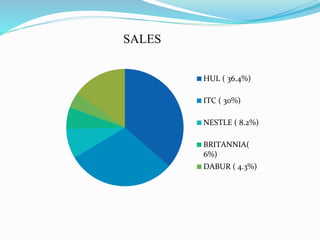
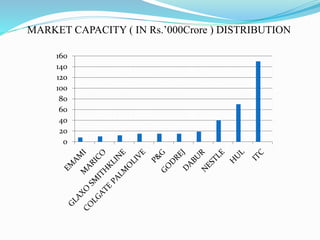
This document provides an overview of the fast moving consumer goods (FMCG) sector in India. It discusses key topics such as major players in the domestic and foreign FMCG market, sector opportunities, growth drivers, and market shares of top companies. The FMCG industry is the fourth largest sector in India and contributes significantly to GDP and employment. Major challenges for FMCG companies include competition and improving distribution networks.