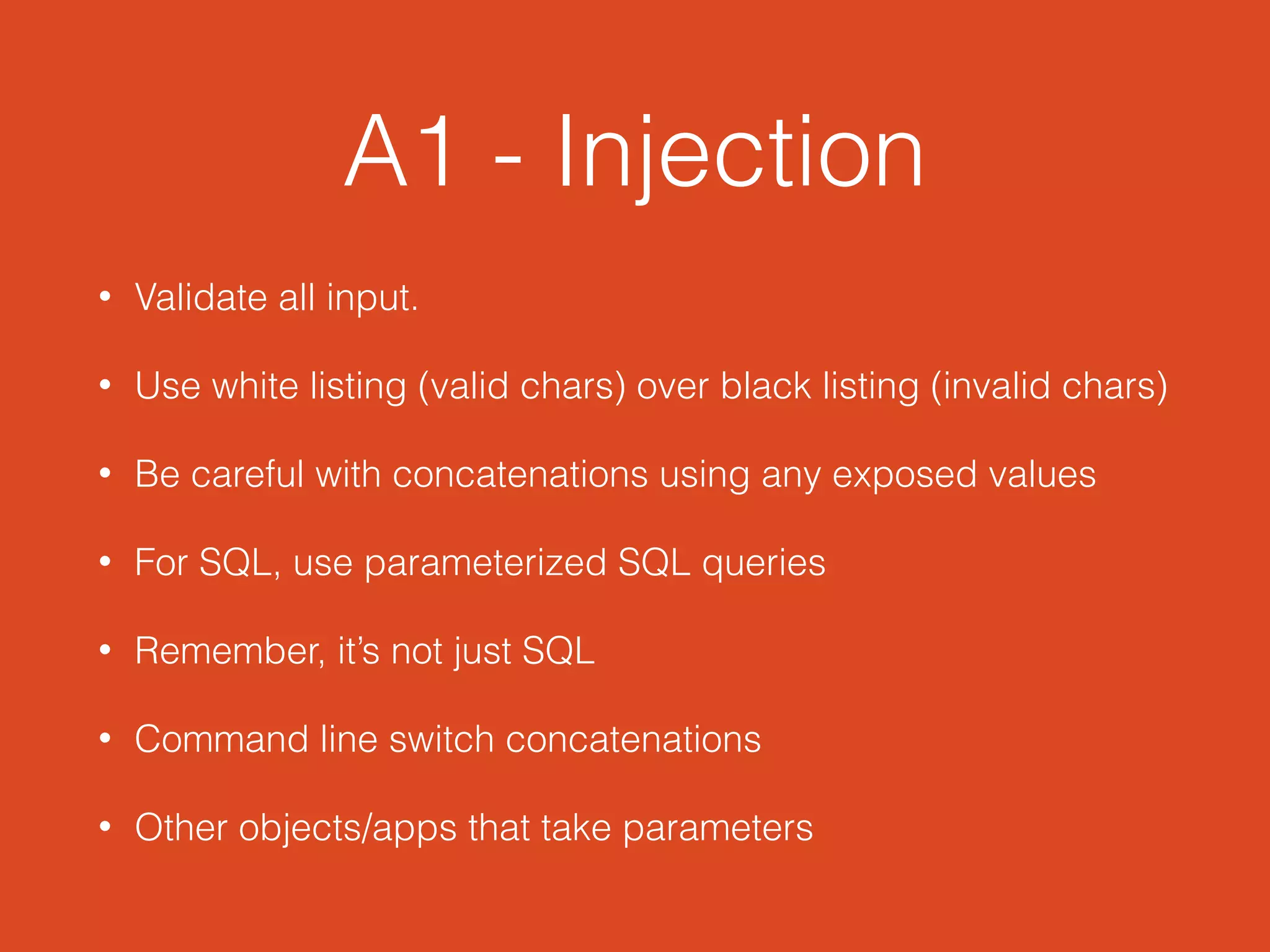
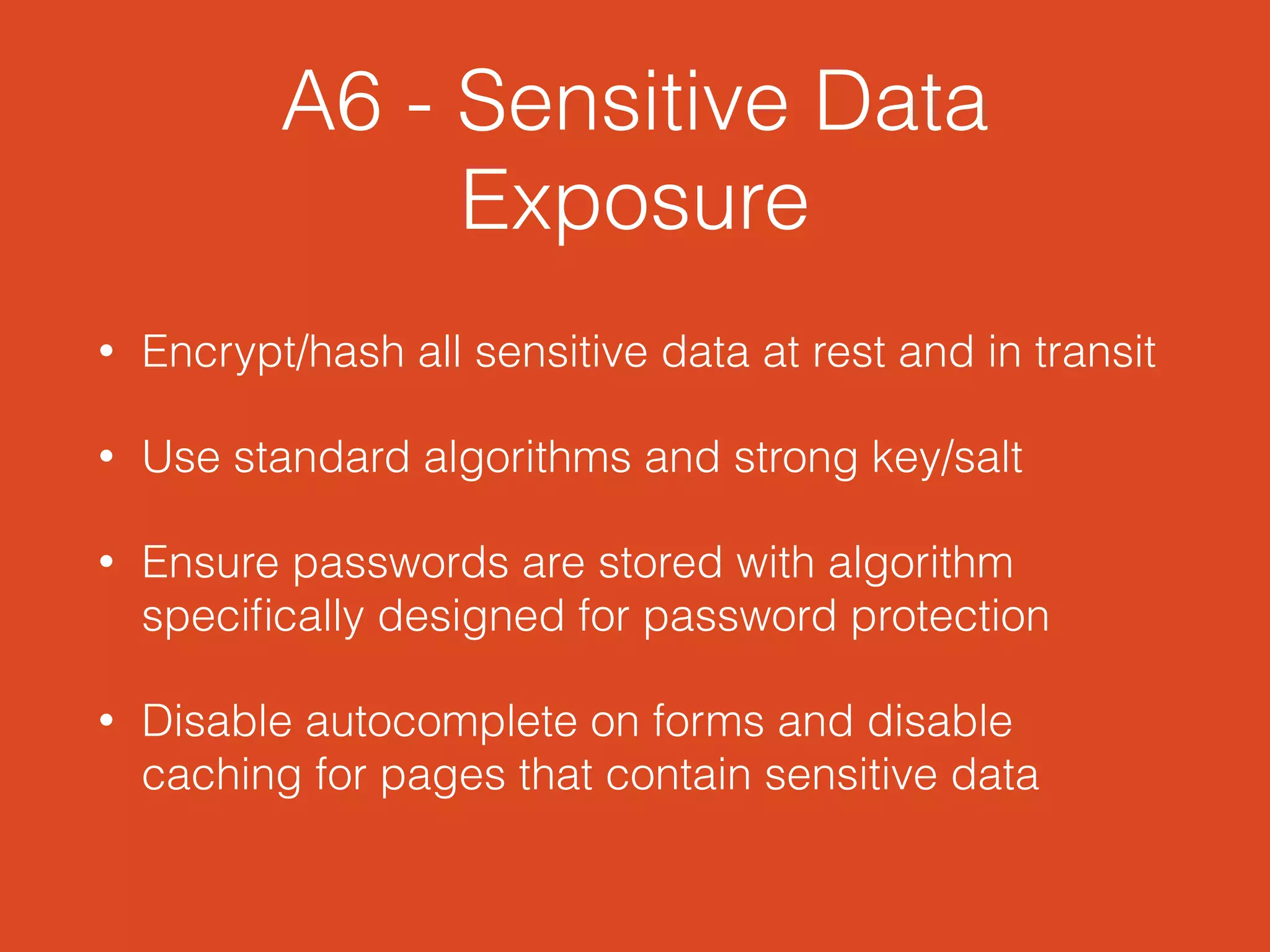
This document summarizes the OWASP Top 10 Web Vulnerabilities as presented by Chris Holwerda at the Desert Code Camp in April 2014. It introduces Chris and his background, discusses general security principles, and provides an overview of the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP). The core of the document lists and briefly explains each of the top 10 vulnerabilities, including injection, broken authentication, cross-site scripting, insecure object references, security misconfiguration, sensitive data exposure, missing access control, cross-site request forgery, use of vulnerable components, and unvalidated redirects/forwards.