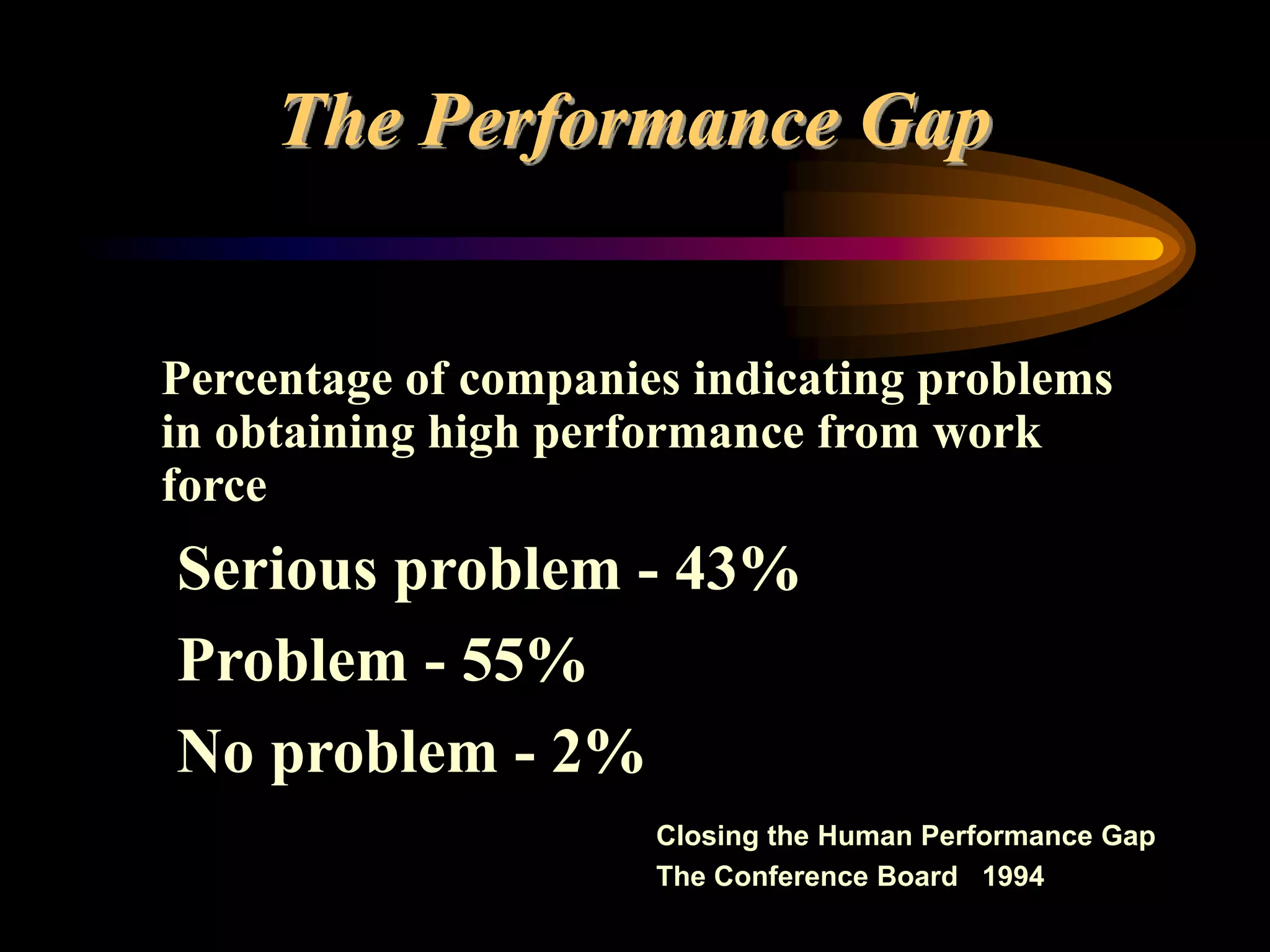
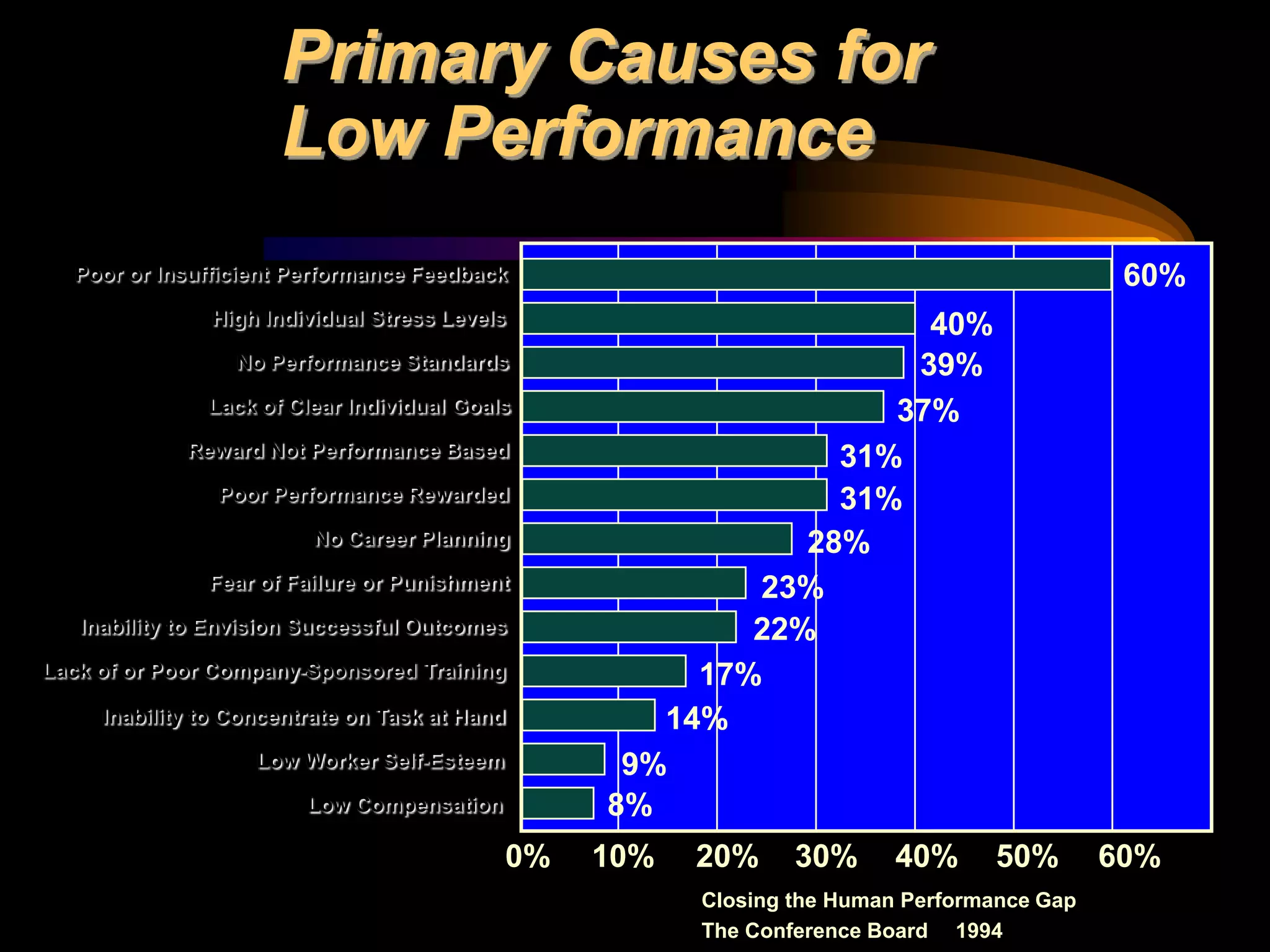
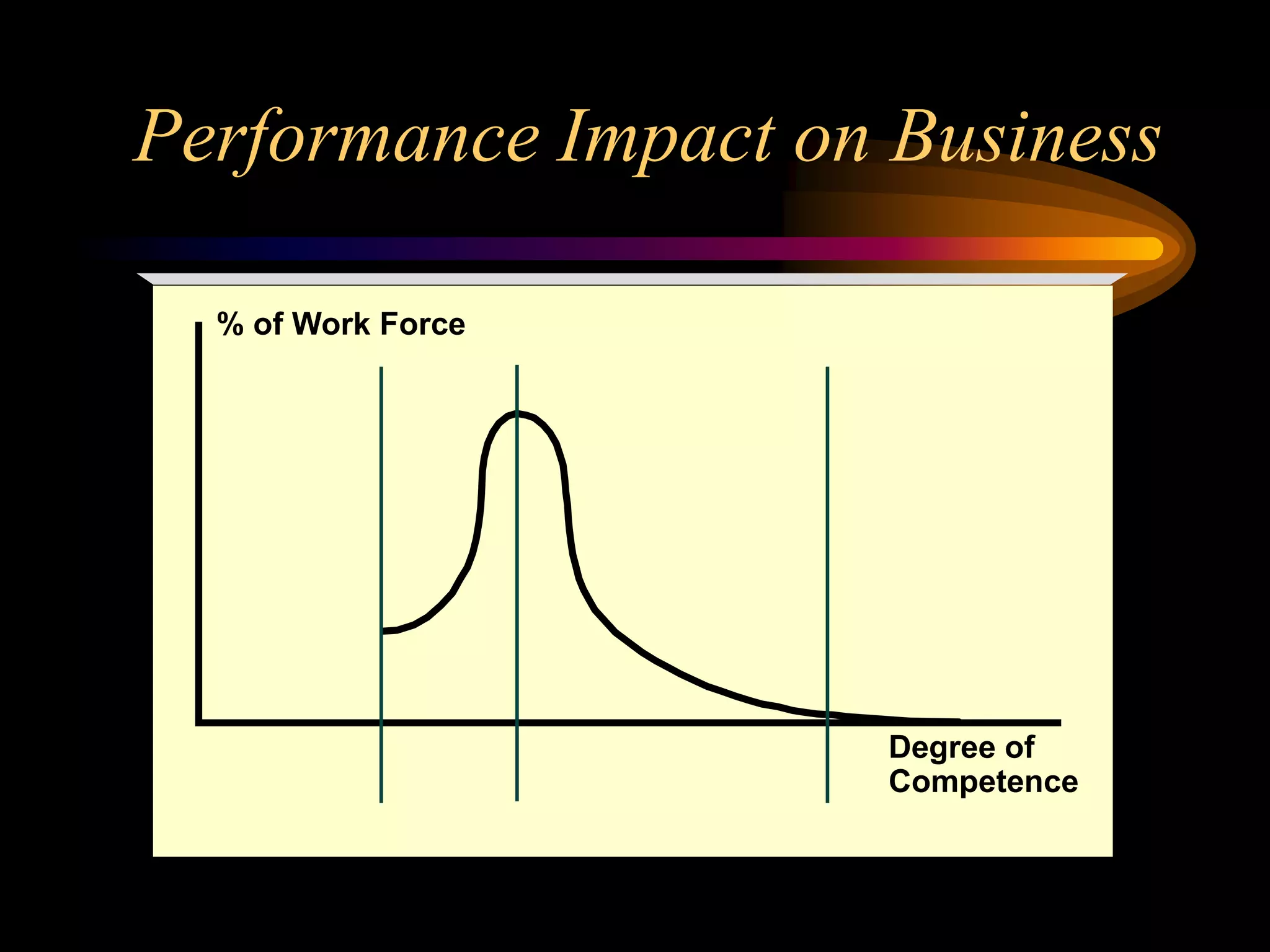
