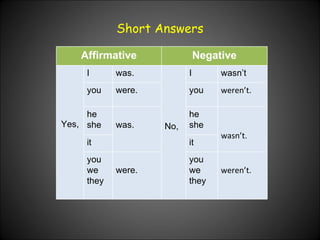
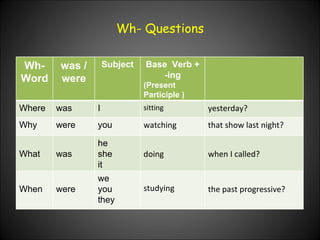
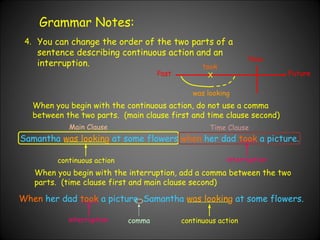
The document provides examples and explanations of how to use the past progressive tense in English. It discusses how to form the past progressive using was/were plus the present participle. It also covers using the past progressive to describe actions that were ongoing at a specific time in the past or that were interrupted by another past action.