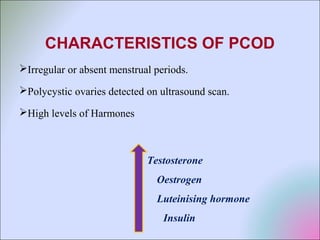
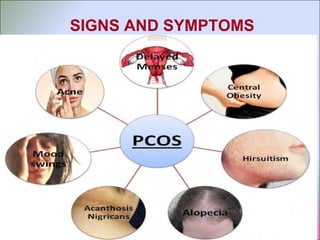
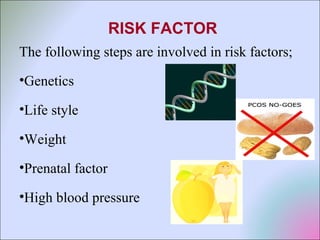
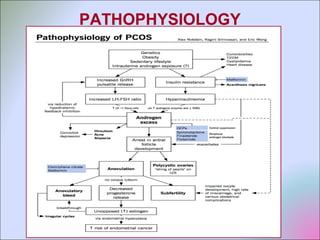
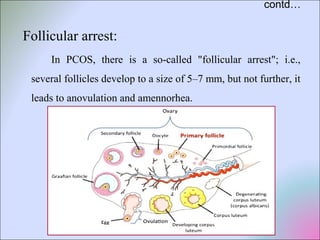
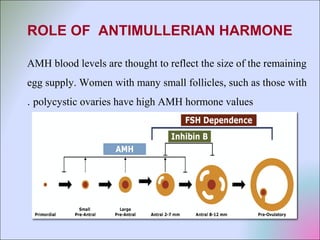
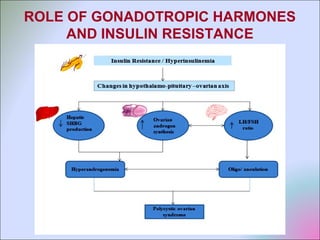
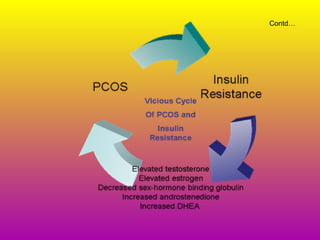
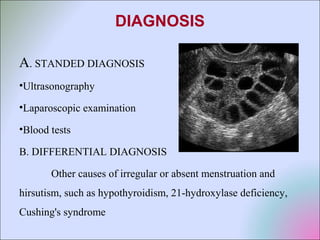
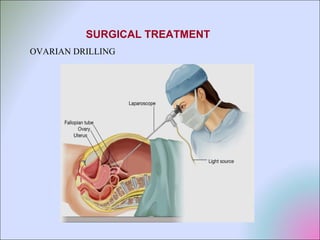
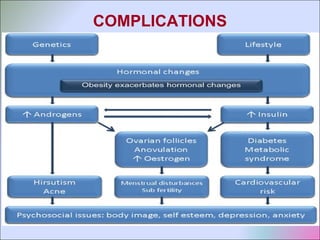
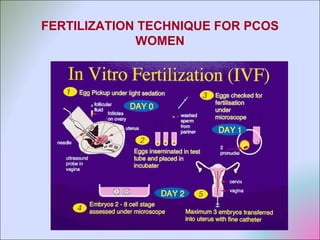
This document discusses polycystic ovarian disorder (PCOD) and its impact on infertility. It begins by defining PCOD as a chronic hyperandrogenic state caused by cysts forming on the ovaries which prevent ovulation. It then discusses the characteristics, epidemiology, risk factors, pathophysiology, diagnosis, consequences such as infertility and increased health risks, and treatment options including lifestyle changes, medication, and surgery. The conclusion emphasizes that while PCOD cannot be cured, the symptoms and infertility can be treated, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle may decrease the risk of developing PCOD.