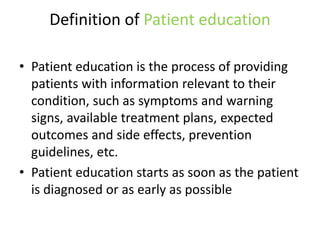
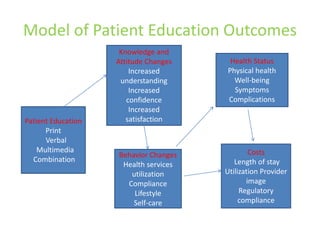
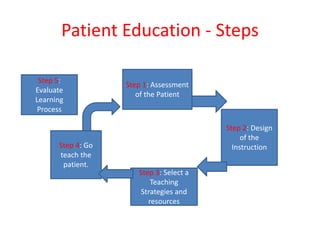
The document provides information about patient education. It defines patient education as the process of providing patients with relevant information about their condition to help them better understand it and available treatment options. The benefits of patient education include patient empowerment, better health outcomes, lower readmission rates, improved quality of life for chronic patients, better healthcare experience and satisfaction, and lower healthcare costs. A model of patient education outcomes shows how education can lead to knowledge, attitude, behavior and health status changes. The document outlines the steps in patient education as assessment of the patient, design of instruction, selection of teaching strategies, providing education, and evaluation.