Embed presentation
Download to read offline

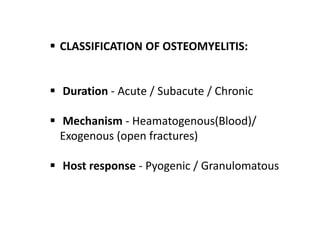

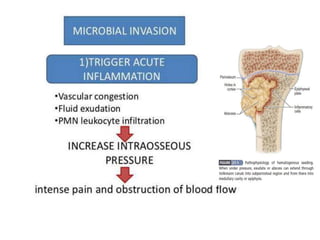
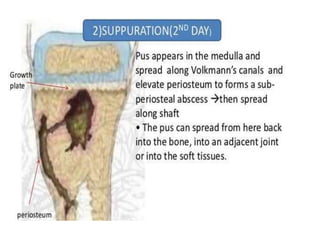
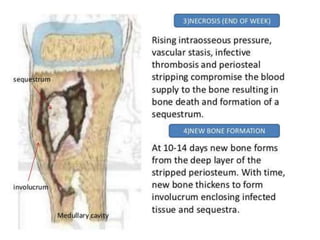
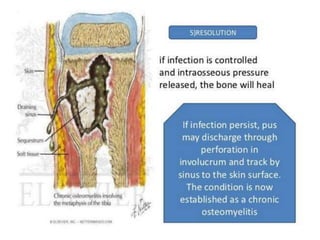
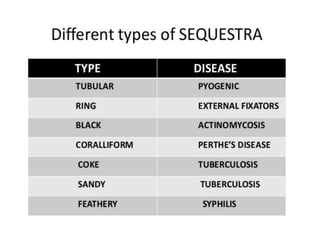

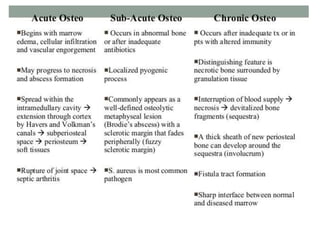
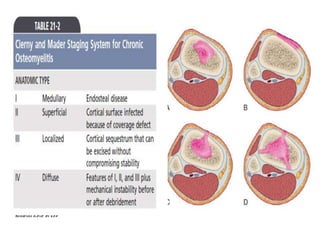


This document discusses the pathophysiology of sequestrum in osteomyelitis. It classifies osteomyelitis by duration, mechanism, and host response. The most common causative microorganisms are Staphylococcus aureus overall and Pseudomonas in IV drug users. Clinical features include pain, swelling, fever and pseudoparalysis. Two specific types discussed are Brodie's abscess, which presents as a bone abscess surrounded by sclerosis, and sclerosing osteomyelitis of Garre, which involves nonsuppurative sclerosis of the jaw.












