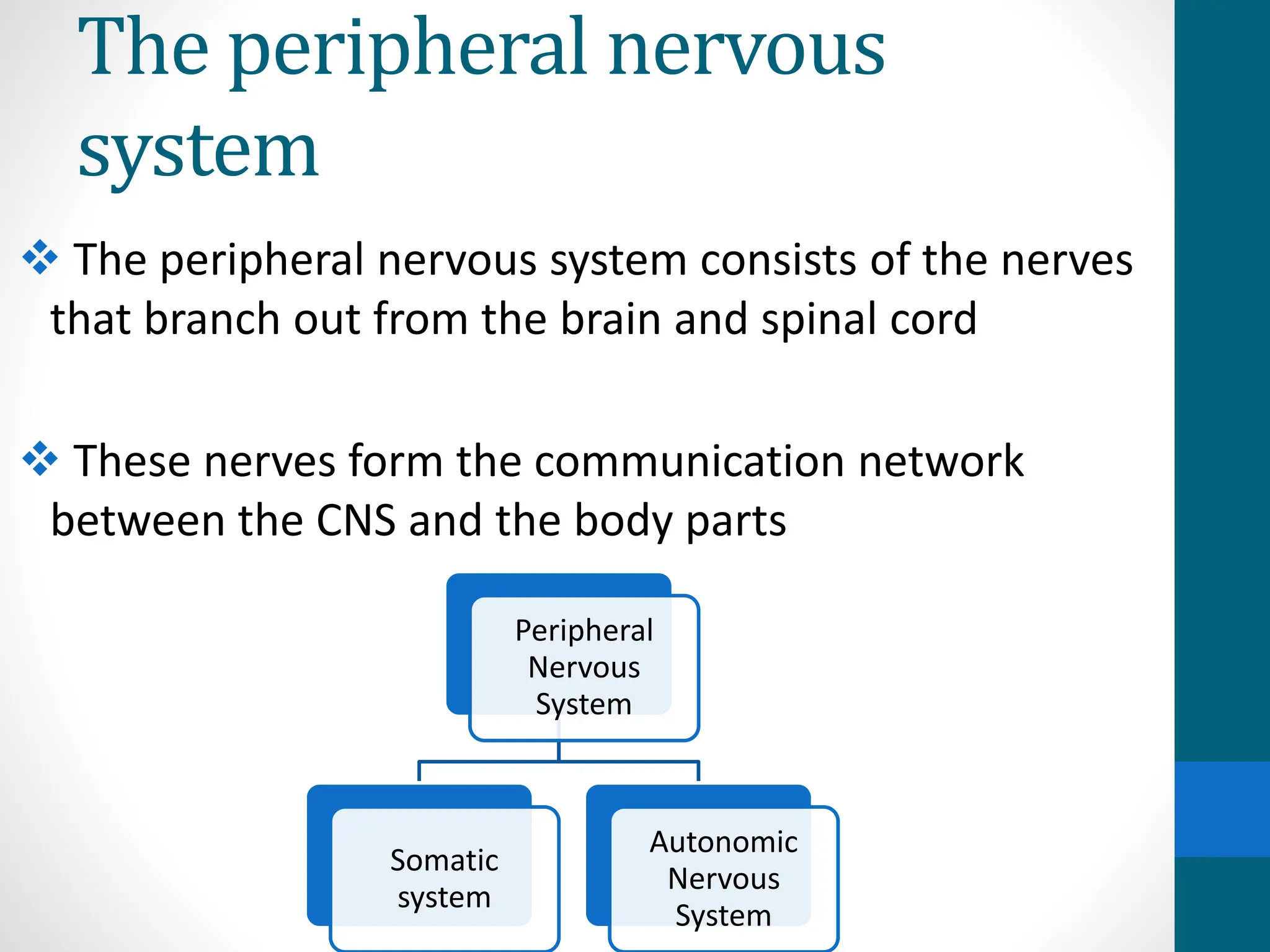
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) connects the central nervous system to the limbs and organs. It consists of nerves that branch out from the brain and spinal cord. The PNS has two main subsystems: the somatic system controls voluntary muscles and skin sensation, while the autonomic system regulates involuntary functions like breathing and heart rate. The autonomic system has sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions that work in opposition to activate the fight-or-flight response or restore the body to rest. Injuries or conditions like diabetes can damage peripheral nerves and disrupt communication between the brain and body.