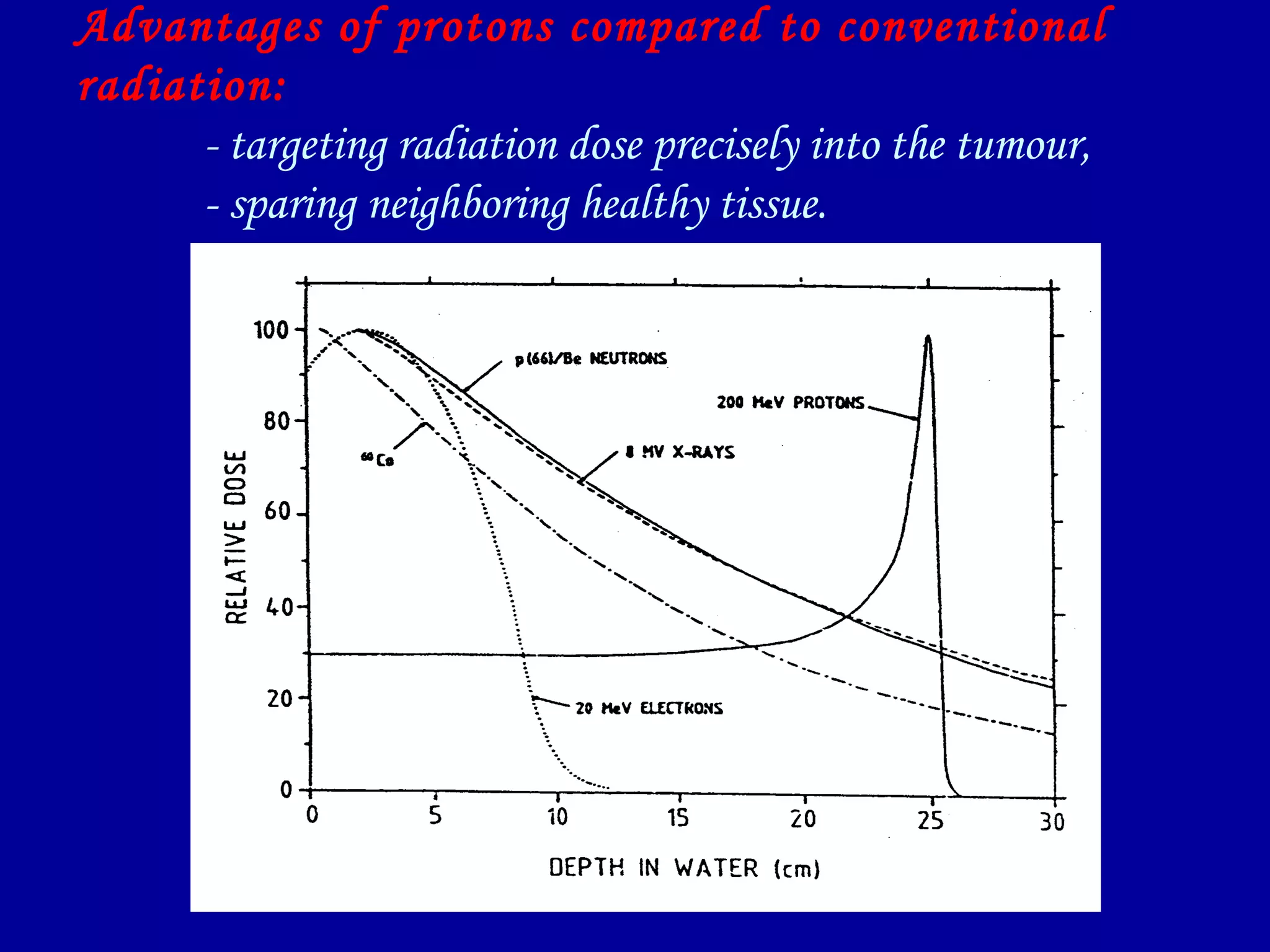
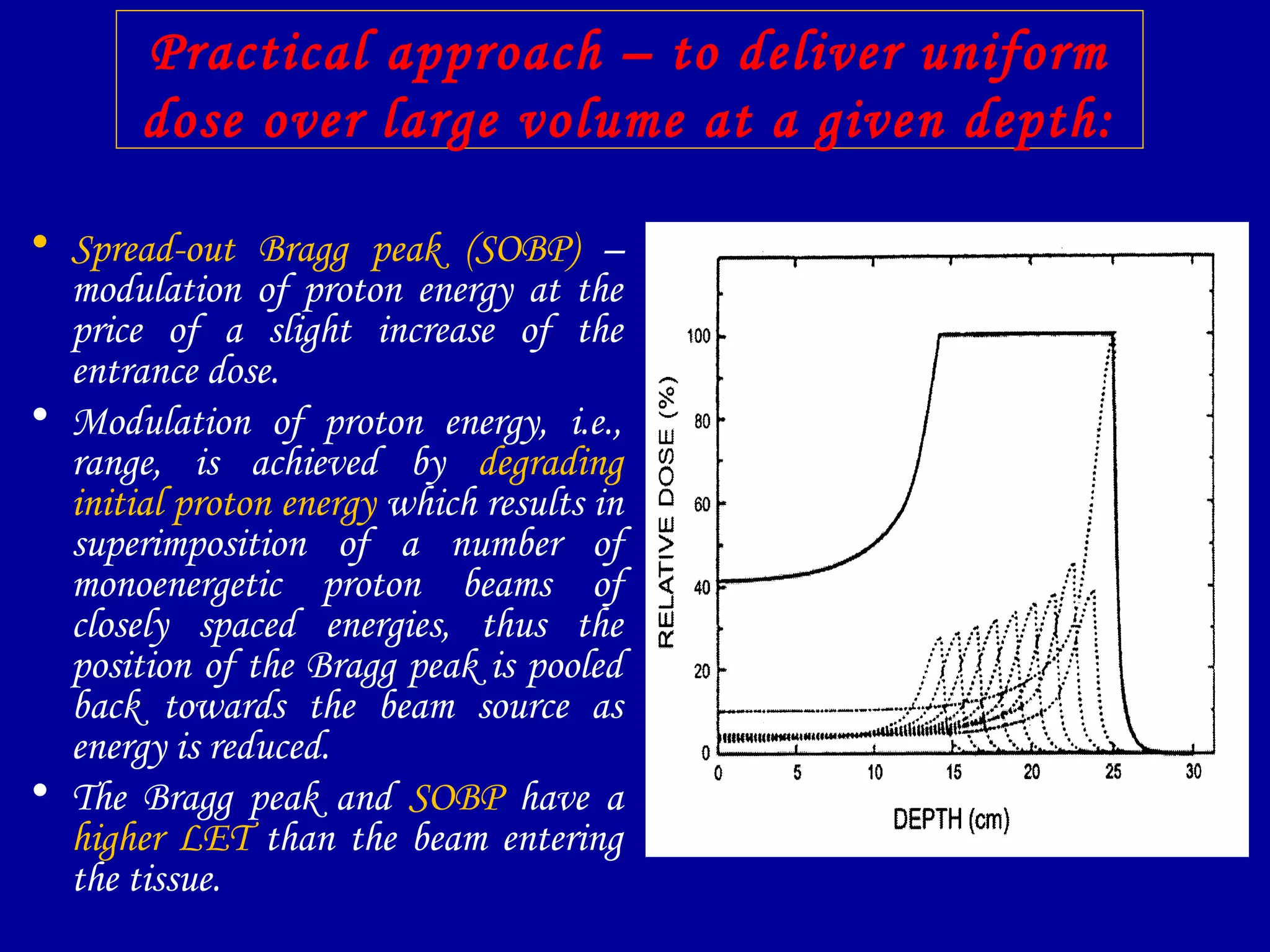
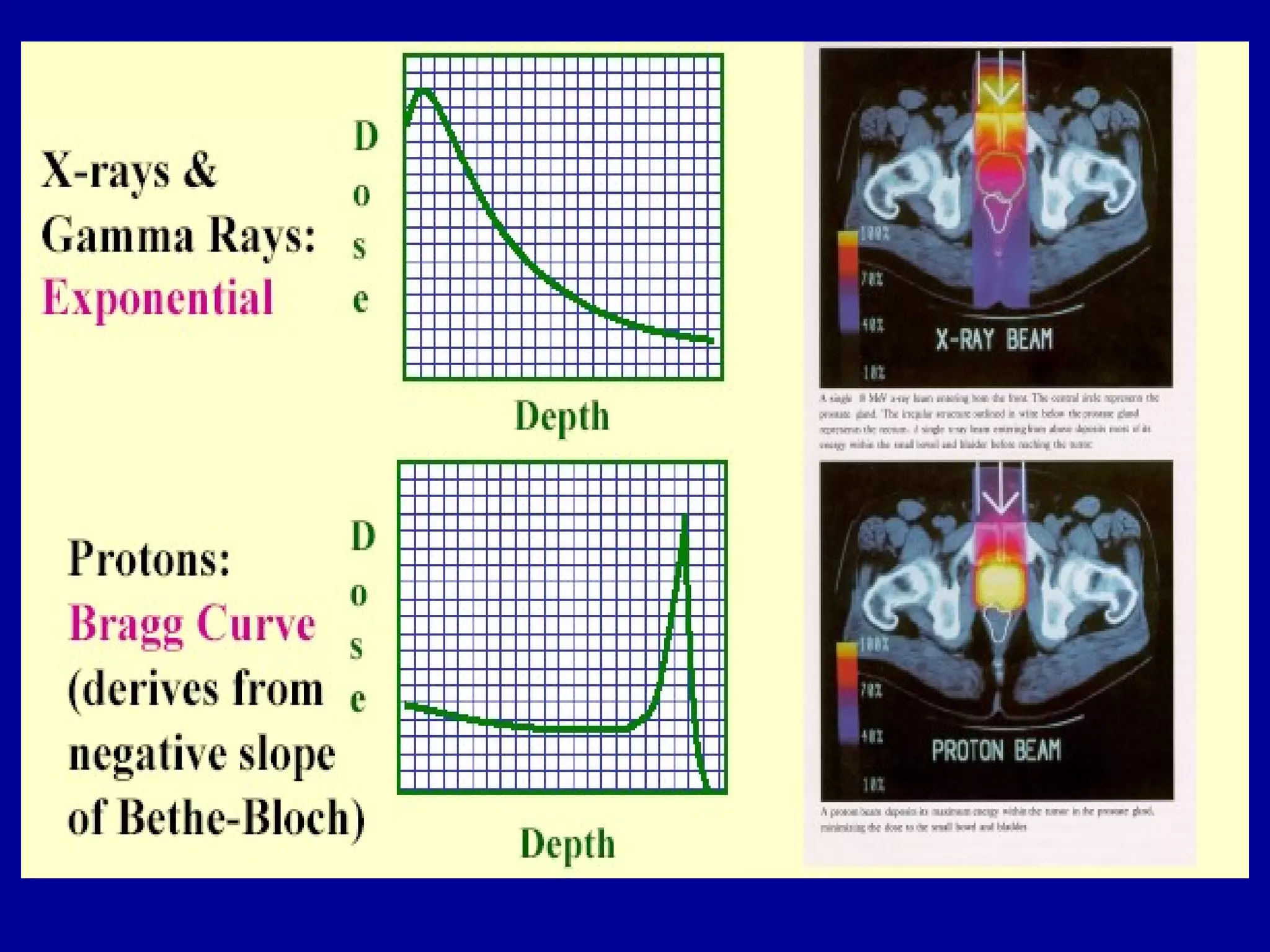
