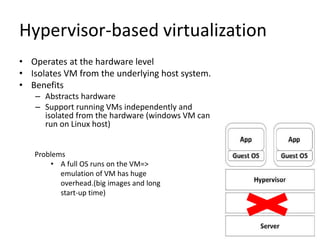
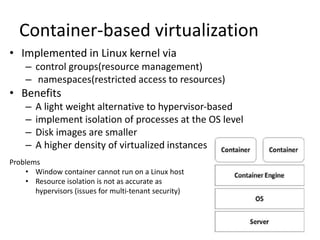
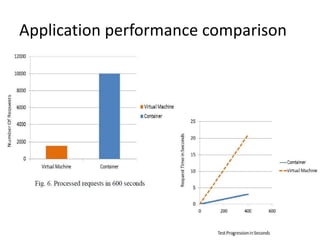
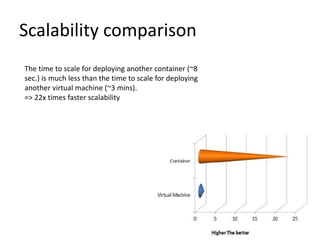
The document compares the performance of Linux containers and virtual machines (VMs) in terms of scalability and efficiency, highlighting virtualization technologies and their benefits. It concludes that containers significantly outperform VMs, being 22 times faster in scaling and better suited for application deployment, though potential security concerns exist for business-critical data. The discussion includes different virtualization methods, their advantages, and a detailed performance testing setup using Docker and AWS EC2.