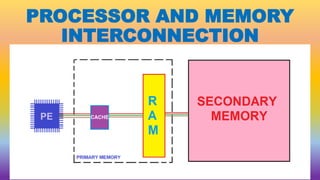
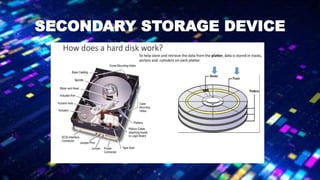
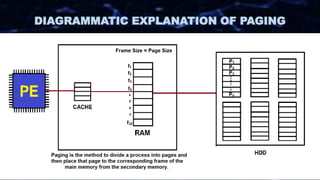
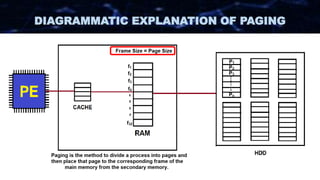
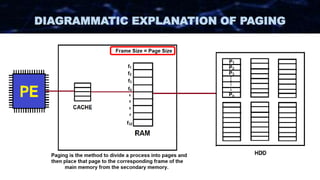
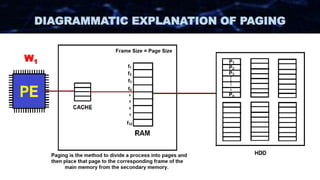
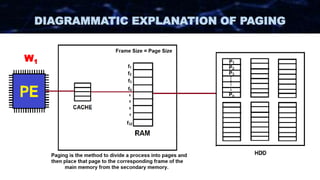
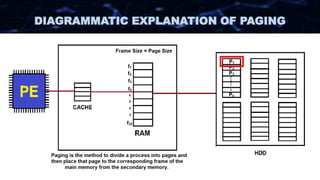
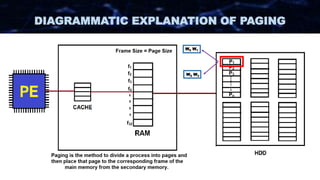
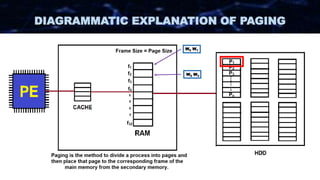
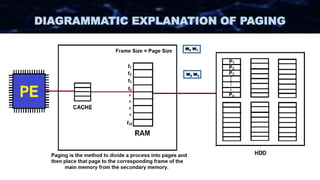
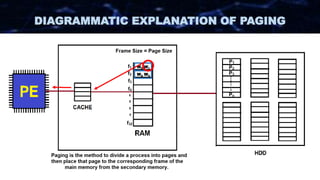
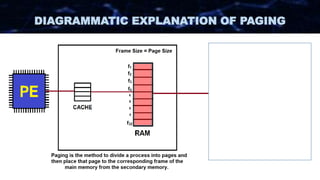
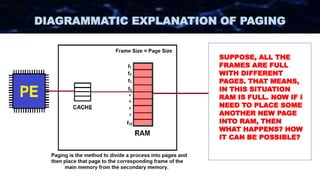
The document discusses the concept of paging in computer memory management, explaining how a process is divided into smaller units called pages for efficient execution by the processor. It describes the interaction between the processor, RAM, and secondary storage, detailing how pages are transferred and managed through a process known as page replacement. Key page replacement algorithms such as FIFO, LRU, and LFU are mentioned, with a promise of further discussion in future classes.