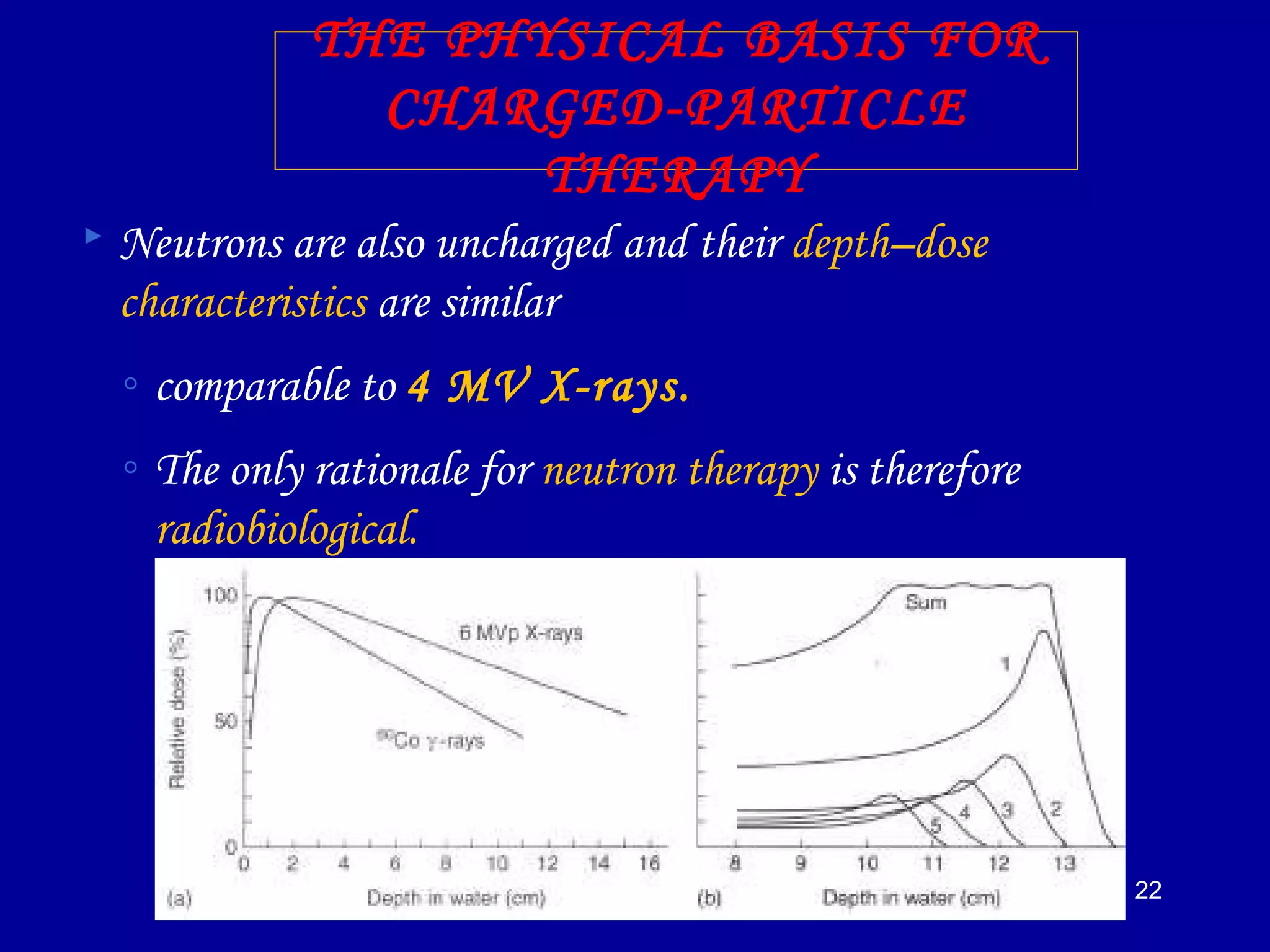
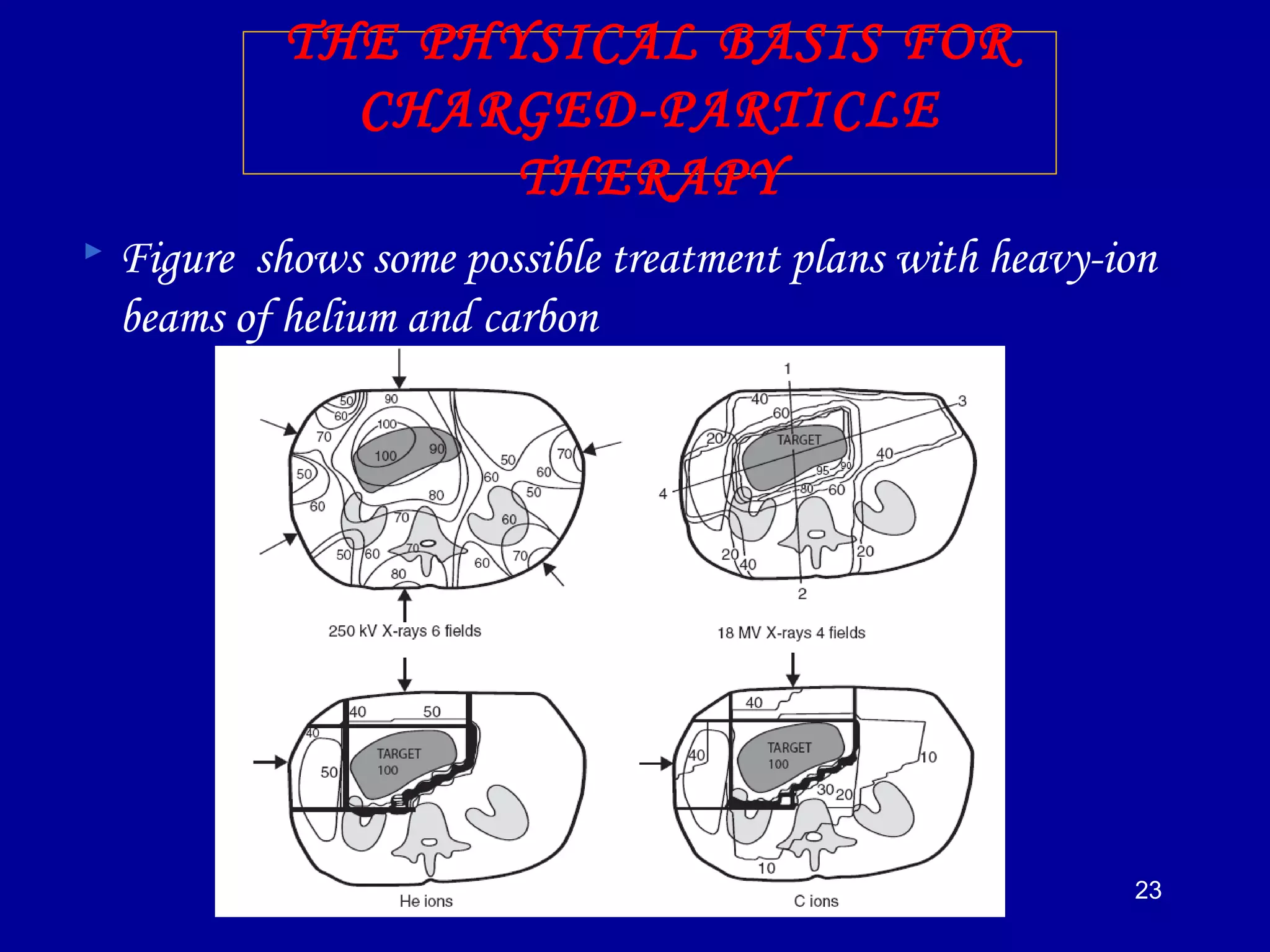
1) The document discusses the biological effects of different types