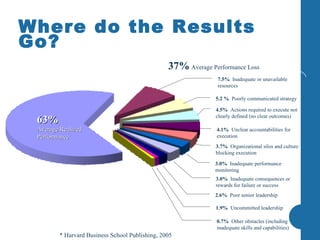
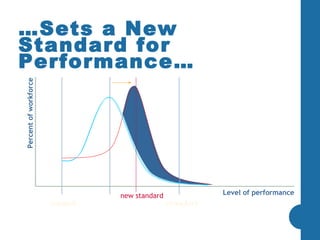
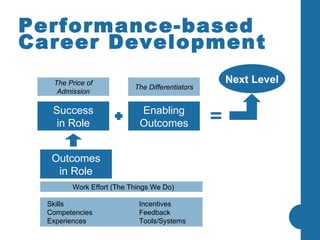
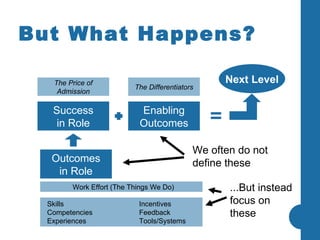
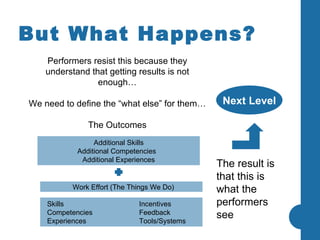
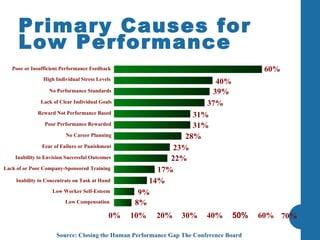
Most company strategies only deliver 63% of their promised financial value due to various obstacles. Common reasons for poor performance include unclear accountabilities, organizational silos blocking execution, and inadequate performance monitoring. A new approach is needed that sets a new standard for performance by selecting best-fit performers, training them to produce outcomes, engineering their work environment, and motivating them. This directly impacts business results by defining outcomes, skills, incentives, and other factors that influence how people accomplish tasks and processes critical to effective performance.