A Handbook for PALS Leaders. Retrieved on August 26, 2011, from
http://www.plymouth.ac.uk/pages/download.asp?file=pals_handbook.pdf§ion=00000
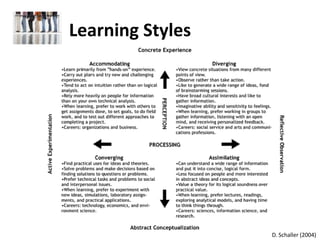
Schaller, D. T. (2004). "Understanding Learning Styles to Improve Teaching Strategies." Retrieved on August 26, 2011, from
http://www.eric.ed.gov/PDFS/ED494050.pdf
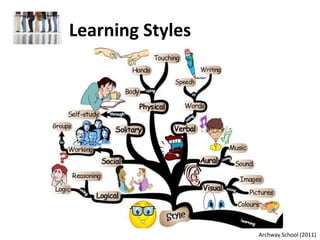
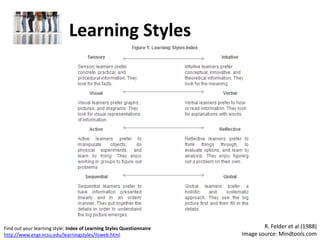
Archway School (2011). "Learning Styles." Retrieved on August 26, 2011, from
http://www.archwayschool.co.uk/learningstyles.html
DHS Training Standards Guide (2008