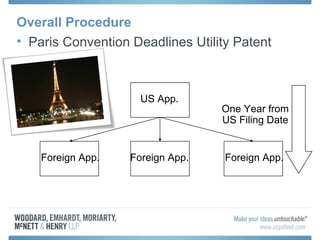
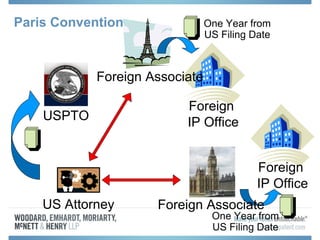
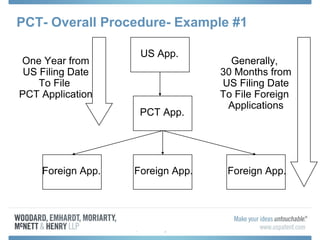
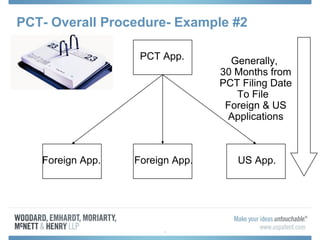
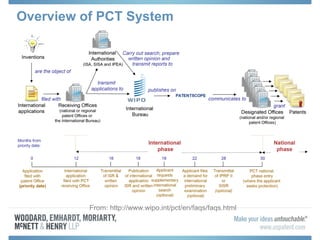
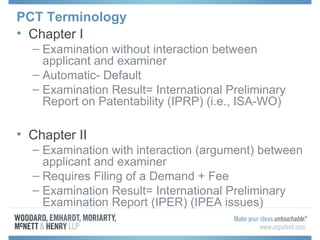
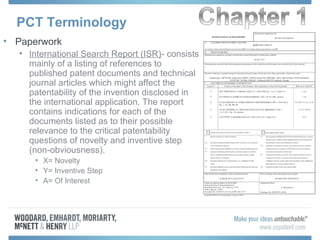
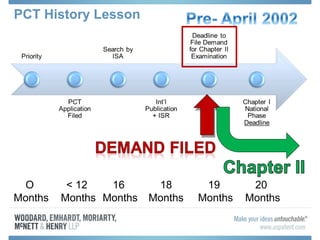
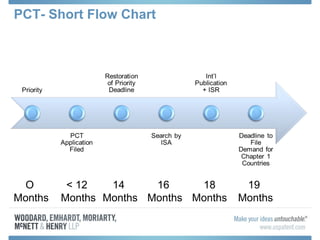
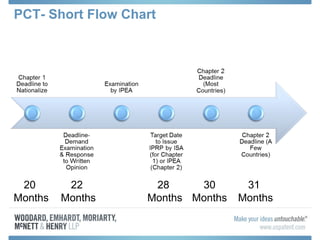
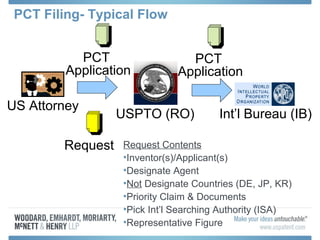
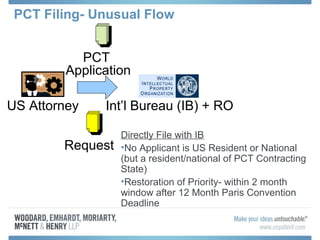
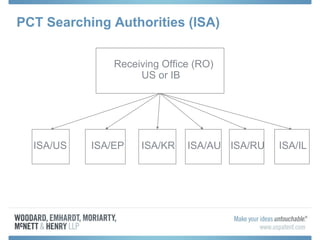
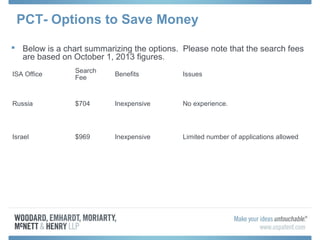
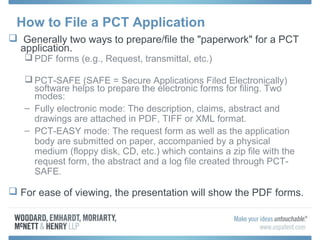
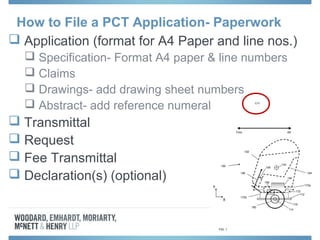
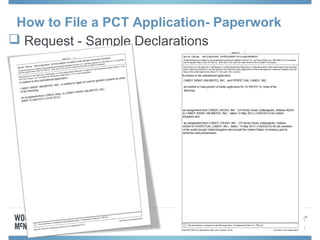
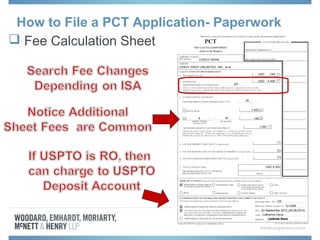
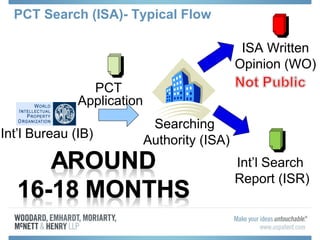
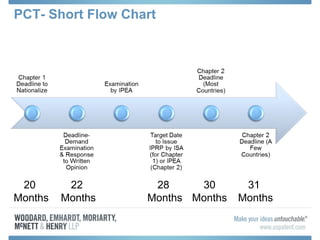
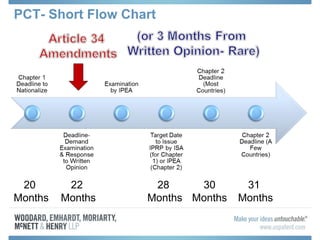
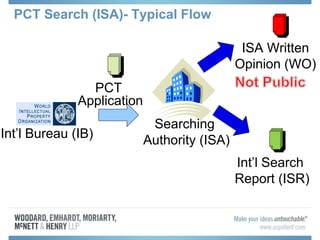
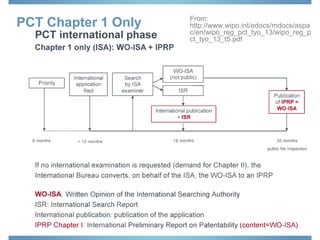
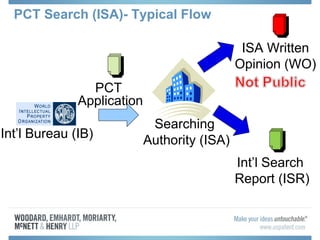
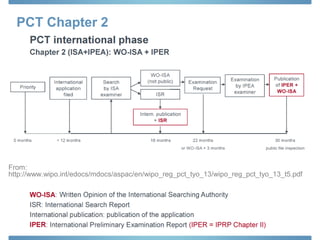
The document discusses options for international patent filing, including directly filing in foreign countries, filing under the Paris Convention, or filing under the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT). It notes key differences between the Paris Convention and PCT, such as deadlines and costs. The document also provides an overview of procedures and paperwork involved in PCT filing, including International Search Reports, Written Opinions, and International Preliminary Reports on Patentability. It highlights considerations for choosing between filing under Chapter I or II of the PCT.