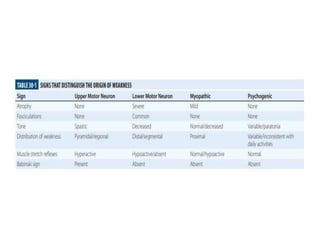
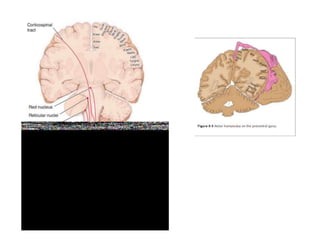
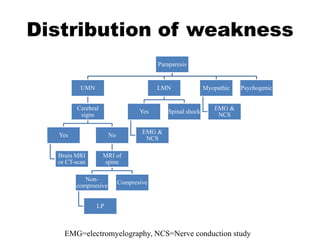
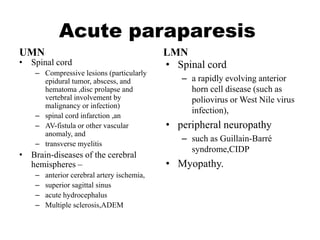
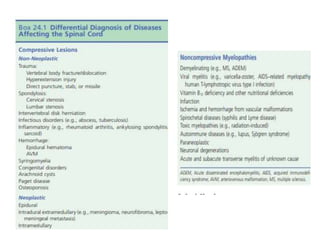
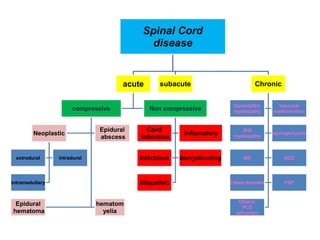
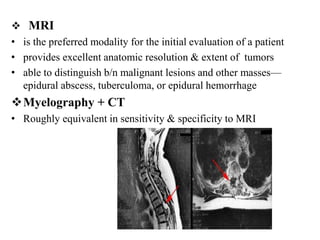
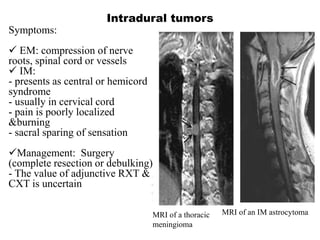
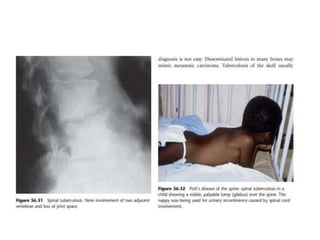
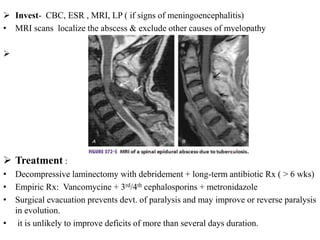
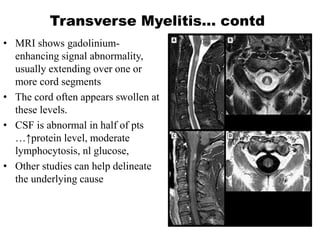
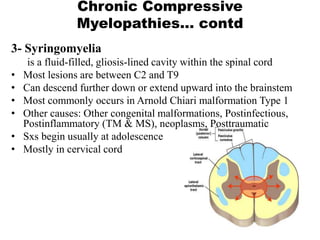
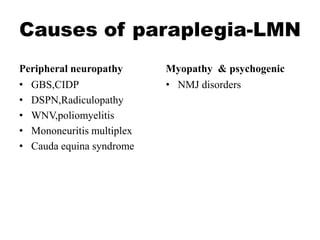
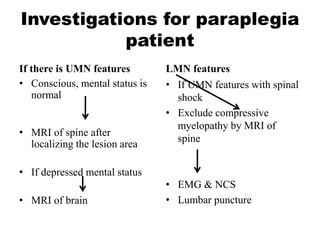
This document discusses paraparesis/paraplegia and compressive myelopathies of the spinal cord. It defines paraparesis as weakness of both legs and provides an overview of upper motor neuron and lower motor neuron lesions. Common causes of acute and chronic paraparesis are described, including tumors, epidural abscesses, and hematomas. The approach to evaluation involves determining the distribution and duration of weakness and assessing for signs of spinal cord compression versus non-compressive etiologies. Imaging such as MRI is important for diagnosis, and treatment depends on the underlying cause and its acuity.