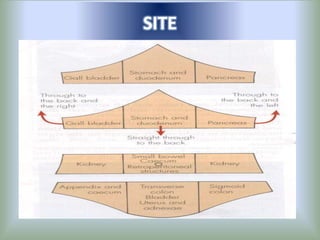
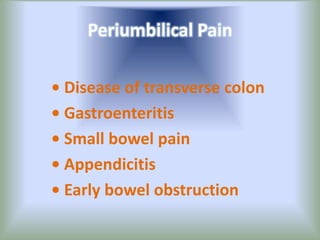
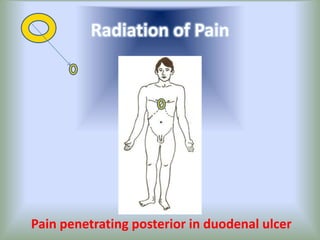
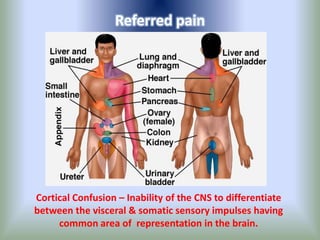
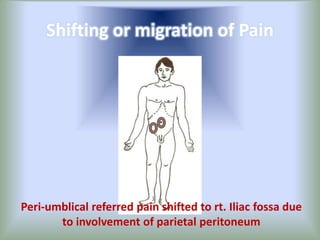
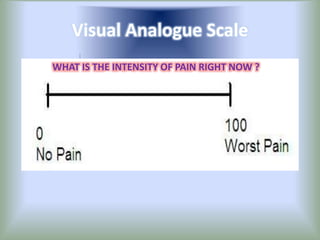
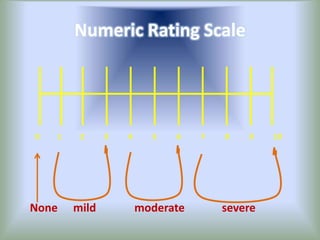
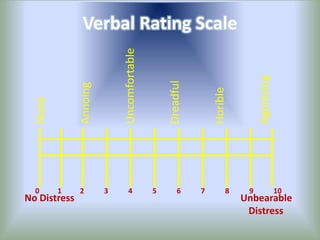
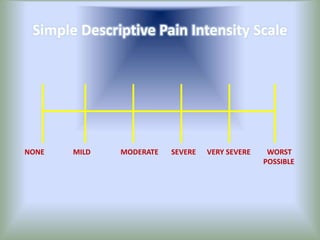
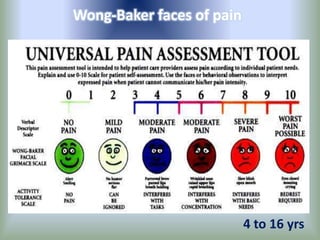
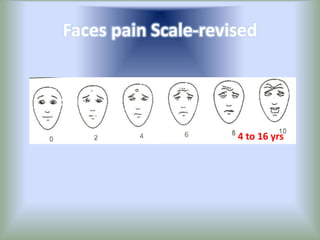
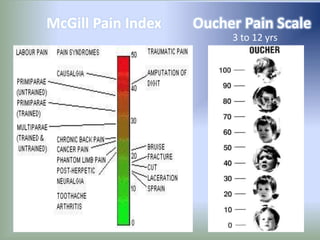
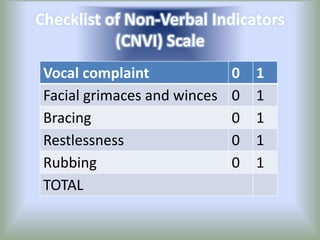
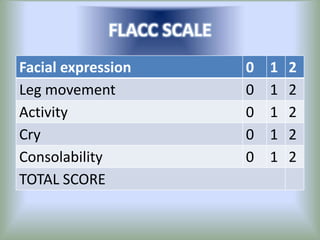
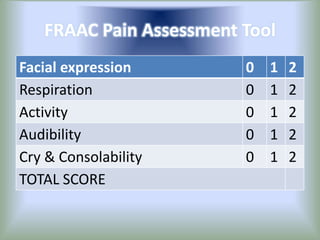
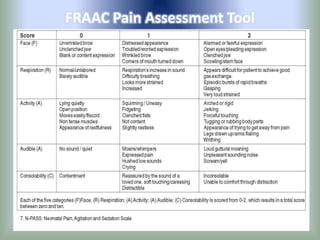
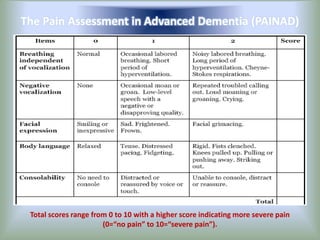
Pain is an unpleasant sensory experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. It serves an important protective function but can limit functions. Pain is classified based on location, type, duration and origin, and is assessed through patient reports and observations. Management involves non-drug approaches like repositioning and relaxation, as well as drug therapies ranging from over-the-counter drugs for mild pain to opioids for severe pain. Ongoing reassessment is needed to adjust the pain management plan effectively over time.