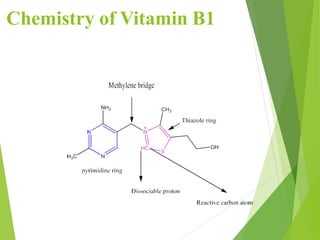
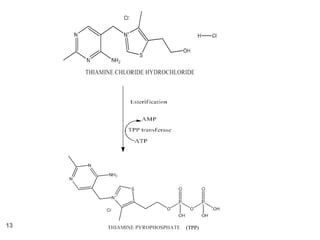
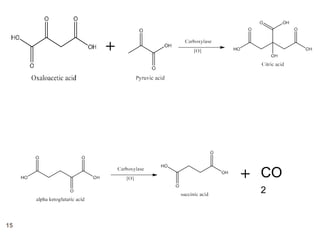
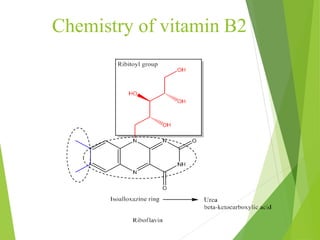
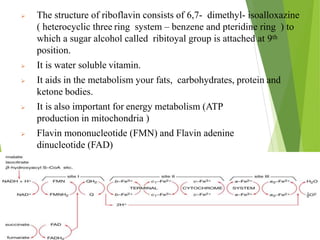
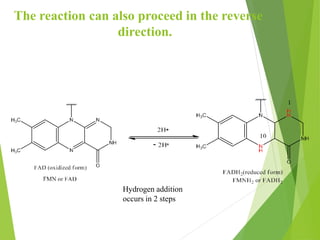
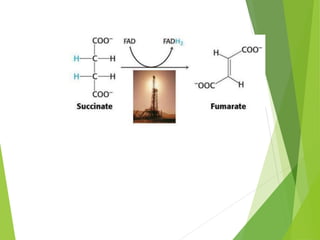
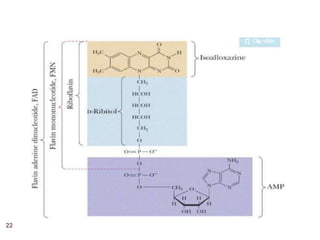
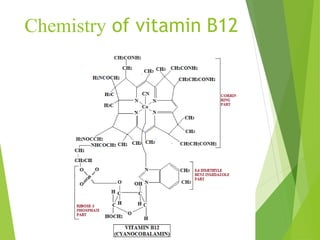
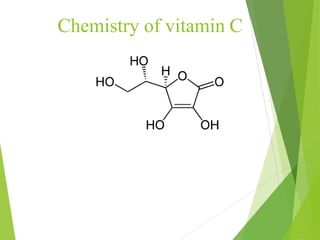
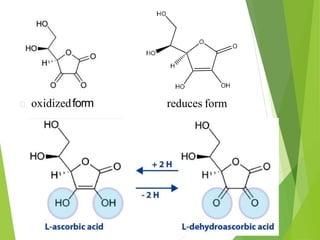
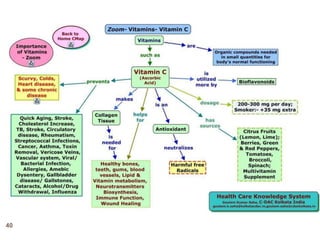
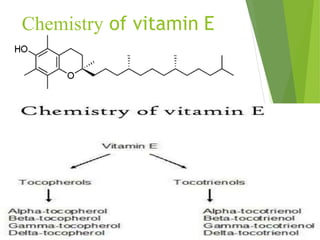
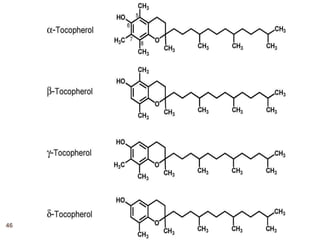
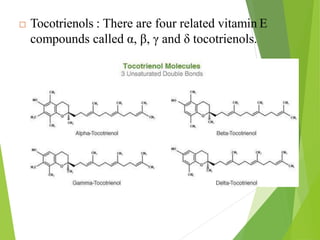
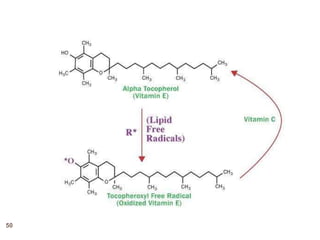
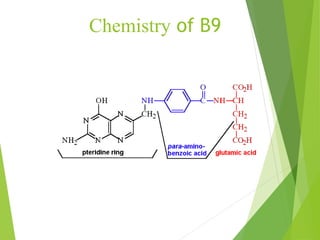
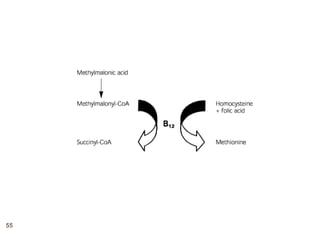
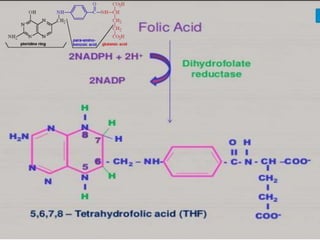
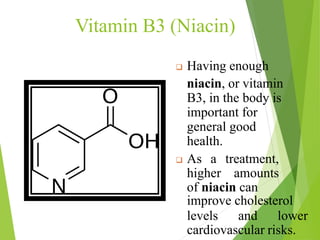
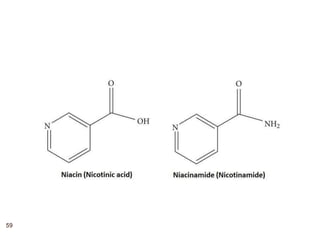
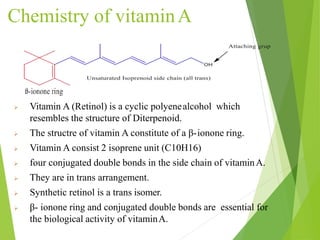
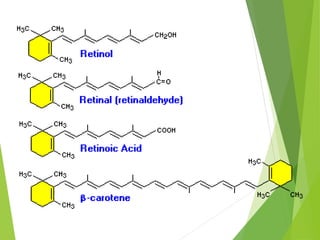
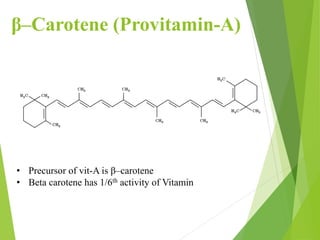
The document provides an overview of various vitamins, their chemistry, physiological significance, and dietary sources. It details the roles of vitamins A, B1, B2, B12, C, E, folic acid (B9), and niacin (B3) in the human body, emphasizing their importance in growth, metabolism, and disease prevention. Each vitamin's chemical structure and its contributions to health and nutrition are discussed, highlighting the need for these essential nutrients in the diet.







![ The deficiency of vitamin A can cause further more dry eye,
ataxia, conjunctivitis, corneal ulcers, skin lesions, disorders of
the epithelia (bronchi, respiratory tracts, salivary glands), bone
formation and nervous system abnormalities, and increased
susceptibility to diseases.
Vitamin A in overdose can lead to bone disorders,
gingivitis, and finally the loss of vision.
8
Rhodopsin
Trans-Retinal Trans-Retinol
Dehydrogenase
(Activation of Rod/Cones)
[Retinal + opsin(protein)]
inactive
Cis-Retinal Cis-Retinol
Dehydrogenase
isomerase
Eyes In Liver](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-iiivitaminscnpsemi-210330174539/85/vitamins-and-its-chemistry-11-320.jpg)