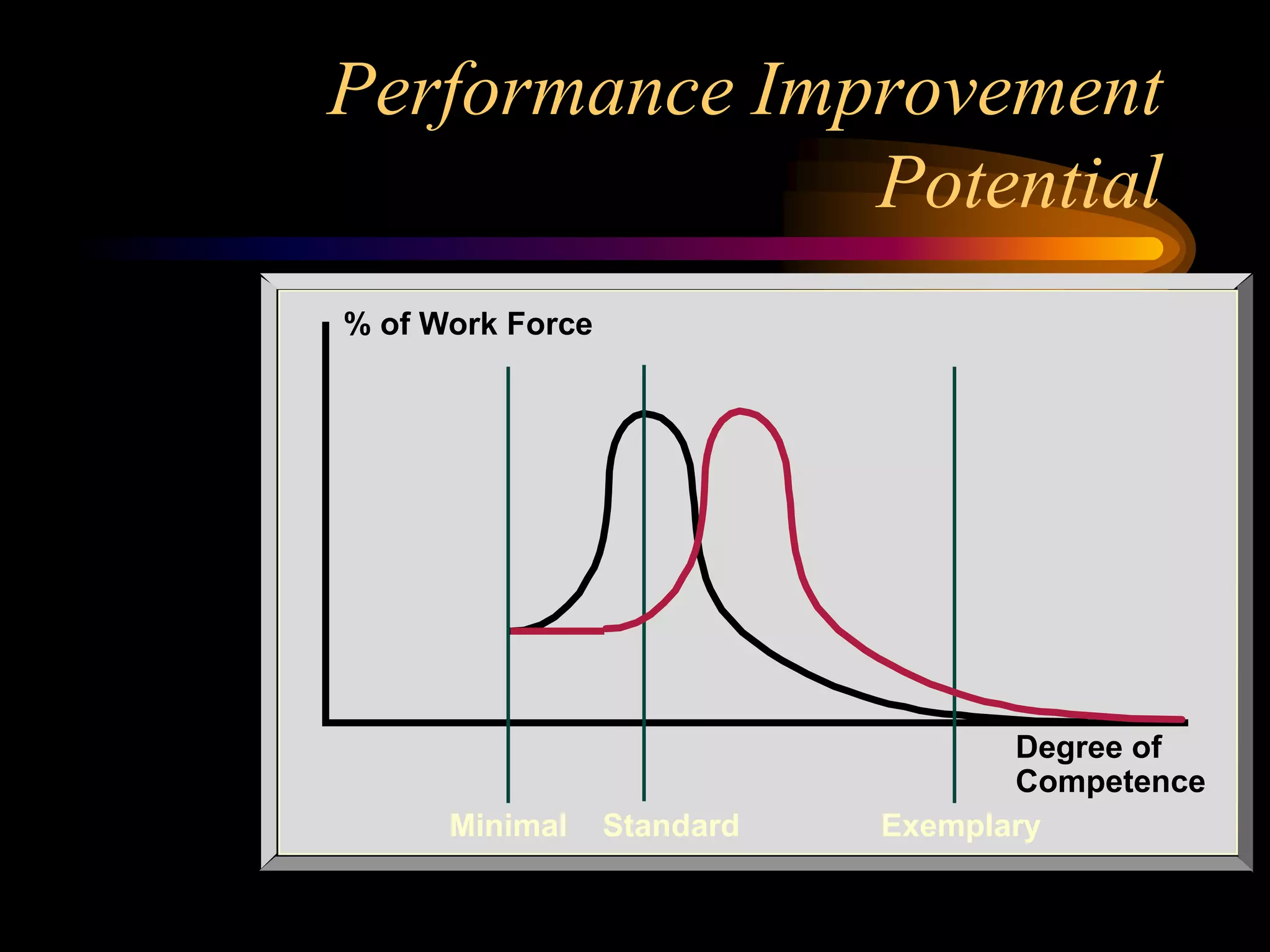
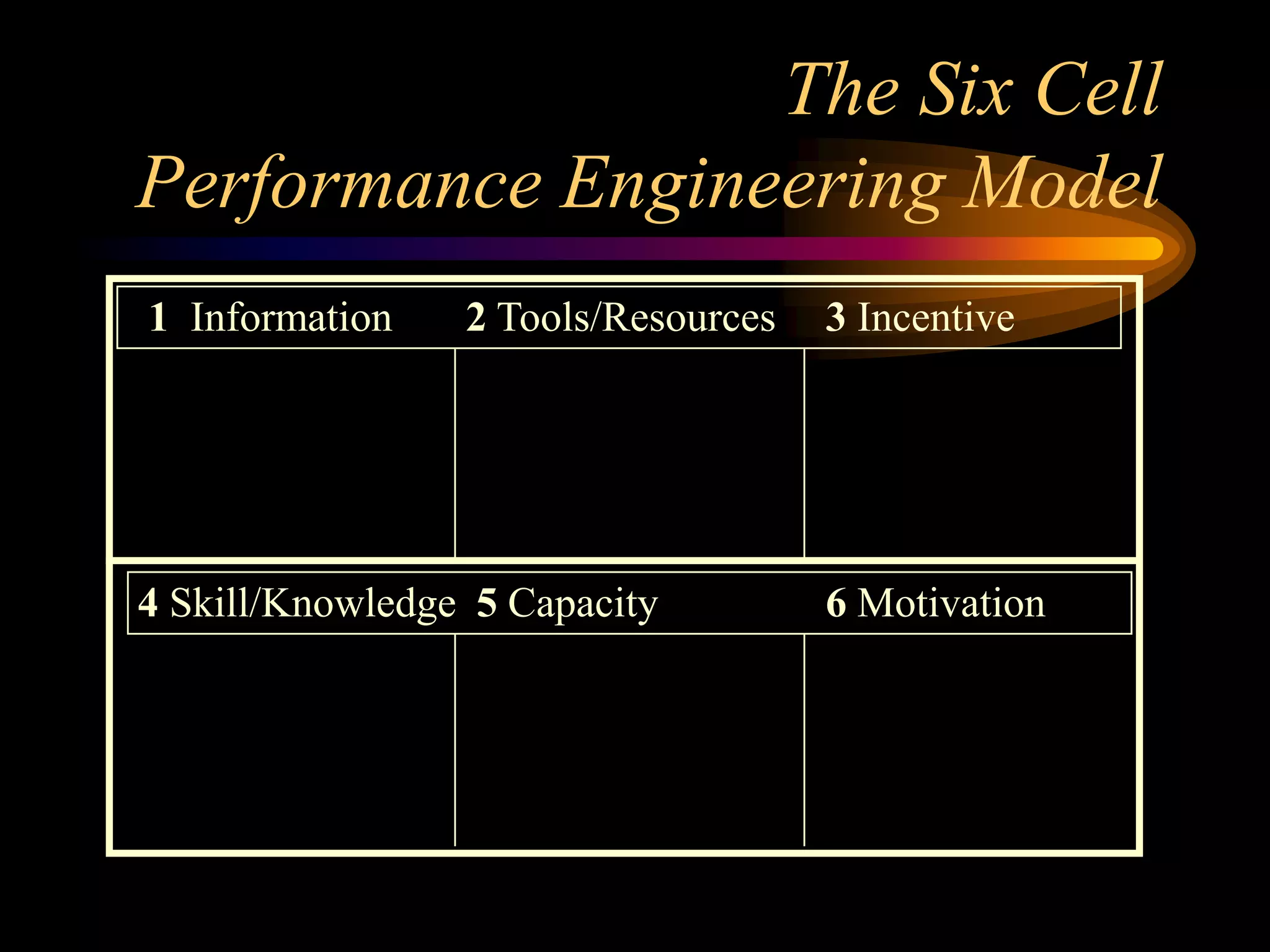
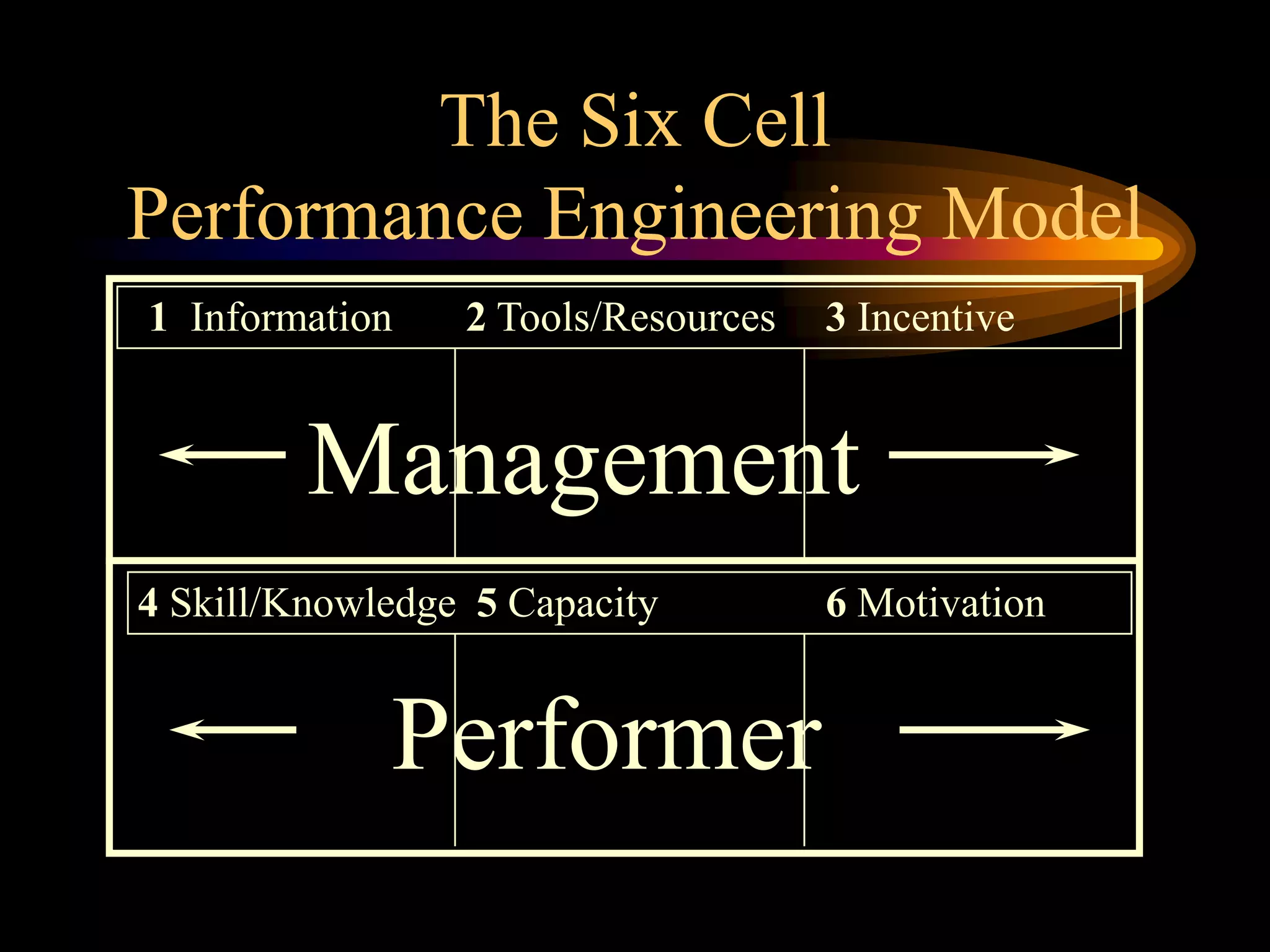