of radiation sources used in radiotherapy, including protons, electrons, neutrons, alpha particles, and heavy ions like carbon ions.
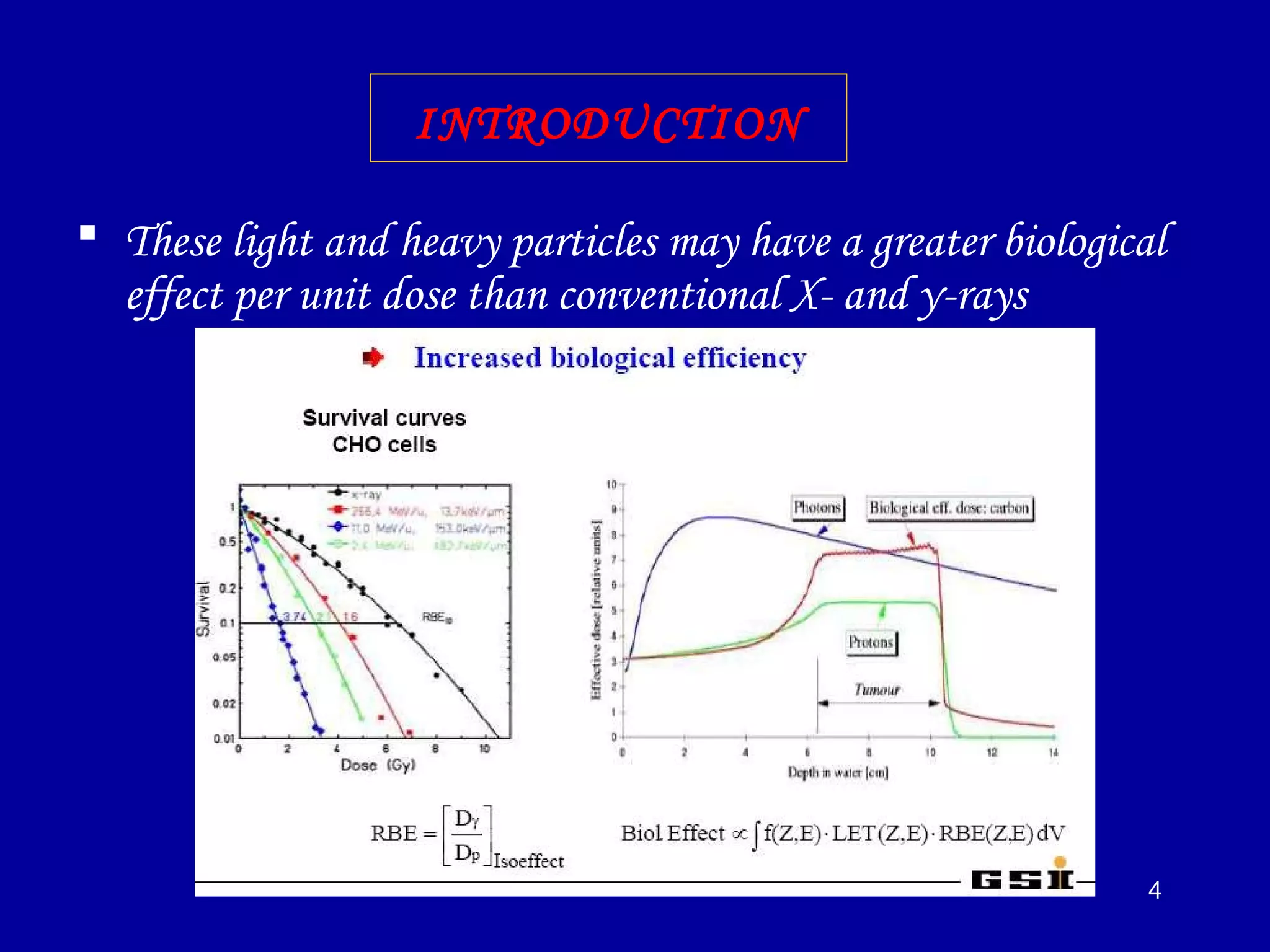
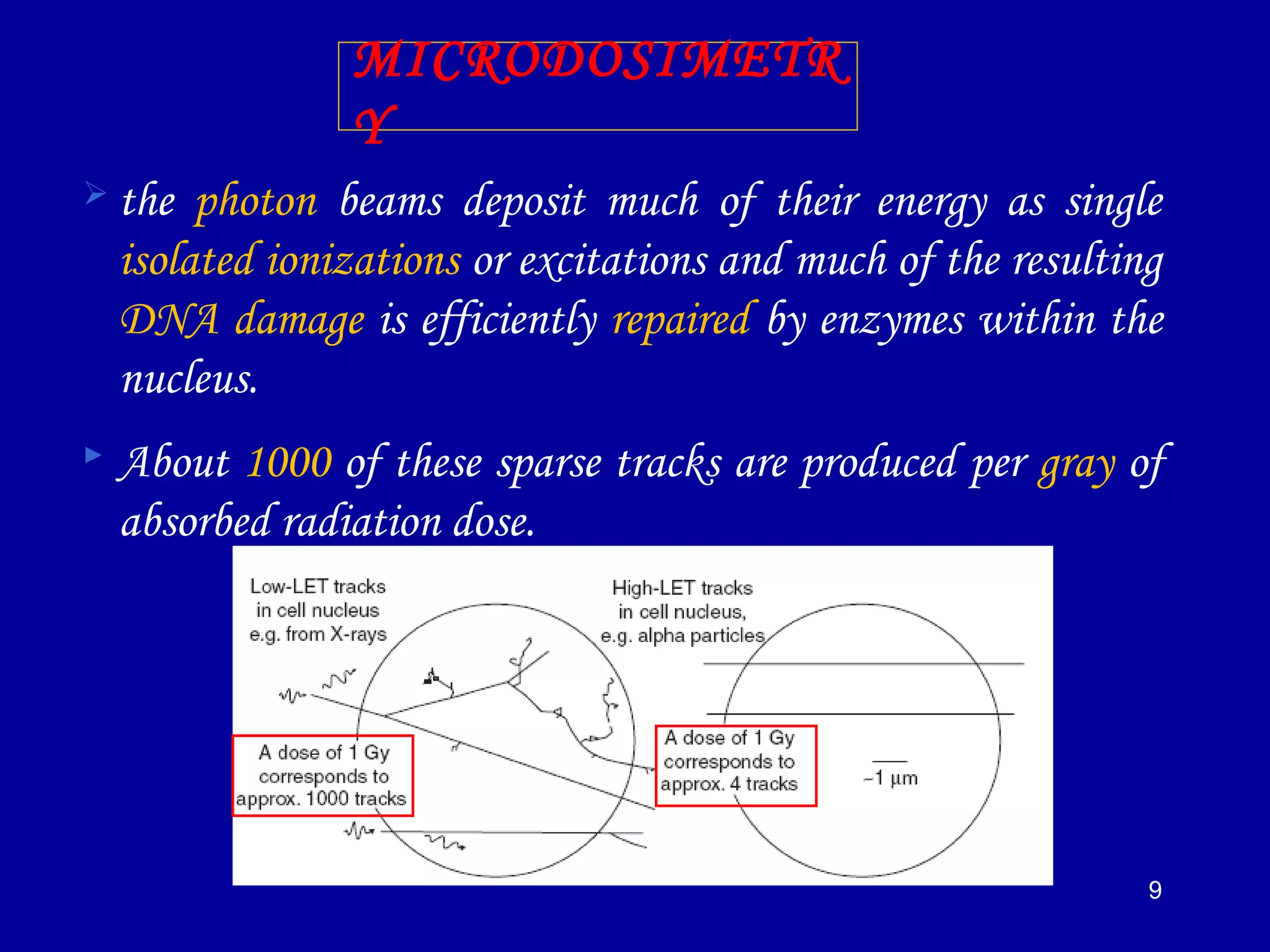
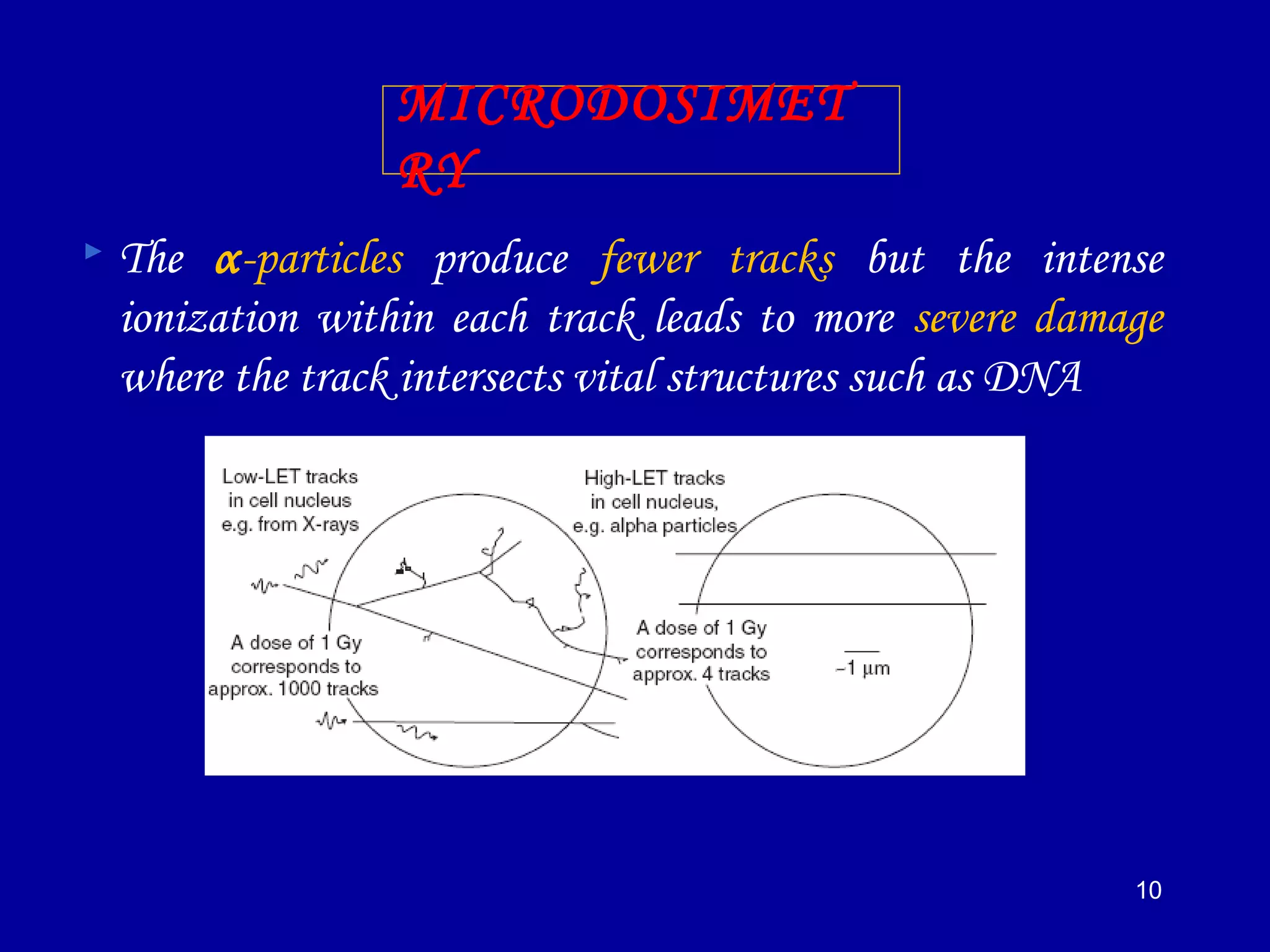
