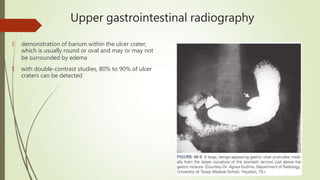
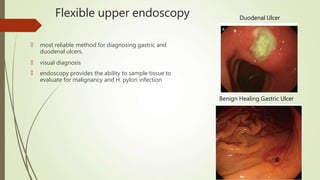
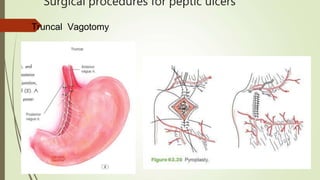
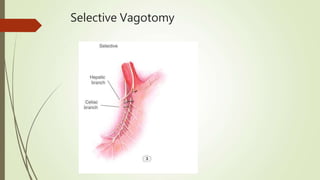
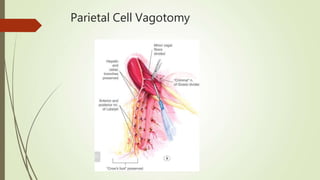
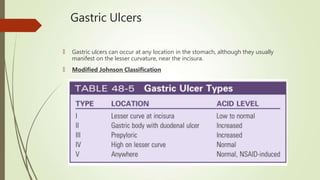
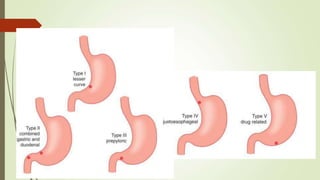
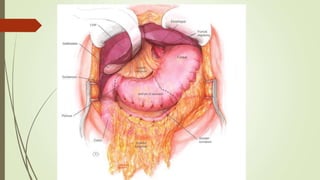
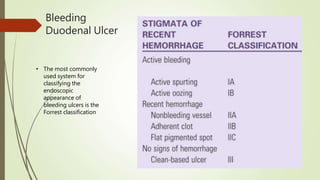
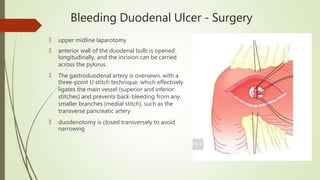
Peptic ulcers are erosions in the stomach or duodenum caused by an imbalance between gastric acids and mucosal defenses. Risk factors include H. pylori infection, NSAIDs, smoking, and stress. H. pylori infection is the leading cause and eradication treatment involves PPIs and antibiotics. Complications of peptic ulcers include bleeding, perforation, and obstruction. Endoscopy is the best diagnostic tool and allows for treatment of bleeding ulcers. Surgery may be needed for complications or intractable disease.