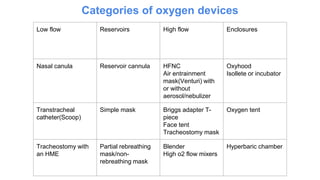
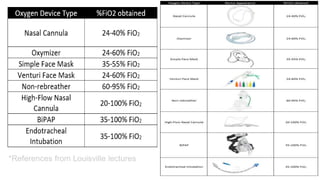
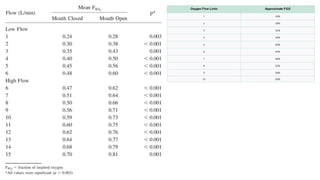
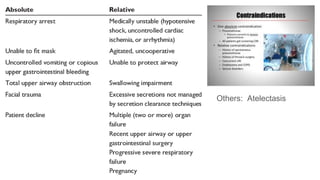
Oxygen therapy involves administering oxygen at higher concentrations to treat conditions like hypoxemia and respiratory distress. It is crucial in various medical situations, including severe trauma and chronic lung diseases. However, prolonged use can lead to oxygen toxicity and requires careful monitoring to avoid increased CO2 levels and other complications.