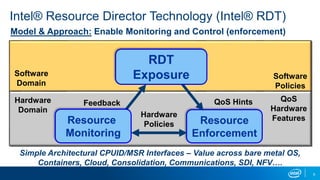
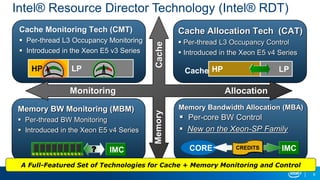
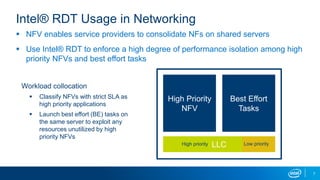
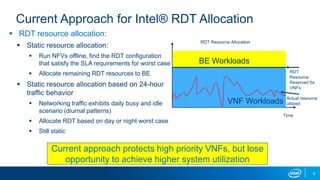
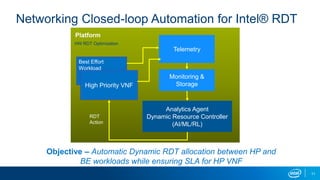
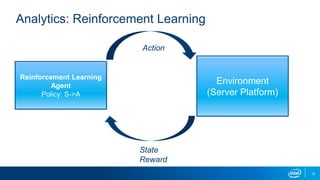
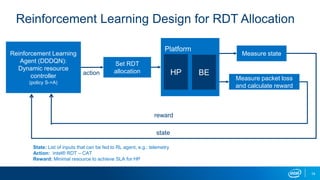
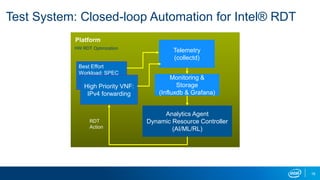
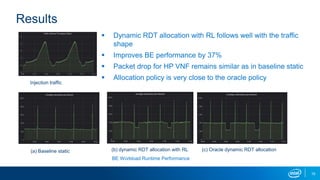
The document discusses using reinforcement learning for dynamic allocation of Intel Resource Director Technology (Intel RDT) resources between high priority network function virtualization (NFV) workloads and best effort workloads. It describes using a Dueling Double Deep Q-Network reinforcement learning agent to allocate cache ways dynamically based on telemetry to improve best effort performance while maintaining service level agreements for NFV workloads. An experiment showed this approach improved best effort workload performance by 37% compared to static RDT allocation, while maintaining similar packet drop rates for high priority workloads.