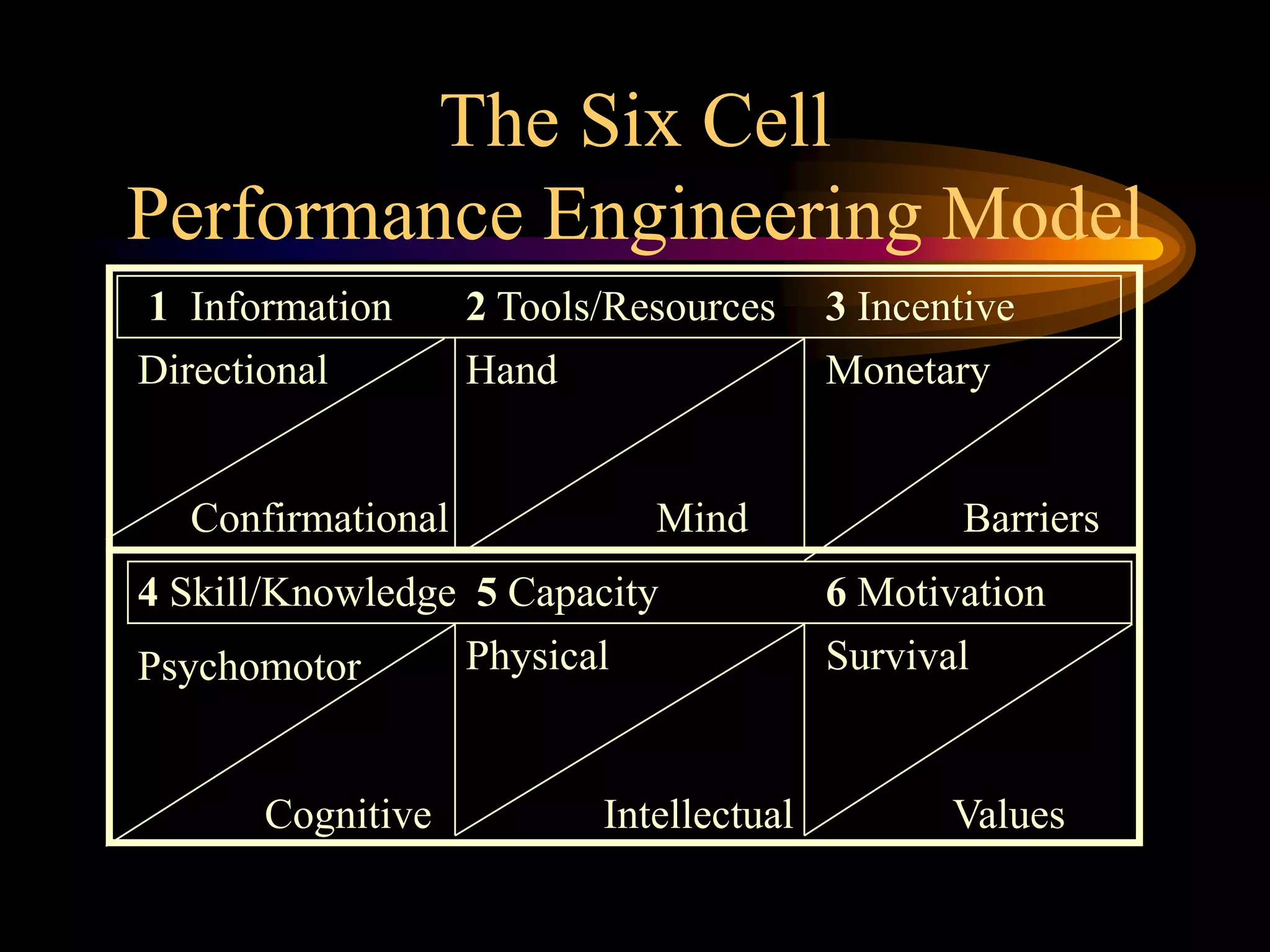
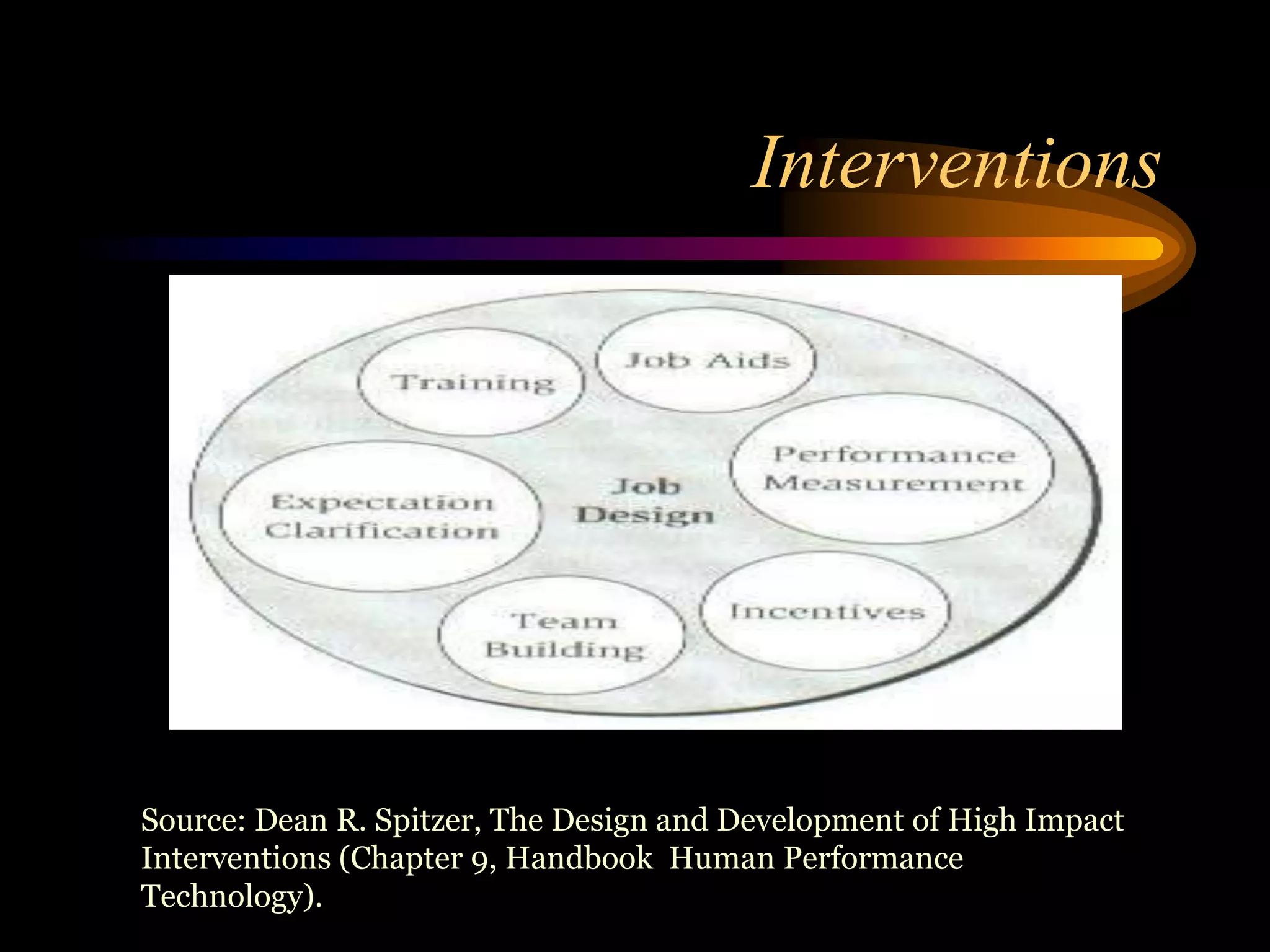
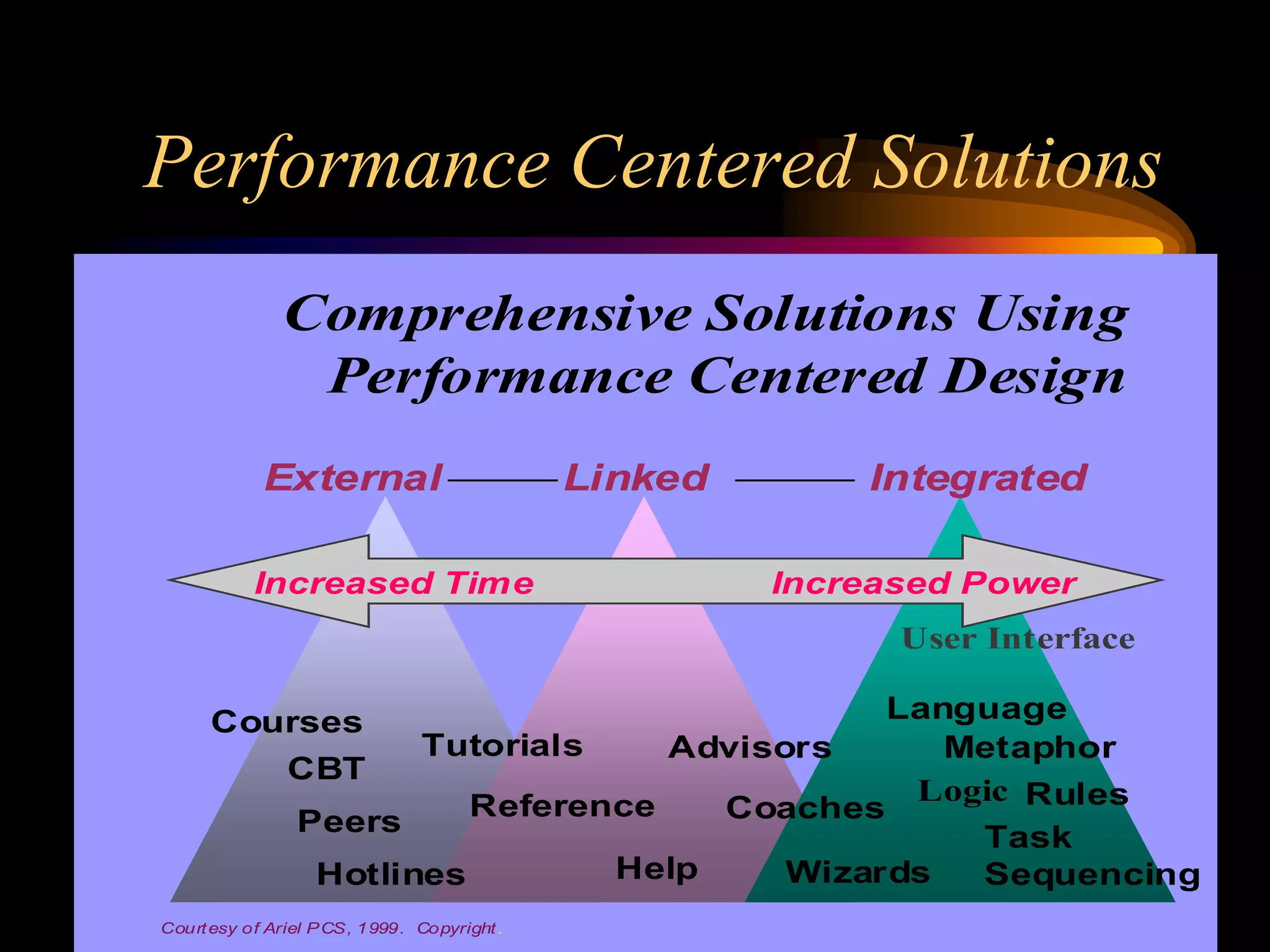
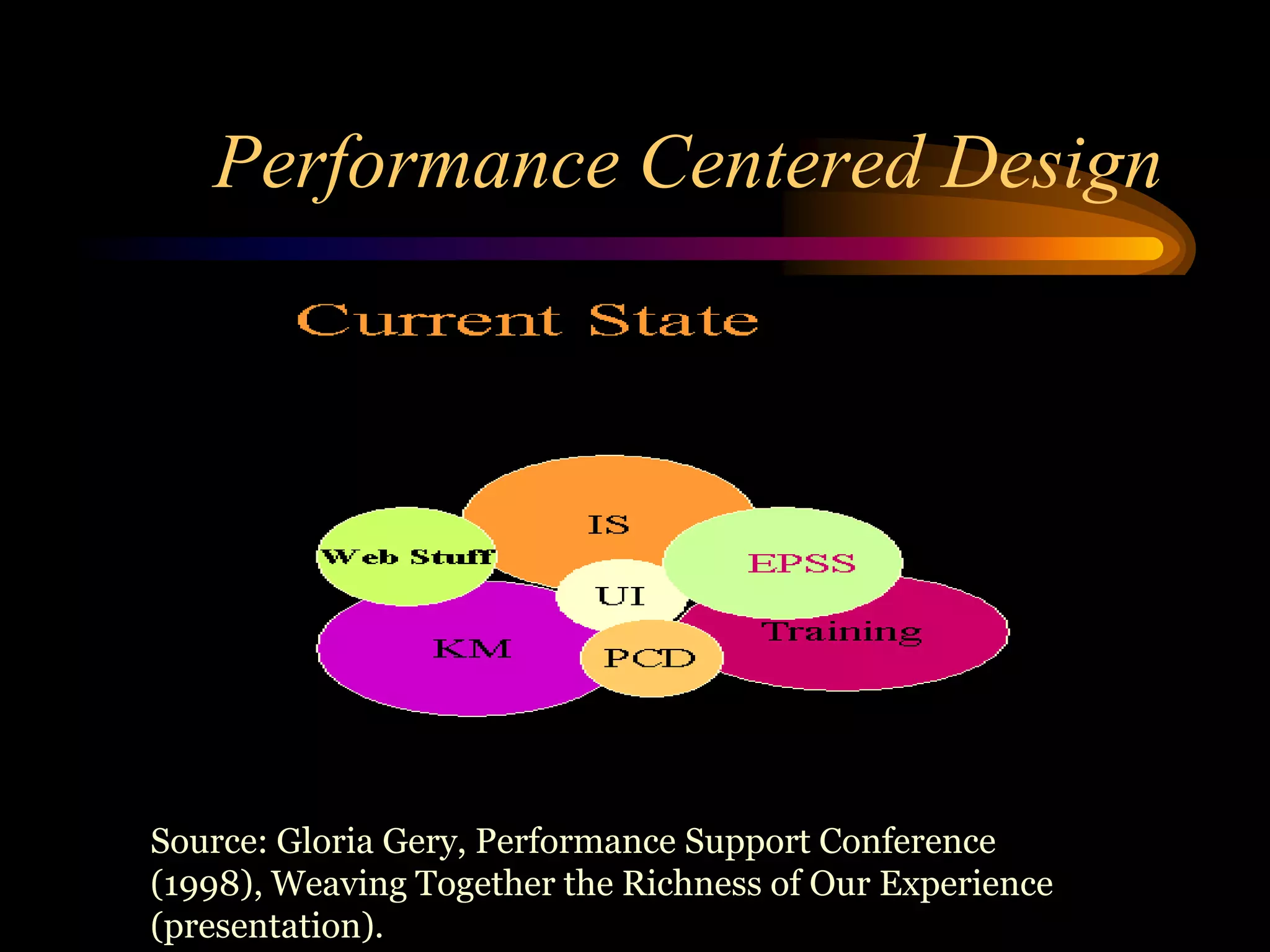
