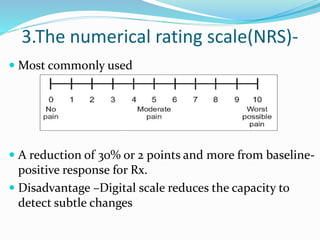
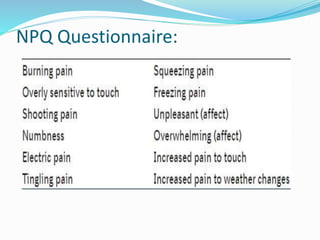
This document discusses various tools used to assess pain. It describes unidimensional and multidimensional instruments for assessing pain intensity, including verbal rating scales, numerical rating scales, and visual analog scales. It also discusses screening tools for neuropathic pain such as the Leeds Assessment of Neuropathic Symptoms and Signs and the Neuropathic Pain Questionnaire. Finally, it outlines scales for assessing psychological factors associated with pain, such as the Beck Depression Inventory, Hamilton Depression Scale, and Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale.