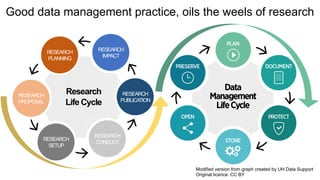
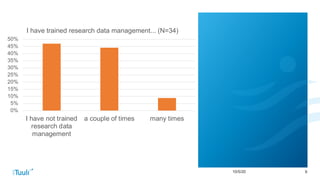
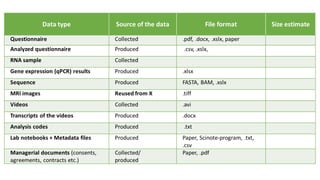
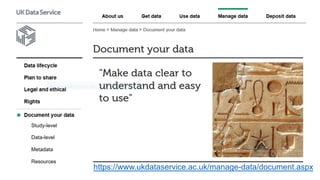
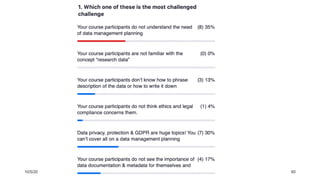
The document discusses challenges trainers may face when training researchers on data management planning and potential strategies to address these challenges. It identifies six common challenges: 1) researchers not understanding the need for data management planning, 2) researchers being unfamiliar with the concept of research data, 3) researchers not knowing how to describe their data, 4) researchers not thinking ethics and legal compliance applies to their work, 5) the complexity of data privacy and GDPR topics, and 6) researchers not understanding documentation and metadata. The document provides examples and explanations to help trainers overcome these challenges and motivate researchers on the importance of data management planning and its components.