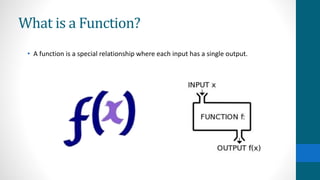
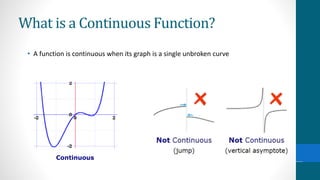
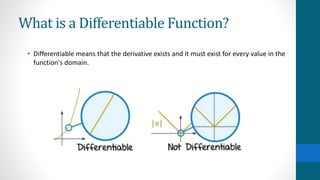
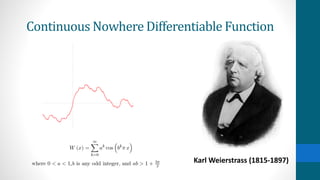
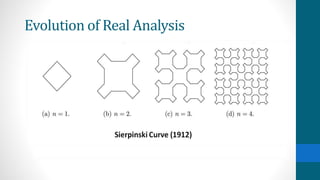
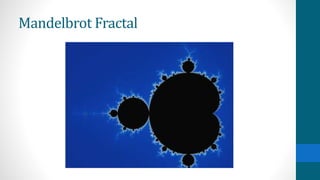
The document discusses pathological functions, specifically the continuous but nowhere differentiable function introduced by Karl Weierstrass, which illustrates a function that is continuous but does not possess a derivative at any point. This idea initially faced skepticism from mathematicians, as it challenged the prevailing belief that continuous functions are differentiable except at certain domain points. The introduction of these concepts marked a significant shift in real analysis, leading to increased rigor and the exploration of new mathematical areas such as fractals and chaos.