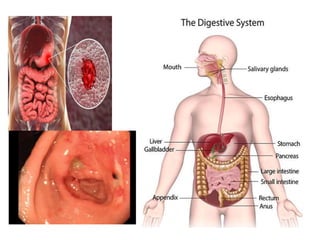
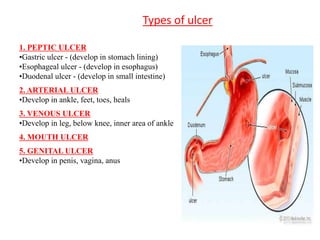
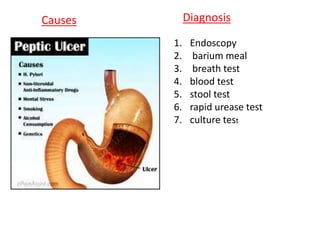
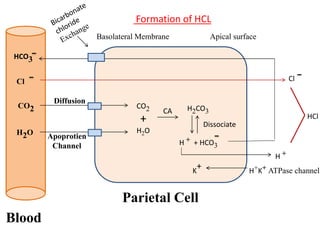
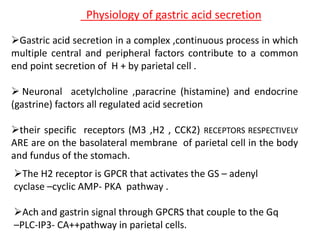
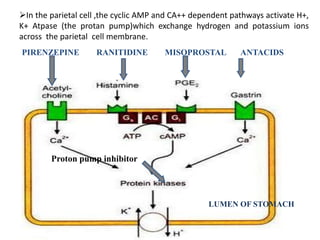
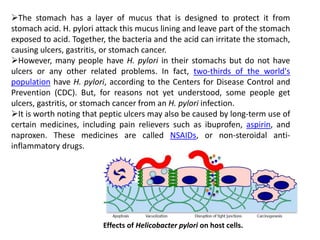
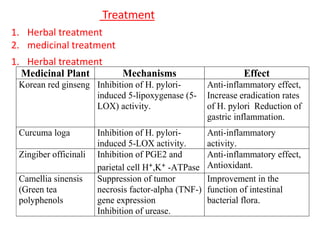
Peptic ulcers develop in parts of the gastrointestinal tract exposed to gastric acid and pepsin. Risk factors include H. pylori infection, NSAID use, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. H. pylori bacteria attack the stomach's mucus lining and expose it to acid, potentially causing ulcers, gastritis, or stomach cancer. Treatment involves antibiotics to eliminate H. pylori along with proton pump inhibitors to reduce acid. Herbal treatments with plants like ginger, turmeric, and green tea can provide anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects as well. Drug interactions must be monitored as some herbs interact with common medications.





![Together with increasing use of herbal supplements worldwide, the number of
adverse eventsand drug interactions is rising.
Panax ginseng induces cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4), which decreases
the effectiveness of calcium channel blockers, certain antihypertensive and
statin medications, and some antidepressants.
Ginkgo biloba could increase bleeding risk, especially in combination with
anticoagulant drugs, due to the inhibition of platelet aggregation
.
Flavonoids in Ginkgo biloba have antiplatelet activity, but do not affect blood
coagulation or platelet function in humans [103]. In combination with NSAIDs,
it can cause severe bleeding.
Zingiberofficinalis prolongs bleeding time by the inhibition of thromboxane
synthetase, but this has not been confirmed in a clinical trial
Herb –drug –interaction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonpepticulcer-190913122420/85/Presentation-on-peptic-ulcer-14-320.jpg)


