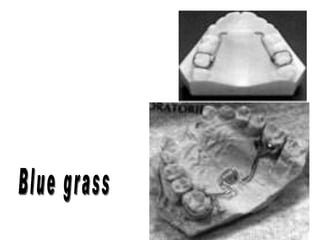
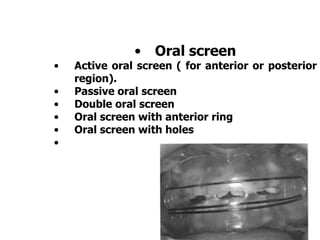
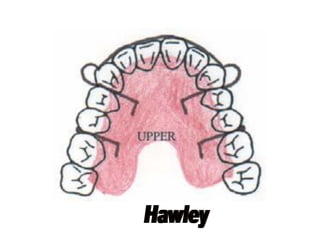
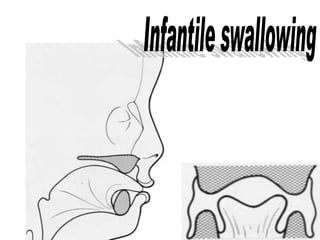
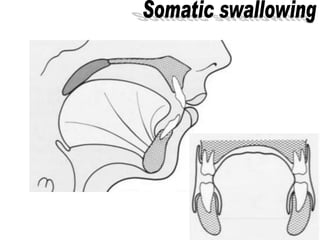
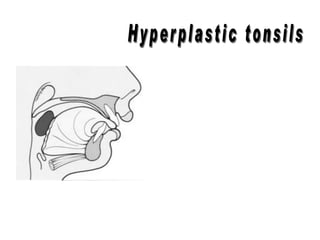
The document discusses various oral habits that can interfere with facial growth and cause malocclusion. It describes habits like digit sucking, tongue thrusting, mouth breathing, lip biting, nail biting, cheek biting, bruxism, abnormal posture, and self-mutilation. For each habit, it discusses the causes, effects on dental development and jawbones, diagnosis, and treatment options like counseling, reminders, appliances, and exercises to help correct undesirable oral behaviors.