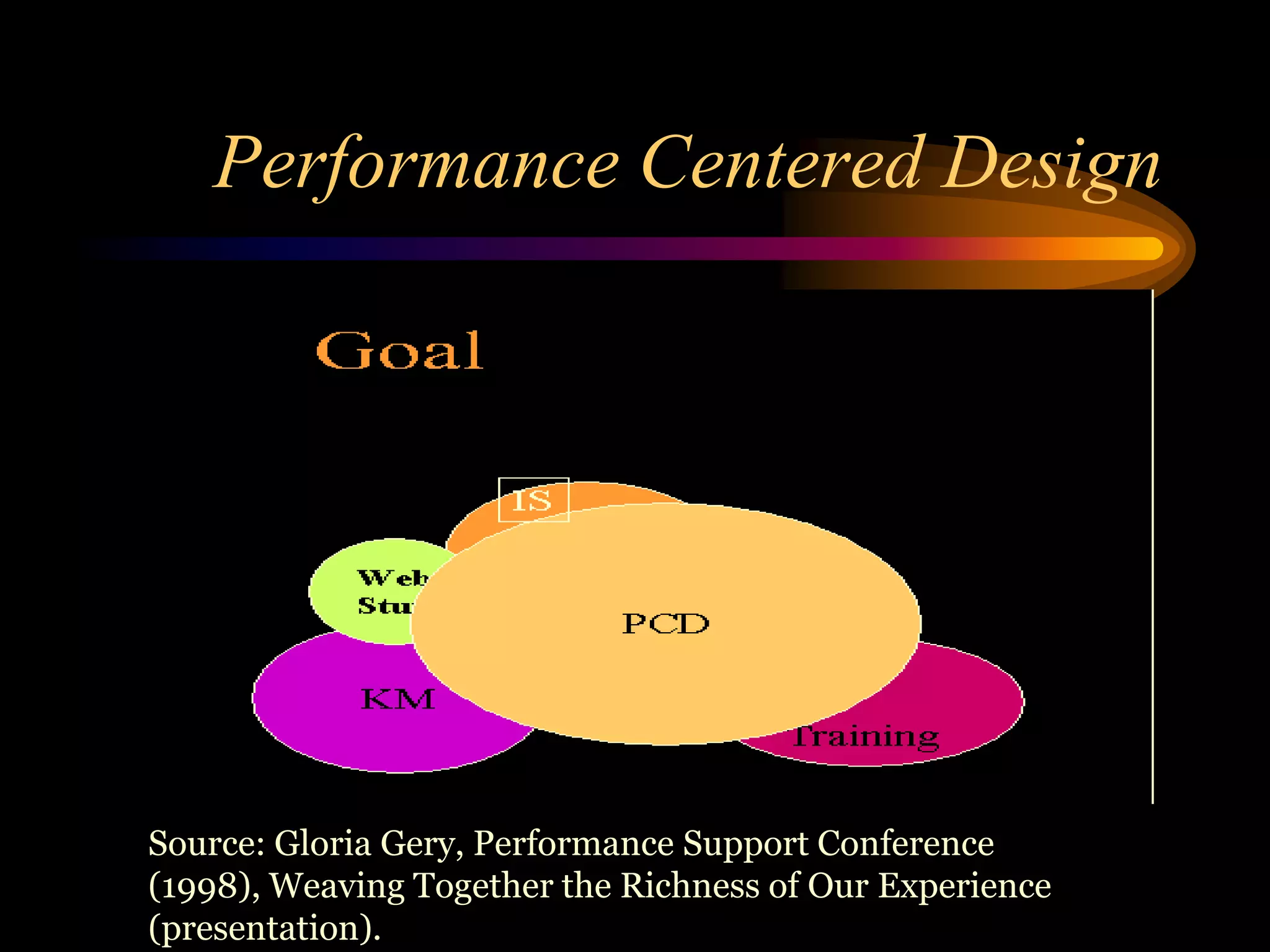
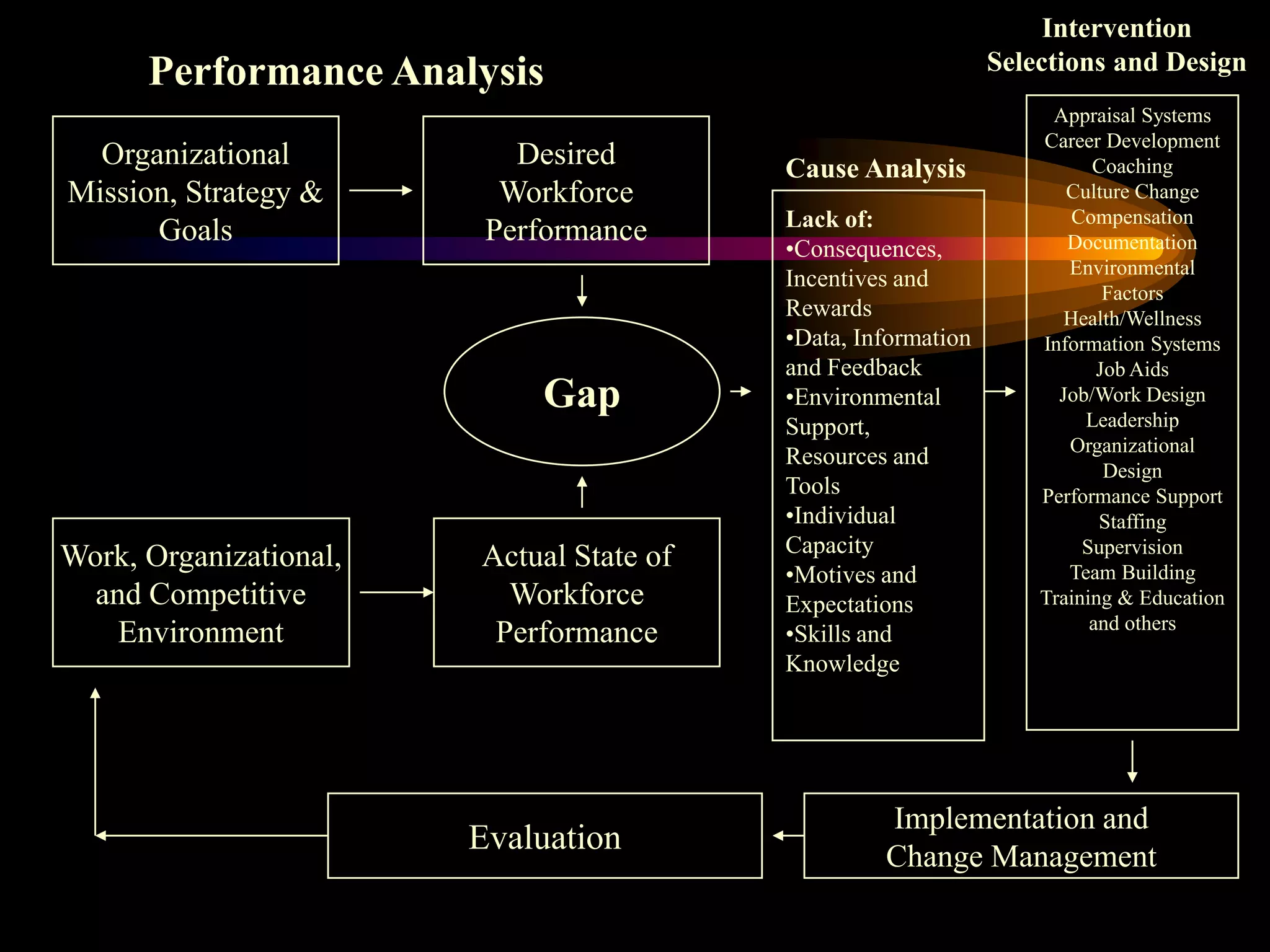
I would conduct a thorough analysis of the performance issue across three levels - organizational, process, and individual performer. This would involve gathering data on sales trends, contractor capabilities and goals, as well as identifying specific performance gaps. Based on the analysis, I would design and implement interventions targeting information, knowledge, and incentives to help the contractor successfully market and sell the company's products. The overall goal would be to close the performance gap and increase sales in a cost-effective manner.