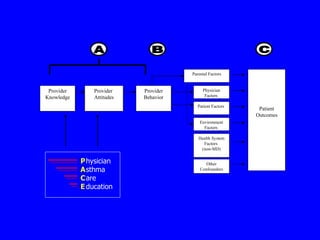
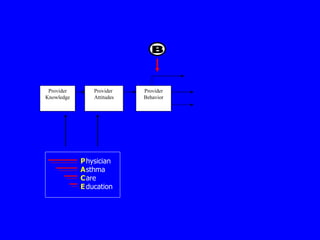
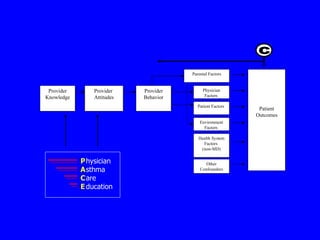
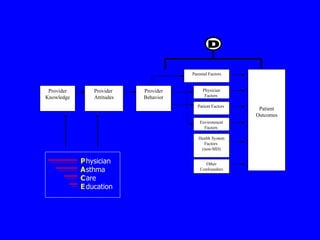
This document discusses different evaluation methods for assessing the impact of physician education programs on asthma care:
A) Provider surveys can measure immediate changes in physician knowledge, attitudes, and reported behaviors through self-administered questionnaires, but provide no information on patient outcomes.
B) Medical record audits can assess changes in physician behavior by reviewing charts, but documentation is often incomplete and consent is required from patients.
C) Parent telephone surveys can evaluate changes in patient outcomes and management, but are difficult to schedule and require patient consent.
D) Claims data can measure utilization of healthcare for asthma, but lack clinical details and attributing claims to specific physicians is challenging.