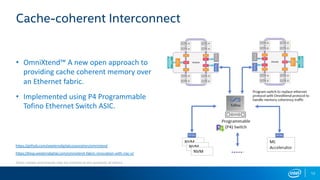
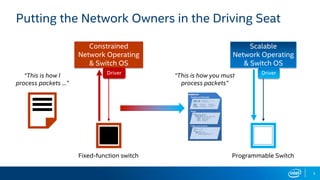
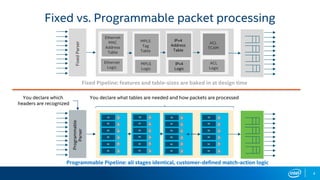
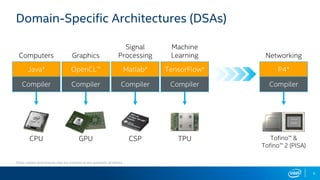
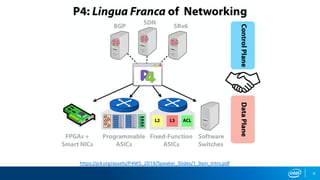
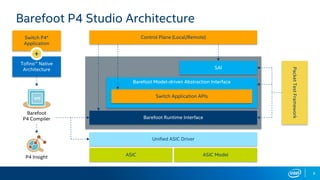
The document outlines the performance characteristics and configurations of Intel technologies, emphasizing variability in performance based on system setup and the importance of consulting additional information for accurate evaluations. It discusses the capabilities of Barefoot Networks' programmable switches, including flexibility in packet processing and application-specific performance enhancements. Furthermore, it highlights the benefits of using P4 programmable switches for network telemetry and efficiency in large-scale applications.




![Segment Routing v6 - Mobile User Plane
Data Network
gNB SRGW UPF1 UPF2
SA : 8000::1
DA : 2000::1
NH : IPV6
UDP
DP :0x0868
GTPU
TEID : 0x1234
SA : 1000::1
DA : 3000::1
NH : UDP
SA : 9000::1
DA : 7000::1
NH : SRH
Type : 4(SRH)
NH : IPv6
Segment List:
[0] 5000::1
[1] 6000::1
SA : 1000::1
DA : 3000::1
NH : UDP
SA : 9000::1
DA :
NH : IPV6
SA : 1000::1
DA : 3000::1
NH : UDP
SA : 1000::1
DA : 3000::1
NH : UDP
User
Equipment
SRv6 Core
Network
End.M.GTP6.D End (PSP) End.DT6
Data Network
gNB UPF1 UPF2
SA : 1000::1
DA : 2000::1
NH : IPV6
SA : 5000::1
DA : 3000::1
NH : IPV6
SA : 1000::1
DA : 2000::1
NH : UDP
SA : 5000::1
DA : 4000::1
NH : IPV6
SA : 1000::1
DA : 2000::1
NH : UDP
SA : 1000::1
DA : 2000::1
NH : IPV6
User
Equipment
SRv6 Core
Network
T.Encaps.Red End.MAP End.DT6
SRv6TrafficFlow−
TraditionalMode
SRv6TrafficFlow−
Enhancedwith
unchangedgNodeB
https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-dmm-srv6-mobile-uplane-02#page-11
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/premjonnalagadda-p4andhigh-performancepacketprocessing-191029214404/85/P4-FPGA-Packet-Acceleration-10-320.jpg)