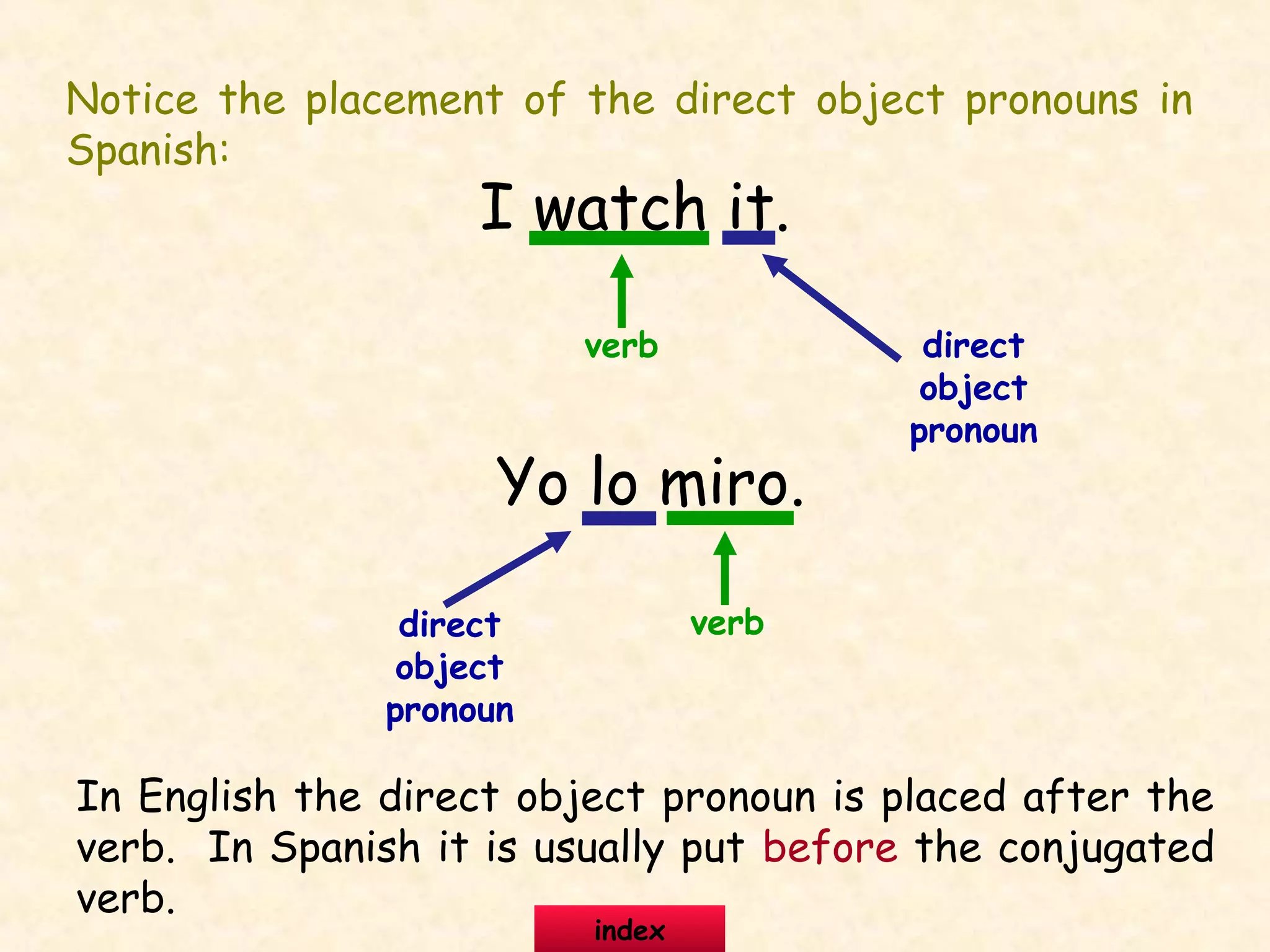
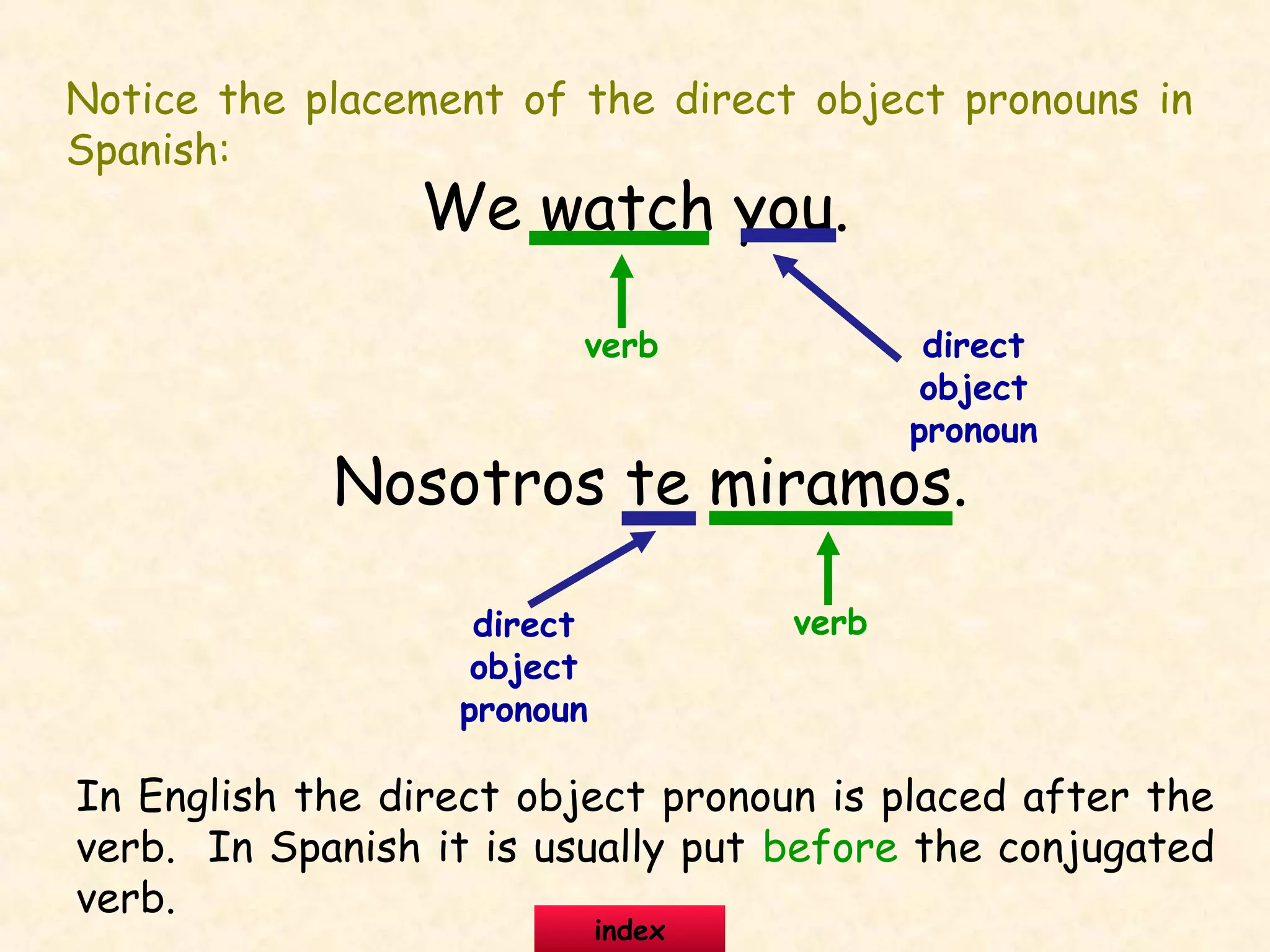
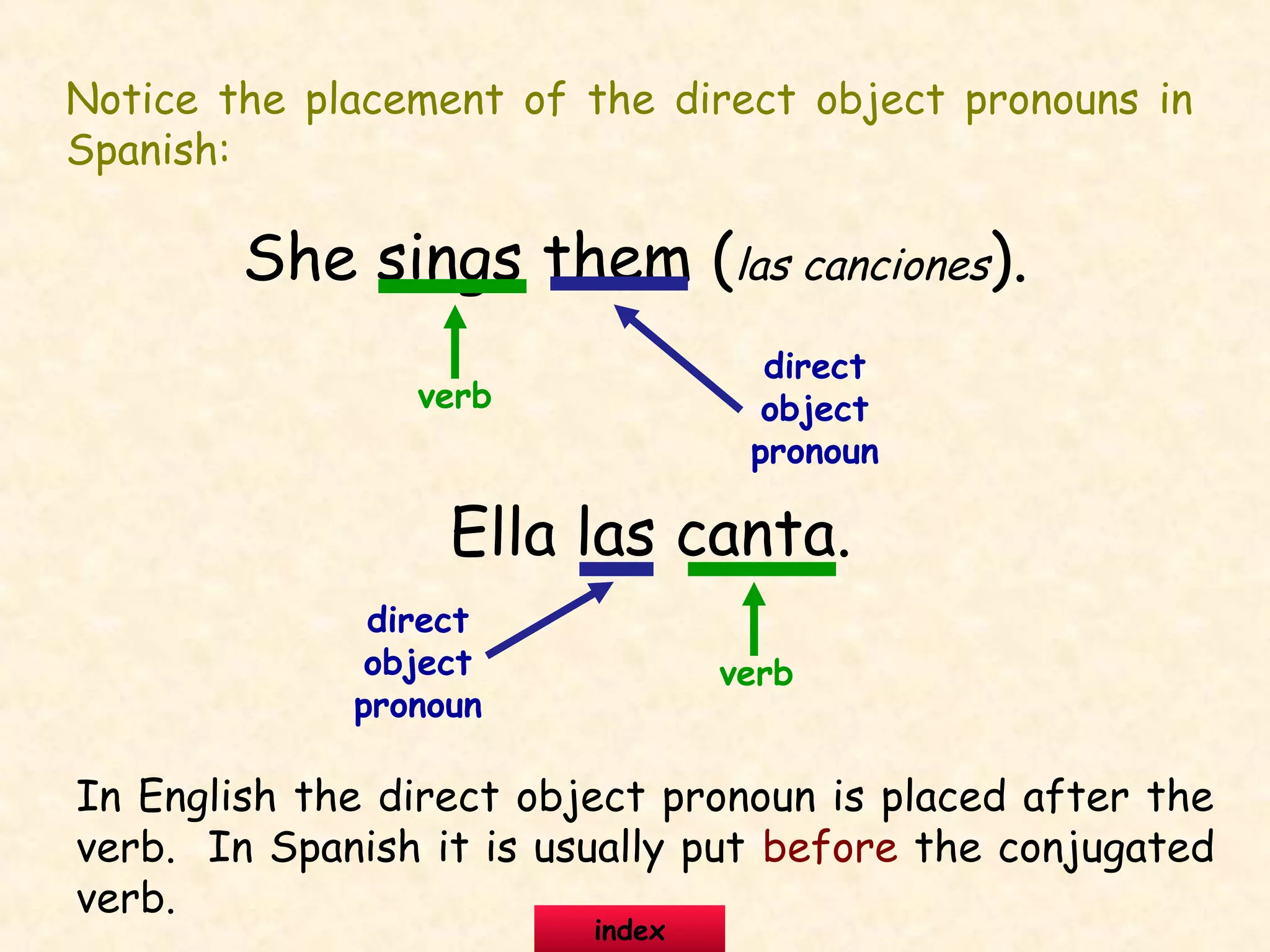
This document provides information about and examples of direct object pronouns in Spanish. It explains that direct object pronouns replace direct objects in sentences. It lists the direct object pronouns in English and Spanish and notes that in Spanish, the pronoun usually comes before the conjugated verb. The document provides multiple examples of replacing direct objects with pronouns in sentences. It also includes exercises for learners to practice replacing direct objects with pronouns and answering questions using pronouns.