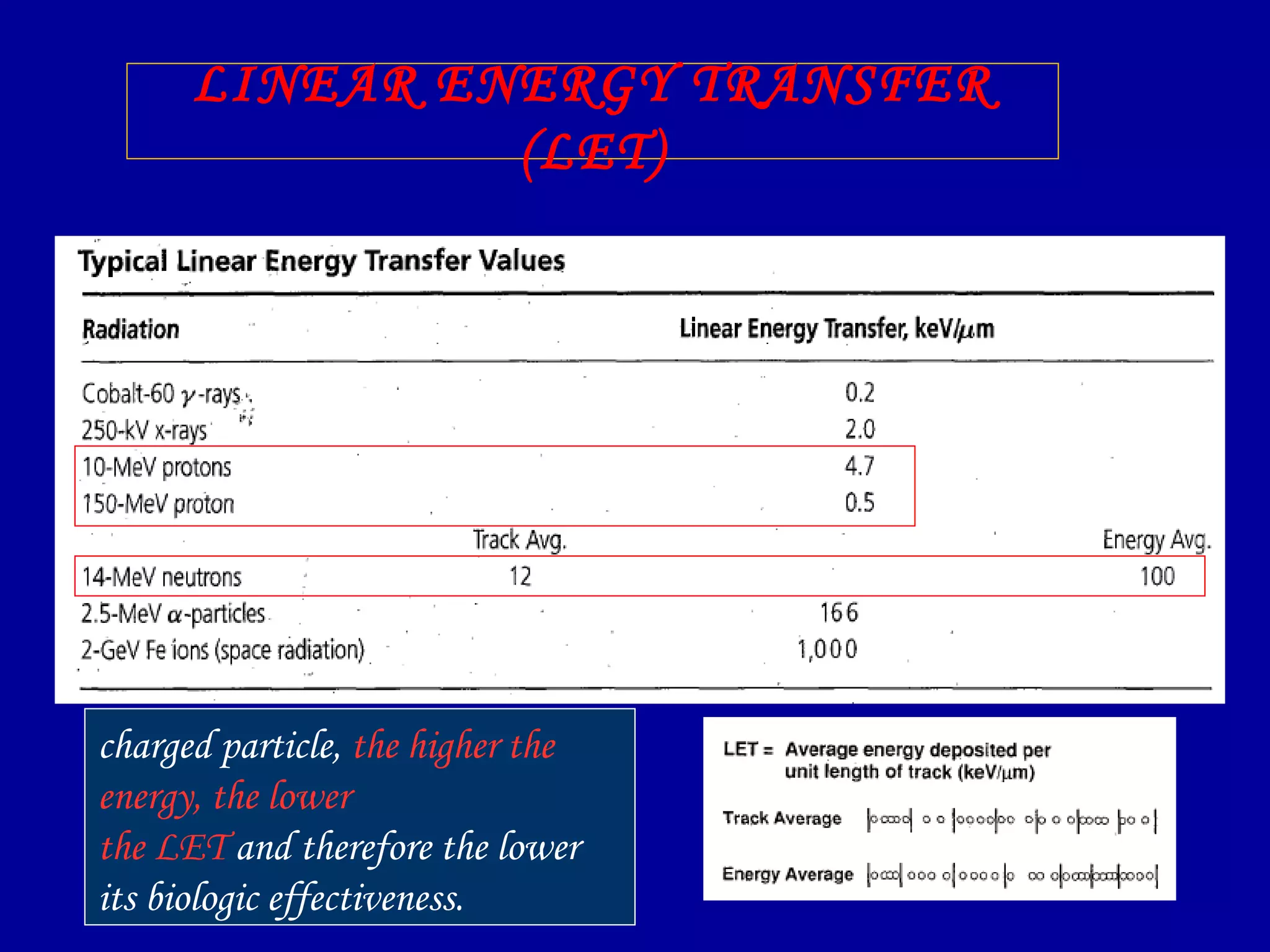
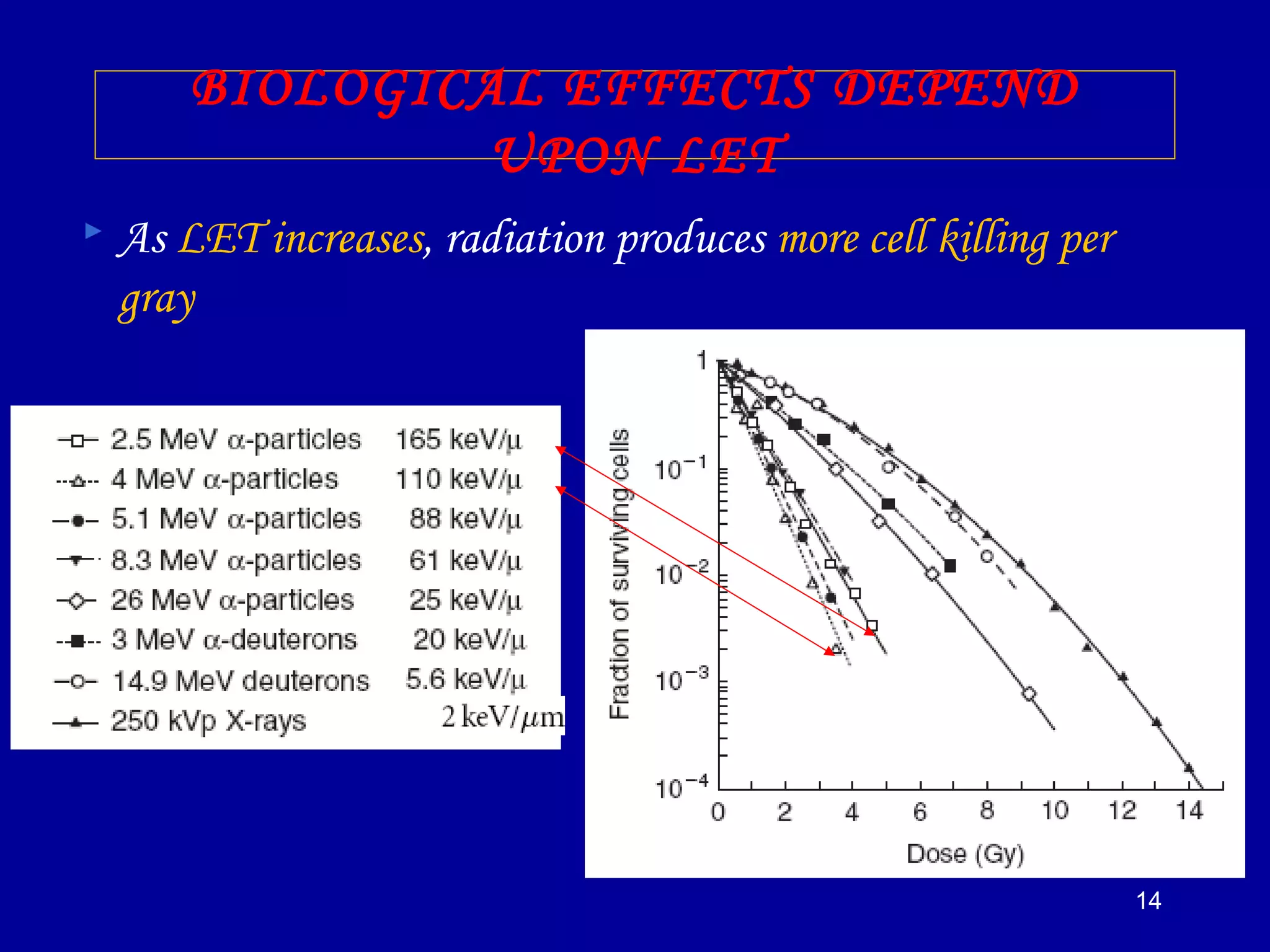
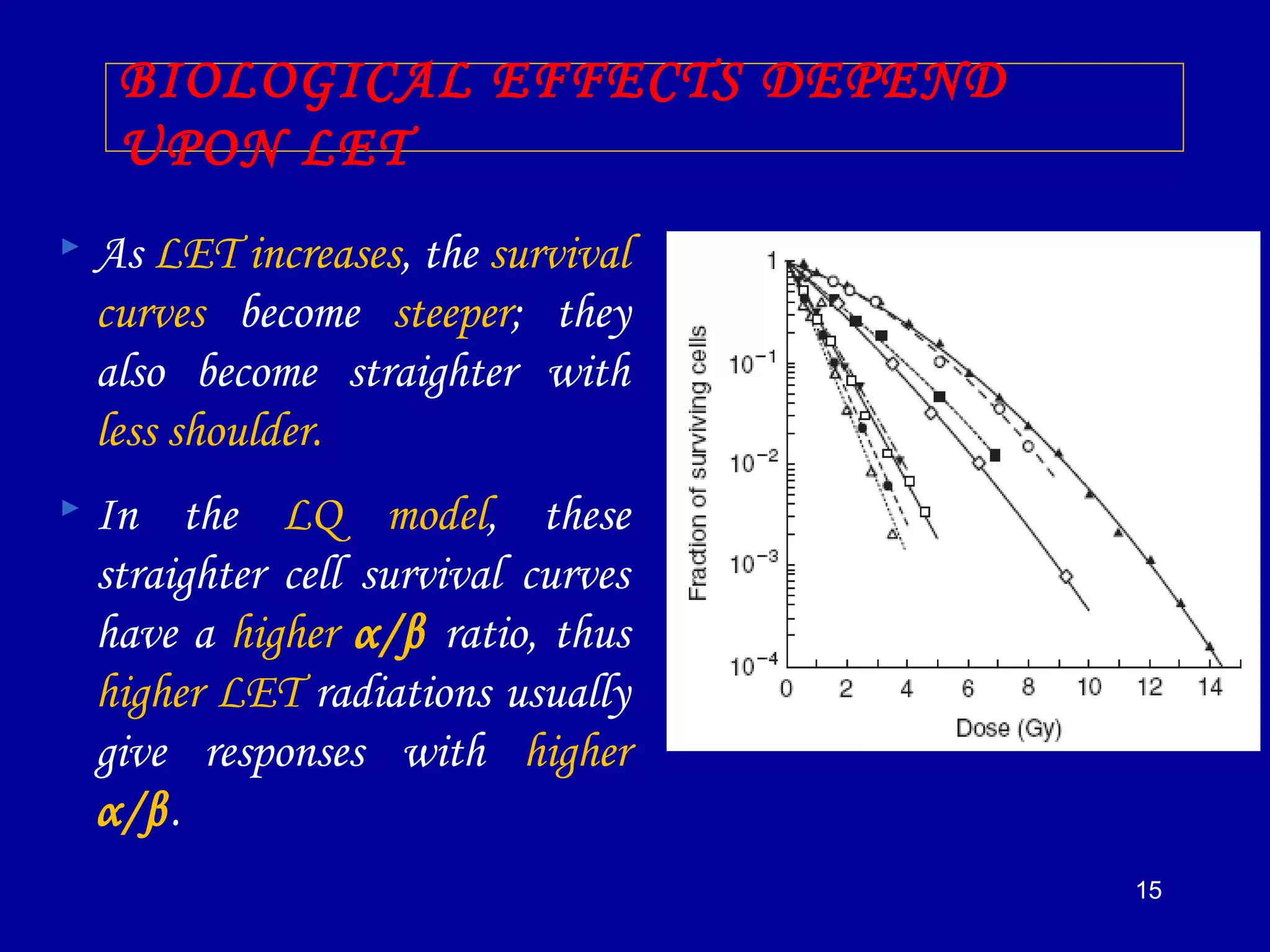
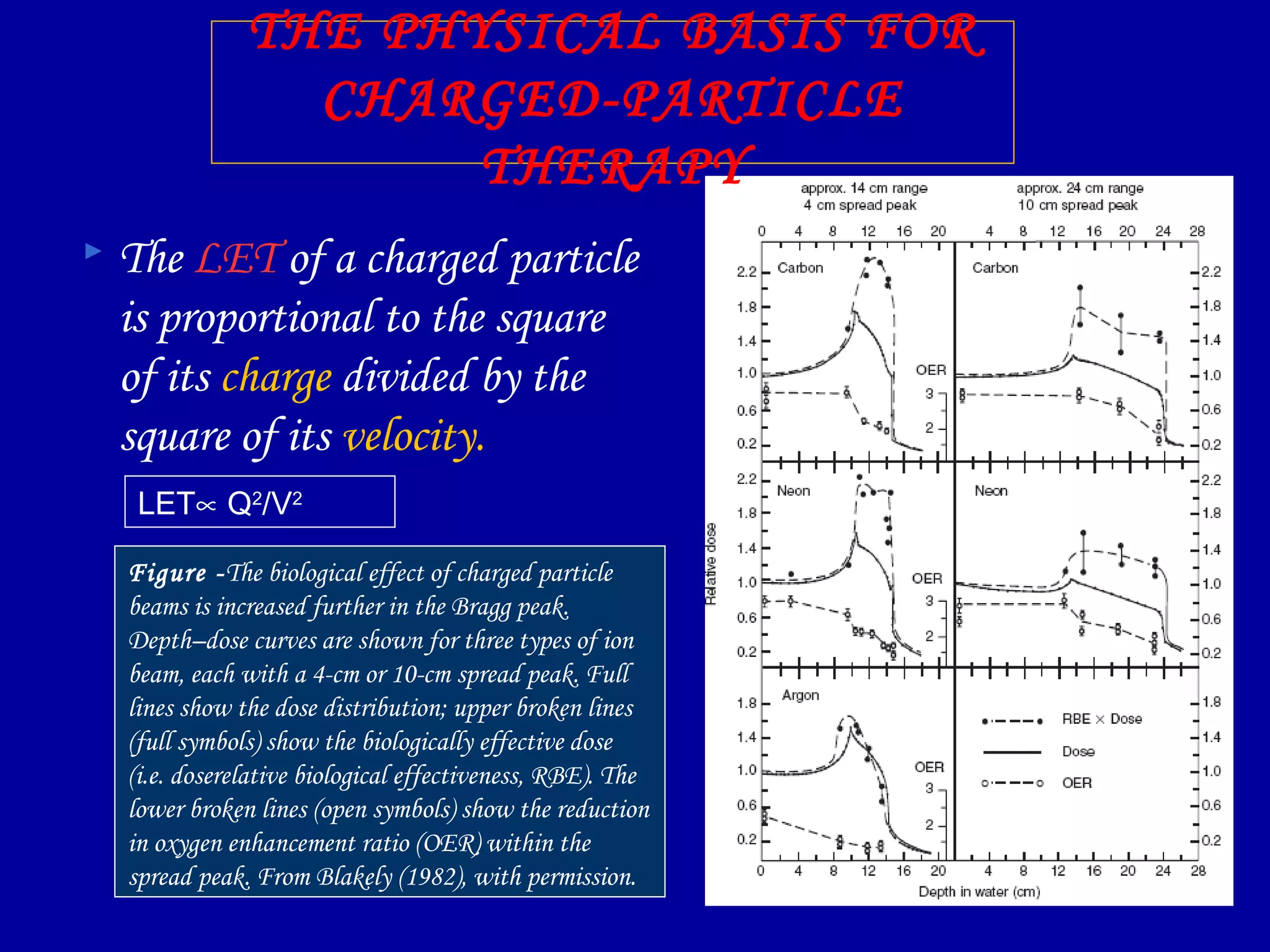
