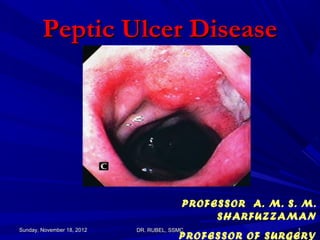
Peptic ulcer disease is defined as an ulcer occurring in areas exposed to gastric acid and pepsin, most commonly the duodenum or stomach. Key risk factors include infection with Helicobacter pylori bacteria and use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Patients may experience abdominal pain relieved by food or antacids, though physical exams are often unremarkable. Complications can include bleeding, perforation, or scarring. Diagnosis involves endoscopy, biopsy, and tests for H. pylori infection.