Embed presentation
Downloaded 59 times








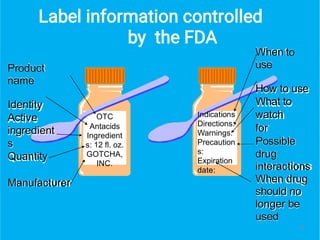




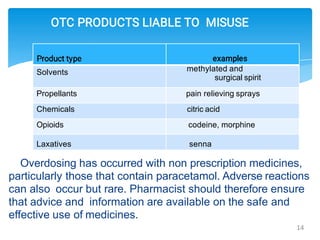























The document discusses over-the-counter (OTC) drugs, which are defined as safe and effective for general public use without a doctor's prescription, accounting for 55% of drug use in India. It covers the various types of OTC medications, their effects, and potential risks, including misuse and drug interactions, emphasizing the importance of proper use and patient education. The paper also highlights the role of pharmacists in providing guidance and ensuring safe consumption of these medications.




































