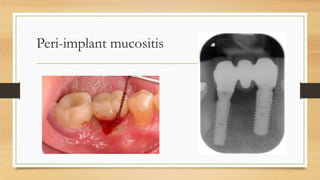
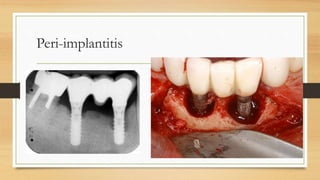
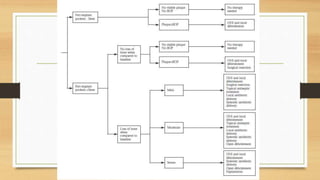
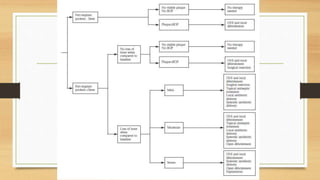
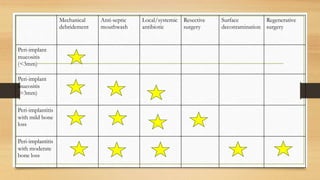
Peri-implantitis is an inflammatory reaction around dental implants that can lead to loss of supporting bone. It has two forms: peri-implant mucositis, which is reversible inflammation confined to soft tissues; and peri-implantitis, which involves progressive bone loss beyond initial remodeling. Risk factors include a history of periodontitis, smoking, residual cement, and implant position/design. Treatment includes non-surgical approaches like mechanical debridement and antibiotics, as well as surgical methods such as regenerative procedures and surface decontamination. The combination of systemic antibiotics, antiseptic mouthwash, and surgical debridement can improve outcomes, though no single surface decontamination method is superior.