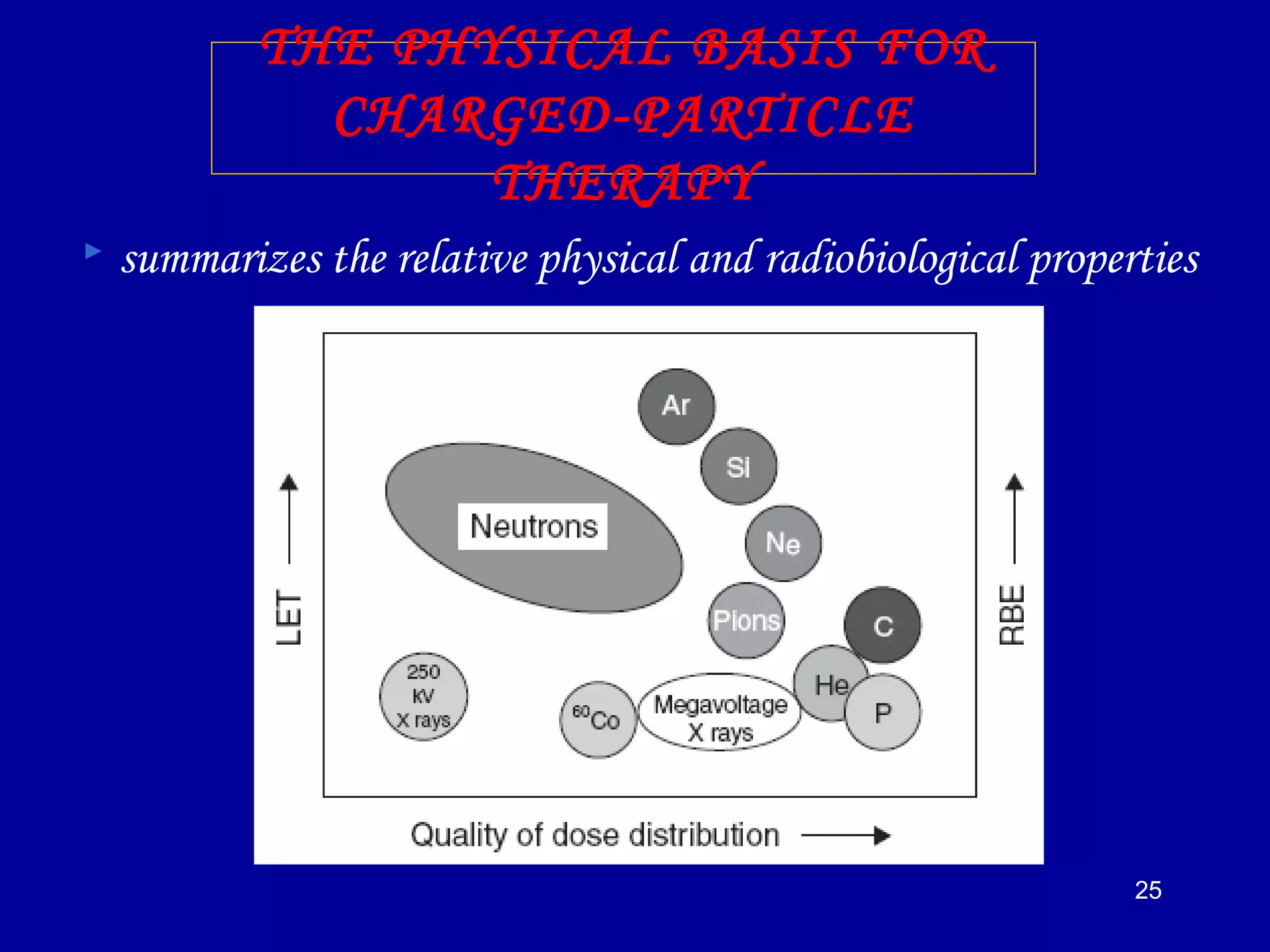
2) High linear energy transfer (LET) radiations like alpha particles and heavy ions produce denser ionization tracks that result in more severe biological damage compared to low LET radiations like X-rays and gamma rays.
