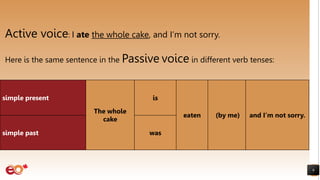
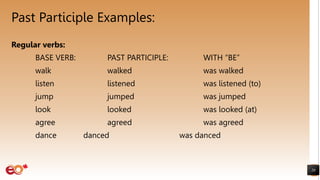
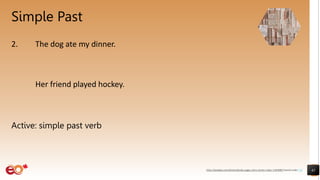
The document discusses active and passive voice in English sentences. It begins by defining active and passive voice, noting that active sentences have the subject performing the action, while passive sentences have the object as the focus of the action. It then covers forming passive sentences using the appropriate form of "to be" plus the past participle of the main verb. The document provides examples of changing active sentences to passive in both the simple present and simple past tenses. It concludes by discussing appropriate uses of the passive voice.