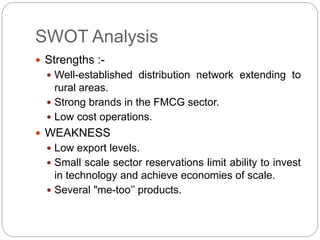
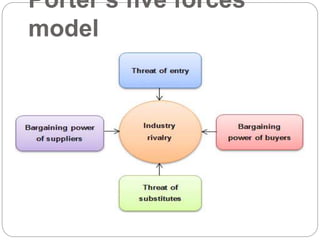
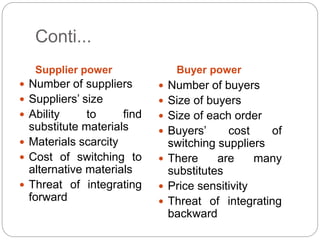
The document discusses the FMCG sector in India. It notes that FMCG includes frequently purchased consumer goods like soaps, dairy, snacks, etc. The top companies in the FMCG sector are listed. It also analyzes the scope, opportunities and threats to the FMCG sector in India through SWOT and PEST analysis. Specifically, it highlights the large domestic market and increasing incomes as opportunities, and imports and regulatory issues as threats.