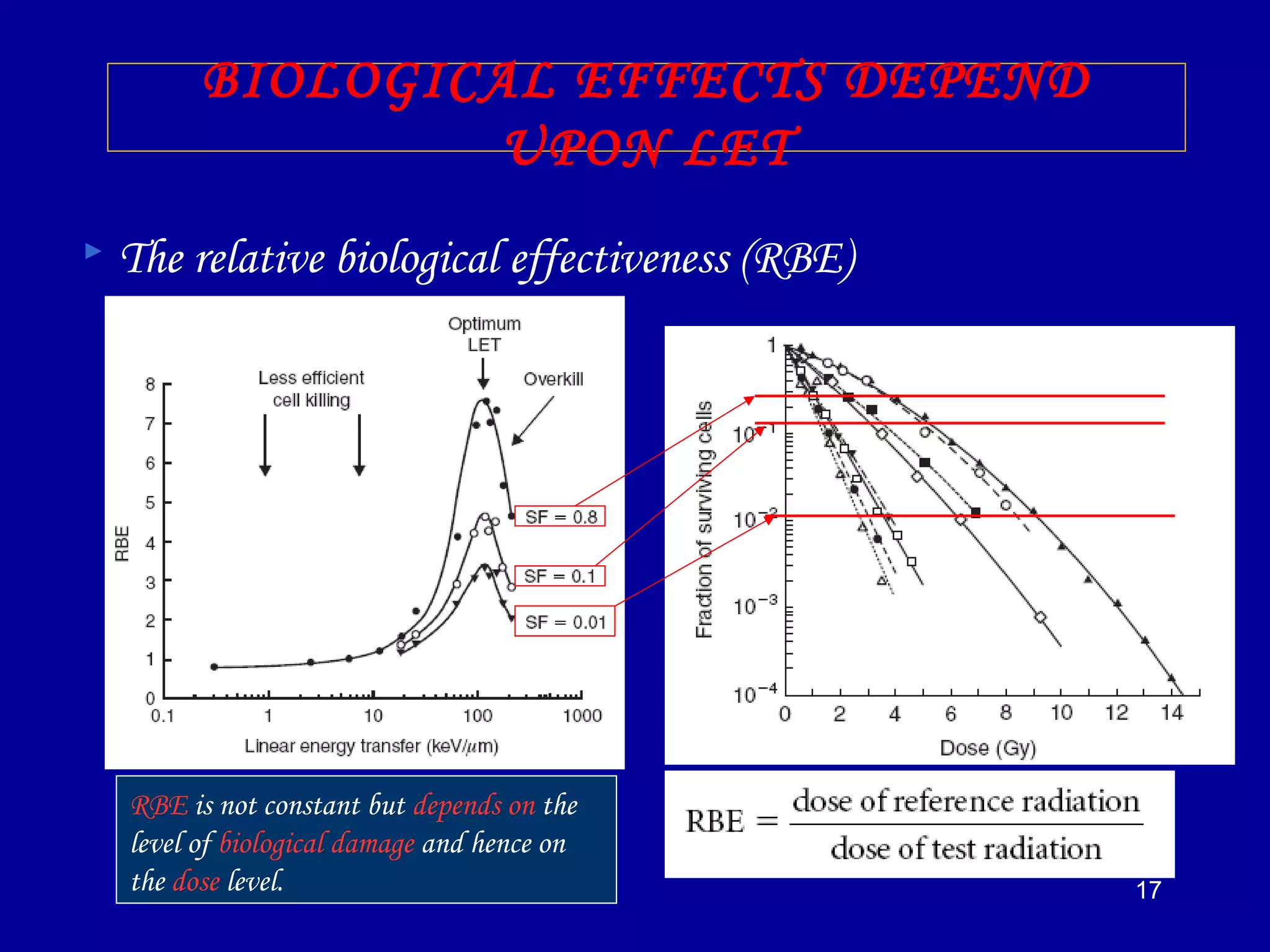
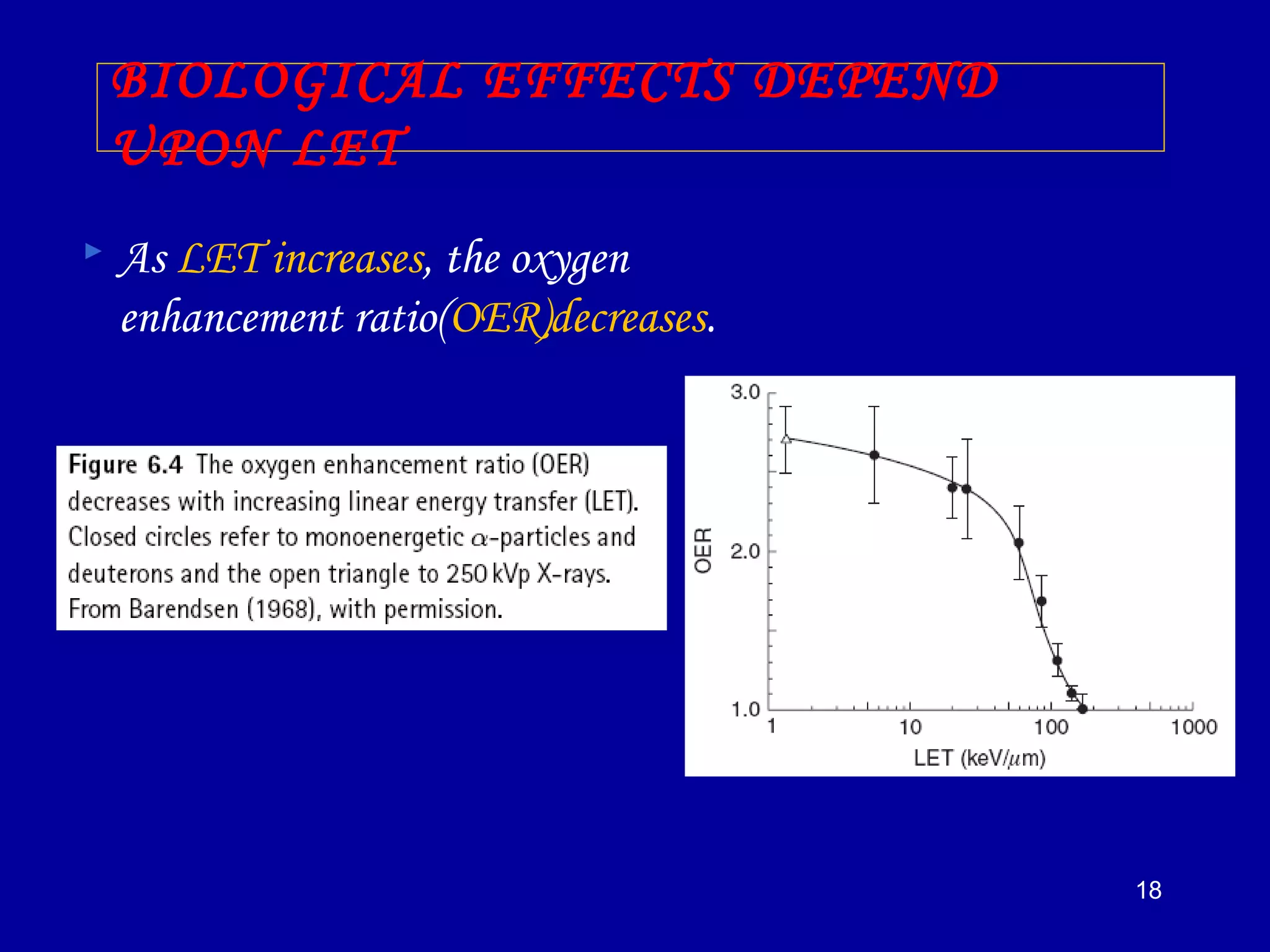
3) The relative biological effectiveness (RBE) of a radiation, which represents its biological damage per unit dose, increases with higher LET but decreases at very high LETs due to cellular overkill. Oxygen enhancement ratios also decrease at higher LETs.