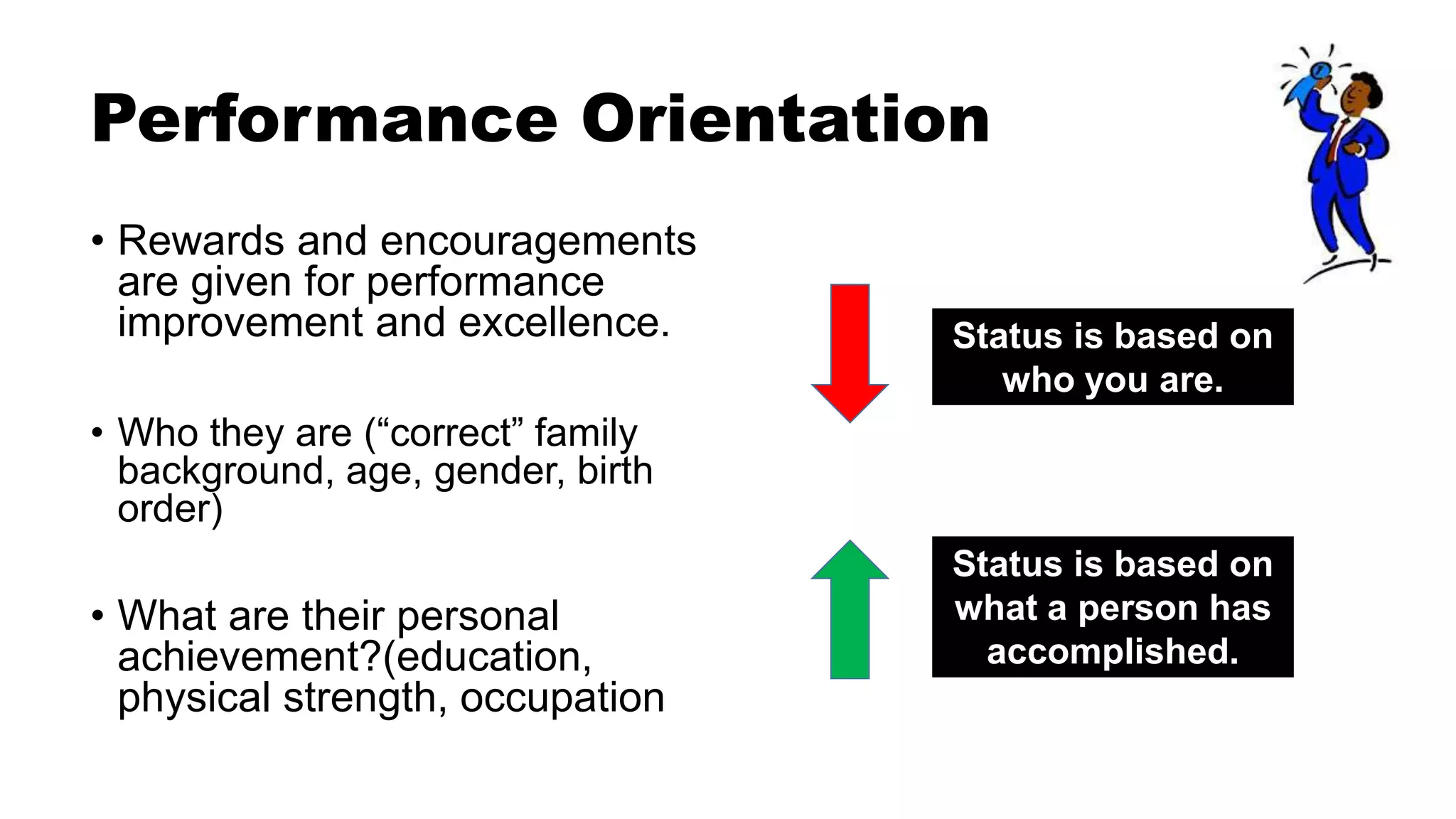
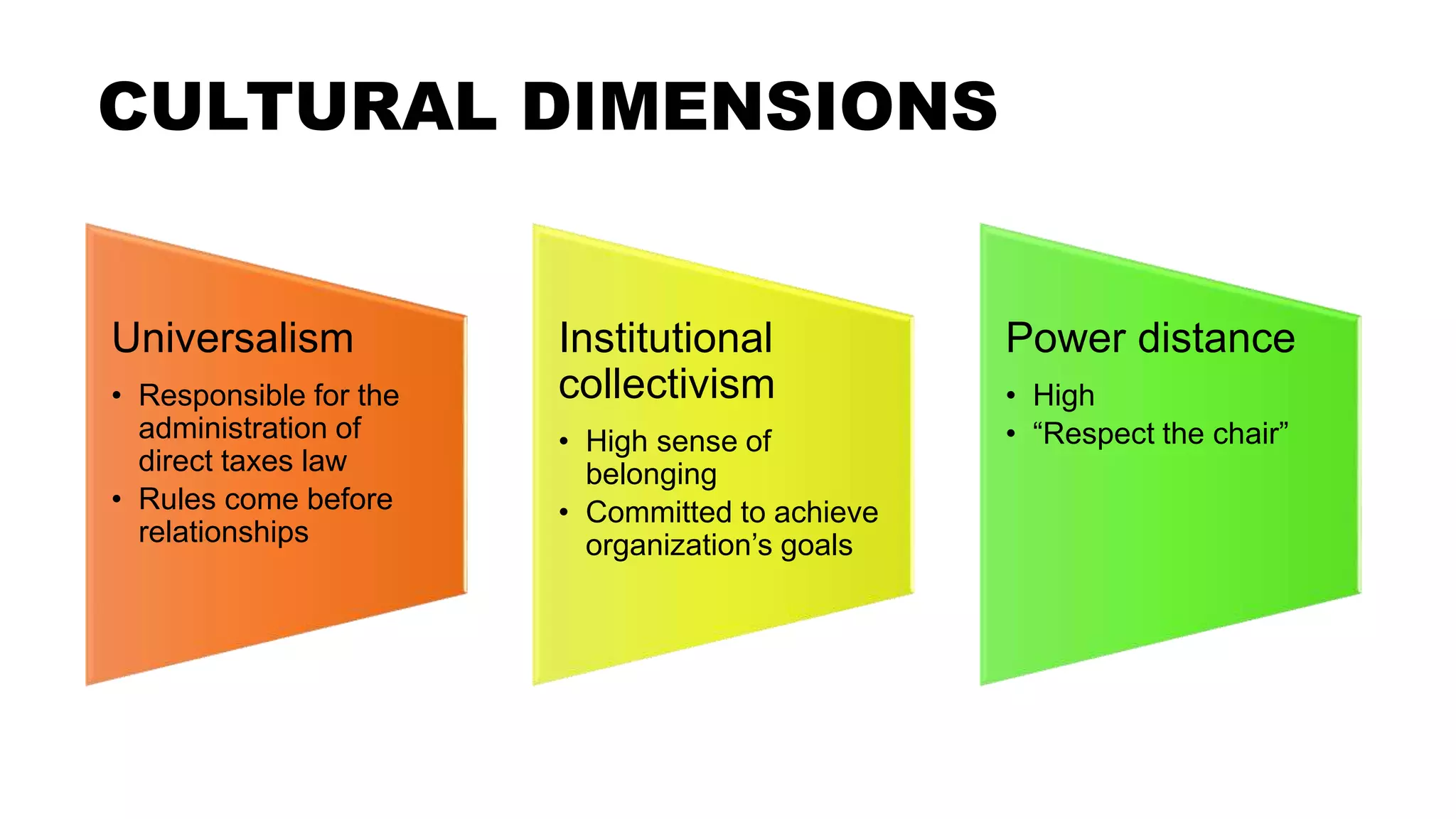
This document discusses cultural dimensions and frameworks for understanding culture, including Schwartz's cultural dimensions model and the GLOBE project cultural dimensions. It then provides examples of how cultural dimensions may manifest in two Malaysian organizations, the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia and Top Glove Corporation Berhad. Finally, it emphasizes the importance of understanding one's own cultural values and perspective.