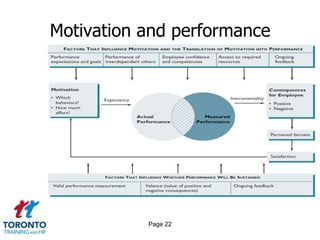
This document provides an overview of performance management. It discusses defining performance expectations, providing feedback and conducting reviews. Key aspects covered include developing goals, monitoring progress, rating and rewarding performance. The document outlines how to select metrics, build engagement and trust, and handle high and low performers. It also provides strategies for ensuring legal compliance and creating a high-performing organizational culture focused on continuous improvement.